Abstract
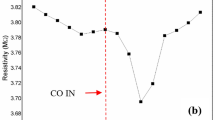
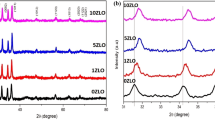
This work explores the thickness effect of RF magnetron-sputtered nickel oxide (NiO) thin films for evaluating their H2S gas-sensing characteristics. NiO thin films were prepared on alumina substrates by varying the deposition time, and the resulting film thicknesses were 25 nm, 52 nm, and 76 nm. X-ray diffraction results demonstrate the polycrystalline nature and cubic structure of NiO thin films. Photoluminescence spectroscopy measurements revealed increased defect content (Ni interstitials and O vacancies) in the 52-nm-thick NiO thin film. Furthermore, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy results confirmed the thickness effect on NiO thin film stoichiometry. Conductivity measurements at working temperatures ranging from 200 to 450 °C were also used to investigate the gas-sensing tests. The NiO thin film with a thickness of 52 nm proved to be an excellent H2S gas sensor, with a remarkable sensor response of 260% and a response/recovery time of ~ 52 s/23 s for 50 ppm H2S at a relatively low operating temperature of 275 °C. Additionally, the film displays a low H2S detection limit of ~ 0.2 ppm. This study investigates the relationship between the thickness, structural, optical, and electrical properties of NiO thin film-based H2S gas sensors and their gas-sensing capabilities.
Graphical abstract











Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Data availability
The raw/processed data required to reproduce these findings cannot be shared at this time as the data also form part of an ongoing study.
References
Liu W, Wu J, Yang Y et al (2018) Facile synthesis of three-dimensional hierarchical NiO microflowers for efficient room temperature H2S gas sensor. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 29:4624–4631. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-017-8413-1
Ganapathi SK, Kaur M, Singh R et al (2019) Anomalous sensing response of NiO nanoparticulate films toward H2S. ACS Appl Nano Mater 2:6726–6737. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsanm.9b01637
Pai SHS, Mondal A, Barathy TR et al (2023) Effect of calcination temperature on NiO for hydrogen gas sensor performance. Int J Hydrogen Energy 50:928–941. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2023.07.345
Godbole R, Godbole VP, Alegaonkar PS, Bhagwat S (2017) Effect of film thickness on gas sensing properties of sprayed WO3 thin films. New J Chem 41:11807–11816. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7nj00963a
Bin JS, Kim HJ, Ahn JH et al (2020) Effects of thin-film thickness on sensing properties of SnO2 -based gas sensors for the detection of H2S gas at ppm levels. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 20:7169–7174. https://doi.org/10.1166/jnn.2020.18854
Barsan N, Simion C, Heine T et al (2010) Modeling of sensing and transduction for p-type semiconducting metal oxide based gas sensors. J Electroceram 25:11–19. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10832-009-9583-x
Liu Y, Liu F, Bai J et al (2019) Direct growth of NiO films on Al2O3 ceramics by electrochemical deposition and its excellent H2S sensing properties. Sens Actuators B Chem 296:126619. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2019.05.096
Nakate UT, Bhuyan P, Yu YT, Park S (2022) Synthesis and characterizations of highly responsive H2S sensor using p-type Co3O4 nanoparticles/nanorods mixed nanostructures. Int J Hydrogen Energy 47:8145–8154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2021.12.115
Li D, Tang Y, Ao D et al (2019) Ultra-highly sensitive and selective H2S gas sensor based on CuO with sub-ppb detection limit. Int J Hydrogen Energy 44:3985–3992. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2018.12.083
Liang YC, Chang YC (2020) The effect of Ni content on gas-sensing behaviors of ZnO–NiO p-n composite thin films grown through radio-frequency cosputtering of ceramic ZnO and NiO targets. CrystEngComm 22:2315–2326. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0ce00052c
Srivastava S, Dwivedi C, Yadav A et al (2023) Enhanced H2S gas sensing of Pd functionalized NiO thin films deposited by the magnetron sputtering process. Mater Lett 351:135040. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2023.135040
Srivastava S, Gangwar AK, Kumar A et al (2023) Impact of O2/Ar gas ratio on the DC reactive magnetron sputtered NiO thin films for ultrafast detection with high sensitivity and selectivity towards H2S gas. Micro Nanostruct 184:207678. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micrna.2023.207678
Srivastava S, Gangwar AK, Kumar A et al (2023) Room temperature RF magnetron sputtered nanocrystalline NiO thin films for highly responsive and selective H2S gas sensing at low ppm concentrations. Mater Res Bull 165:112330. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2023.112330
Ngoc Hoa TT, Hoa ND, Van Duy N et al (2019) An effective H2S sensor based on SnO2 nanowires decorated with NiO nanoparticles by electron beam evaporation. RSC Adv 9:13887–13895. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9ra01105f
Rajesh K, Pothukanuri N, Dasari SG, Reddy MR (2023) Investigations of spray-deposited NiO thin films for ultrasensitive formaldehyde detection. J Alloys Metall Syst 1(2):100009. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jalmes.2023.100009
Dastan D, Shan K, Jafari A et al (2023) Influence of heat treatment on H2S gas sensing features of NiO thin films deposited via thermal evaporation technique. Mater Sci Semicond Process 154:107232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mssp.2022.107232
Soleimanpour AM, Jayatissa AH, Sumanasekera G (2013) Surface and gas sensing properties of nanocrystalline nickel oxide thin films. Appl Surf Sci 276:291–297. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2013.03.085
Zhang J, Zeng D, Zhu Q et al (2015) Effect of grain-boundaries in NiO nanosheet layers room-temperature sensing mechanism under NO2. J Phys Chem C 119:17930–17939. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.5b04940
Chou PC, Chen HI, Liu IP et al (2015) Hydrogen sensing performance of a nickel oxide (NiO) thin film-based device. Int J Hydrogen Energy 40:729–734. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2014.10.142
Souissi R, Bouguila N, Bouricha B et al (2020) Thickness effect on VOC sensing properties of sprayed In2S3films. RSC Adv 10:18841–18852. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0ra01573c
Wilson RL, Simion CE, Blackman CS et al (2018) The effect of film thickness on the gas sensing properties of ultra-thin TiO2 films deposited by atomic layer deposition. Sensors 18(3):735. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18030735
Ritala M, Leskela M, Niinisto L, Haussalo P (1993) Titanium isopropoxide as a precursor in atomic layer epitaxy of titanium dioxide thin films. Chem Mater 5:1174–1181. https://doi.org/10.1021/cm00032a023
Balakarthikeyan R, Santhanam A, Anandhi R et al (2021) Fabrication of nanostructured NiO and NiO: Cu thin films for high-performance ultraviolet photodetector. Opt Mater 120:111387. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optmat.2021.111387
Musevi SJ, Aslani A, Motahari H, Salimi H (2016) Offer a novel method for size appraise of NiO nanoparticles by PL analysis: synthesis by sonochemical method. J Saudi Chem Soc 20:245–252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jscs.2012.06.009
Hammad AH, Abdel-Wahab MS, Vattamkandathil S, Ansari AR (2019) Growth and correlation of the physical and structural properties of hexagonal nanocrystalline nickel oxide thin films with film thickness. Coatings 9:615. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings9100615
Kumari L, Li WZ, Vannoy CH et al (2009) Vertically aligned and interconnected nickel oxide nanowalls fabricated by hydrothermal route. Cryst Res Technol 44:495–499. https://doi.org/10.1002/crat.200800583
Gandhi AC, Wu SY (2017) Strong deep-level-emission photoluminescence in NiO nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 7:231. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7080231
Mochizuki S, Saito T (2009) Intrinsic and defect-related luminescence of NiO. Phys B Condens Matter 404:4850–4853. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2009.08.166
Mauraya AK, Mahana D, Jhaa G et al (2022) Heterostructure nanoarchitectonics with ZnO/SnO2 for ultrafast and selective detection of CO gas at low ppm levels. Ceram Int 48:36556–36569. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2022.08.215
Duan H, Chen Z, Xu N et al (2021) Non-stoichiometric NiOx nanocrystals for highly efficient electrocatalytic oxygen evolution reaction. J Electroanal Chem 885:114966. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2020.114966
Salunkhe P, Muhammed MA, Kekuda D (2021) Structural, spectroscopic and electrical properties of dc magnetron sputtered NiO thin films and an insight into different defect states. Appl Phys A Mater Sci Process 127:390. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-021-04501-0
Ai L, Fang G, Yuan L et al (2008) Influence of substrate temperature on electrical and optical properties of p-type semitransparent conductive nickel oxide thin films deposited by radio frequency sputtering. Appl Surf Sci 254:2401–2405. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2007.09.051
Cheng M, Fan H, Song Y et al (2017) Interconnected hierarchical NiCo2O4 microspheres as high-performance electrode materials for supercapacitors. Dalton Trans 46:9201–9209. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7dt01289f
Ding C, Yan D, Zhao Y et al (2016) A bubble-template approach for assembling Ni–Co oxide hollow microspheres with an enhanced electrochemical performance as an anode for lithium ion batteries. Phys Chem Chem Phys 18:25879–25886. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6cp04097g
Singh P, Srivatsa KMK, Barvat A, Pal P (2016) X-ray photoelectron spectroscopic studies of CeO2 thin films deposited on Ni-W (100), c-Al2O3 (0001) and Si (100) substrates. Curr Appl Phys 16:1388–1394. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cap.2016.07.013
Ciftyurek E, Li Z, Schierbaum K (2023) Adsorbed oxygen ions and oxygen vacancies: their concentration and distribution in metal oxide chemical sensors and influencing role in sensitivity and sensing mechanisms. Sensors 23:29. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23010029
Srivastava R (2012) Investigation on temperature sensing of nanostructured zinc oxide synthesized via oxalate route. J Sens Technol 02:8–12. https://doi.org/10.4236/jst.2012.21002
Shankar P, Bosco J, Rayappan B (2015) Gas sensing mechanism of metal oxides: the role of ambient atmosphere type of semiconductor and gases—a review. Sci Lett J 4:126.
Hu J, Wang Y, Wang W et al (2017) Enhancement of the acetone sensing capabilities to ppb detection level by Fe-doped three-dimensional SnO2 hierarchical microstructures fabricated via a hydrothermal method. J Mater Sci 52:11554–11568. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-017-1319-8
Shringi AK, Kumar A, Das M et al (2023) Ag catalysts boosted NO2 gas sensing performance of RF sputtered α-Fe2O3 films. Sens Actuators B Chem 393:134307. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2023.134307
Dang TK, Cuong ND, Sinh VH et al (2023) Hexagonal annular-NiO nanoarchitecture with local p-n homojunctions: novel formation mechanism and H2S gas sensing properties. J Alloys Compd 933:167782. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2022.167782
Mahana D, Mauraya AK, Kumaragurubaran S et al (2023) Synthesis of CuO thin films by a direct current reactive sputtering process for CO gas sensing application. Phys Scr 98:035709. https://doi.org/10.1088/1402-4896/acb866
Mahana D, Mauraya AK, Pal P et al (2022) Comparative study on surface states and CO gas sensing characteristics of CuO thin films synthesised by vacuum evaporation and sputtering processes. Mater Res Bull 145:111567. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2021.111567
Kaur M, Dadhich BK, Singh R et al (2017) RF sputtered SnO2: NiO thin films as sub-ppm H2S sensor operable at room temperature. Sens Actuators B Chem 242:389–403. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2016.11.054
Mokoena TP, Tshabalala ZP, Hillie KT et al (2020) The blue luminescence of p-type NiO nanostructured material induced by defects: H2S gas sensing characteristics at a relatively low operating temperature. Appl Surf Sci 525:146002. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2020.146002
Jiang H, Sui L, Zhao D et al (2023) In situ growth of hierarchical NiO microspheres via ionic liquid-assisted synthesis for ppb-level detection of H2S. Sens Actuators B Chem 378:133161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2022.133161
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to the Director, CSIR-NPL, India, for his continuous encouragement and financial support (Project No. OLP-220332). S.S. would like to gratefully acknowledge the University Grant Commission (UGC) for the Senior Research fellowship (SRF) award. C.D. is thankful to the Department of Science & Technology (DST), New Delhi, India, for support through Project (DST/WOS-A/PM-49/2021) Dr. K.K. Maurya from CSIR-NPL, and Prof. R. Chandra from IIT Roorkee, India, is highly acknowledged for their help in characterizations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SS contributed to conceptualization, methodology, validation, formal analysis, writing—original draft; CD contributed to investigation; AK contributed to investigation; GG contributed to investigation, writing—review and editing; PS contributed to supervision, visualization, writing—review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Additional information
Handling Editor: N. Ravishankar.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Srivastava, S., Dwivedi, C., Kumar, A. et al. Exploring the role of film thickness and oxygen vacancies on the H2S gas-sensing performance of RF magnetron-sputtered NiO thin films. J Mater Sci (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-024-10204-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-024-10204-7