Abstract
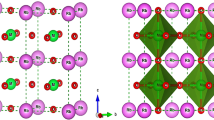
Here, using first-principles density functional theory (DFT), we investigated the structure cubic calculations of perovskite RbTaO3: bulk and surface (1 0 0). The Ta and O atoms in the TaO2-(1 0 0) termination appear to have a large atomic displacement (ΔZ) for the top and ninth layers, while the Rb atoms appear to have a minor value of ΔZ. In the RbO-(1 0 0), the Rb and O atoms in the first layer appear to have a large ΔZ, while the Ta atoms appear to have a major value of ΔZ in the second and eighth layers. We describe the thermodynamic formality used to evaluate the stability of RbTaO3 bulk, as well as RbO and TaO2-terminations. Our calculations showed that both the bulk system and the terminations are stable with the surrounding O atoms. The RbTaO3 bulk system appears to have semiconducting behavior with a band gap (Eg) of 2.25 eV. New RbO- and TaO2-terminations appeared half-metallic ferromagnetic (HMF) with a spin magnetic moment of 1.00 μβ. We found the Eg for RbO- and TaO2-terminations to be 2.25 and 2.40 eV, respectively. Also, the atomic populations (Q) and the variation (ΔQ) for (1 0 0)-RbTaO3 terminations were analyzed and compared with the bulk system. We calculated the optical properties of the RbTaO3 alloy and RbO- and TaO2-(1 0 0) surfaces. We found weak reflectivity, excellent optical conductivity, and higher absorption of incident energetic photons. Depending on the above properties, it is possible to use the bulk, RbO and TaO2 terminations in spintronics and optoelectronic applications.





Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Data Availability
The raw/processed data can be shared with reasonable request to the corresponding author.
References
Iles N, Finochi F, Khodja KD (2010) A systematic study of ideal and double layer reconstructions of ABO3 (0 0 1) surfaces (A = Sr, Ba; B = Ti, Zr) from first principles. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 22(30):305001. https://doi.org/10.1088/0953-8984/22/30/305001
Eglitis R, Kruchinin SP (2020) Ab initio calculations of ABO3 perovskite (0 0 1) (0 1 1) and (1 1 1) nano-surfaces, interfaces and defects. Mod. Phys. Lett. B 34(19):2040057. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0217984920400576
Roberts I (2020) Eglitis et al, comparative Ab Initio calculations of ReO3, SrZrO3, BaZrO3, PbZrO3 and CaZrO3 (0 0 1) surfaces. Crystals 10(9):745. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10090745
Heifets E, Eglitis RI, Kotomin EA, Maier J, Borstel G (2001) Ab initio modeling of surface structure for SrTiO3 perovskite crystals. Phys. Rev. B 64(23):235417. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.64.235417
Heifets E, Piskunov S, Kotomin EA, Zhukovskii YF, Ellis DE (2007) Electronic structure and thermodynamic stability of double-layered SrTiO3(0 0 1) surfaces: Ab initio simulations. Phys. Rev. B: Condens Matter. Mater. Phys. 75(11):115417. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.75.115417
Umeno Y, Shimada T, Kitamura T, Elsässer C (2006) Ab initio density functional theory study of strain effects on ferroelectricity at PbTiO3 surfaces. Phys. Rev. B 74(17):174111. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.74.174111
Wolfram T, Hurst R, Morin FJ (1977) Cluster surface states for TiO2, SrTiO3, and BaTiO3. Phys. Rev. B 15:1151–1160. https://doi.org/10.1103/Phys.B.15.1151
Wang YX, Arai M, Sasaki T, Wang CL (2006) First-principles study of the(0 0 1) surface of cubic CaTiO3. Phys. Rev. B 73(3):035411. https://doi.org/10.1103/Phys-RevB.73.035411
Bickel N et al (1989) Ferroelectric relaxation of the SrTiO3(1 0 0) surface. Phys. Rev. Lett. 62:2009–2011. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.62.2009
Santhosh Kumar R, Muthu Austeria P, Sagaya Selvam Neethinathan C, Ramakrishnan S, Sekar K, Kim AR, Kim DH, Yoo PJ, Yoo DJ (2023) Highly mixed high-energy d-orbital states enhance oxygen evolution reactions in spinel catalysts. Appl. Surf. Sci. 641:158469. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2023.158469
Pramod Ashna K, Gayathri Palanichamy, Subramaniam Mohan Raj, Ghosh Saurabh, Yoo Dong Jin, Batabyal Sudip K (2024) Sensing and ionovoltaic power generation of two-dimensional Cs3Sb2X9 (X = Cl/Br/I) perovskite microcrystals. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 6(7):5255–5268. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsaelm.4c00818
Kido Y, Nishimura T, Hoshino Y, Namba H (2000) Surface structures of SrTiO3(0 0 1)and Ni/SrTiO3 (0 0 1) studied by medium-energy ion scattering and SR-photoelectron spectroscopy. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B 161–163:371–376. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-583X(99)00715-6
Hudson LT et al (1993) Surface core-level shifts of barium observed in photoemission of vacuum-fractured BaTiO3 (1 0 0). Phys. Rev. B. 47:10832–10838. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.47.10832
Ahmad Mir S, Quyoom Seh A, Gupta DC (2020) New ferromagnetic half-metallic perovskites for spintronic applications: BaMO3 (M = Mg and Ca). RSC Adv. 10:36241–36252. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0ra06739c
Kotomin EA, Piskunov S, Zhukovskii YuF, Eglitis RI, Gopejenkoa A, Ellise DE (2008) The electronic properties of an oxygen vacancy at ZrO2-terminated (001) surfaces of a cubic PbZrO3: computer simulations from the first principles. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 10:4258–4263. https://doi.org/10.1039/B802740D
Megaw HD (1952) Origin of ferroelectricity in barium titanate and other perovskite-type crystals. Acta Cryst. 5:739–749. https://doi.org/10.1107/S0365110X52002069
Hussain Muhammad Iqbal et al (2020) Probing the structural, electronic, mechanical strength and optical properties of tantalum-based oxide perovskites ATaO3 (A=Rb, Fr) for optoelectronic applications: first-principles investigations. Optic 219:165027. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2020.165027
Syrotyuk SV, Hussain Moaid K (2021) The effect of Cr impurity and Zn vacancy on electronic and magnetic properties of ZnSe crystal. Phys. Chem. Solid State. 3:529–534. https://doi.org/10.15330/pcss.22.3.529-534
Hussain MK (2021) Investigations of the stability, electronic and magnetic structures in the Zr2Ni-based Heusler compounds: first principles study. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 264:114922. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mseb.2020.114922
Hussain MK, Inad KI (2018) Theoretical study of surface properties of new (0 0 1)- and (1 1 1)-surface YCoCrGe quaternary Heusler compounds. Thin Solid Films 663:100–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsf.2018.08.017
Moaid KH, Gao GY, Yao KL (2015) Investigations of the electronic and magnetic structures at heusler alloy surface: Co2TiGe (0 0 1). J. Electron. Spectrosc. Relat. Phenom. 203:45–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.elspec.2015.05.015
Hussain MK, Yao Kl (2019) Spin polarization calculations and related properties of the surfaces of CoVTe alloy and interface with a BeTe semiconductor. Appl. Phys. Mater. Sci. Process 125:463. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-019-2752-0
Hussain MK, Alwazzan MJ, Paudel R (2021) (1 1 1), (0 0 1), and (1 1 0) surface effects on the stability and electronic-magnetic properties of Mn3P alloy. Phys. E 131:114717. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physe.2021.114717
Hussain MK, Kahdum BJ, Paudel R, Syrotyuk S (2023) Cubic mixed semiconductor BAs: N compounds for energy harvesting and photovoltaic applications. J. Electron. Mater. 52(1):258–269. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-022-09981-1
Paudeletl R (2021) Electronic, magnetic, and optical properties of bulk and (111)-surfaces of CoMnZnSi quaternary Heusler alloy. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 539:168425. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2021.168425
Moaid KH, Asmaa NA (2021) Stability, electronic-magnetic, dynamical and optical properties of the Mn3P alloy based on the D03-Type. Optik 226:165948. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2020.165948
Hussain MK, Hassan OT, Algubili AM (2018) Investigations of the electronic and magnetic structures of Zr2NiZ (Z=Ga, In, B) heusler compounds: first principles study. J. Electron. Mater. 47:6221–6228. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-018-6512-2
Moaid Hussain K (2019) Effects of strain on the half-metallic and elastic properties of FeCrTe and CoCrSi with Cl structure. SPIN 9:1950018. https://doi.org/10.1142/S2010324719500188
Hussain MK et al (2019) Half-metallic properties of the new Zr2RhB inverse Heusler alloy with CuHg2Ti–type structure. Mater. Today Proc. 18:2590–2594. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2019.07.117
Hussain MK (2018) Investigations of the electronic and magnetic properties of newly (001) surface LiCrS and LiCrSe half-Heusler compounds. Appl. Phys. A 124:343. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-018-1760-9
Hussain MK, Saeed SR, Saeed MR, Syrotyuk S (2021) Surface effects on the electronic and optical properties of the Mn3P alloy for optoelectronic applications. Optik 242:166667. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2021.166667
Syrotyuk Stepan, Hussain Moaid K (2023) Influence of pressure on the electronic and magnetic properties of the ZnSeTe solid solution doped with fe atoms. J. Nano. Electron. Phys. 15(5):05002. https://doi.org/10.21272/jnep.15(5).05002
Moaid HUSSAIN K (2020) Half-metallicity of bulk and (001) Surface In The Co2FeGa heusler compound: a theoretical study. Surf. Rev. Lett.27. 04:1950130. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0218625X19501300
Hussain M, Gao G, Yao K (2015) Half-metallic properties of the new Ti2YPb(Y = Co, Fe) Heusler alloys. Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 29(27):1550175. https://doi.org/10.1142/S02179792155017510
Hussain M, Gao G, Yao K (2015) Half-metallic properties in the new Ti2NiB Heusler alloy. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 28(15):3285–3291. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-015-3149-8
Luo B, Wanga X, Tianb E, Lic G, Li L (2015) Structural and electronic properties of cubic KNbO3(0 0 1) surfaces: a first-principles study. Appl. Surf. Sci. 351:558–564. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.05.140
Eglitis RI, Rohlfing M (2010) First-principles calculations of the atomic and electronic structure of SrZrO3 and PbZrO3(0 0 1) and (0 1 1) surfaces. J. Phys. Condens. Matter. 22(41):415901. https://doi.org/10.1088/0953-8984/22/41/415901
Eglitis RI, Vanderbilt D (2008) Ab initio calculations of the atomic and elec-tronic structure of CaTiO3 (0 0 1) and (0 1 1) surfaces. Phys. Rev. B 7(15):155420. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.78.155420
Eglitis RI, Vanderbilt D (2007) Ab initio calculations of BaTiO3. Phys. Rev. B 76(15):155439. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.76.155439
Eglitis RI (2007) First-principles calculations of BaZrO3(0 0 1) and (0 1 1) surfaces. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 19(35):356004. https://doi.org/10.1088/0953-8984/19/35/356004
Pan Y (2021) The influence of N-vacancy on the electronic and optical properties of bulk InN nitrides. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 271:115265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mseb.2021.115265
Pan Y (2021) The influence of Ag and Cu on the electronic and optical properties of ZrO from first-principles calculations. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process 135:106084. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mssp.2021.106084
Mohammed khadier H, Al Husseini HB, Mashot Jafar A (2024) An analysis comparing the performance of lead and tin halides organic Perovskite Solar Cells and numerical simulation with SCAPS. Optical Materials 155:115814. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optmat.2024.115814
Jafar Aqel Mashot et al (2022) Study of the structural, electronic, mechanica,l electro-thermal and optical properties of double perovskite structures Cs2SbAgX6, (X = I, Br, or Cl). Phys. Scr. 97(8):085509. https://doi.org/10.1088/1402-4896/ac8189
Acknowledgements
One of the authors (Moaid K. Hussain) expresses gratitude to Al-Hussain University College for providing the laboratories.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Methodology was done by M.K.H.; software was done by R. P.; investigation was done by M.K.H.; resources were done by S.S.; writing—original draft preparation were done by R. P.; writing—review and editing were done by M.K.H.; visualization was done by M.K.H.; supervision was done by M.K.H.. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
Ethical Approval
A statement approval was granted to carry out experiments involving human tissue by an institutional review board or equivalent ethics committee.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Kevin Jones.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hussain, M.K., Paudel, R. & Syrotyuk, S. A new half-metallic structure of the RbO and TaO2 termination in the cubic perovskite RbTaO3: for spintronics and optoelectronic applications. J Mater Sci 59, 16604–16617 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-024-10151-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-024-10151-3