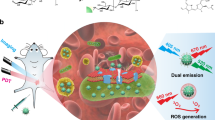
Abstract
Bacterial and biofilm infections pose great challenges to clinical treatments. This study reports the application of long-wavelength-emitting silicon quantum dots (SiQDs) as antibacterial and antibiofilm agents, and for multi-colored bacterial imaging. Several SiQDs–protein complexes were prepared and screened to obtain high-efficient antibacterial nanocomplex, and SiQDs–polylysin (SiQDs–PLL) exhibited the best antibacterial behavior with minimum inhibitory concentration values against Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) and Escherichia coli (E. coli) at 10 and 15.62 μg mL−1, respectively, superior to the ability of pure SiQDs. Compared to Cu2+ and Mn2+, Zn2+ combined with SiQDs–PLL also showed enhanced antibacterial activity because of the synergistic effect. Furthermore, compared to SiQDs, SiQDs–PLL showed an excellent inhibitory effect against the S. aureus biofilm, by completely inhibiting its growth and achieving 62.13% biofilm removal rate at the concentrations of 60 and 200 μg mL−1, respectively. The antibacterial mechanisms of SiQDs and SiQDs–PLL were explored: SiQDs and SiQDs–PLL exerted antibacterial effects by destroying the bacterial cell membrane and promoting the leakage of cell content (DNA and RNA), thus exhibiting the potential as ideal candidates as antimicrobial agents in clinical settings. SiQDs and SiQDs–PLL also exhibit potential in bacterial imaging due to their excellent optical properties and low cytotoxicity.
Graphical abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Wang Z, Wu FG (2022) Ultrasmall silicon nanoparticles for imaging and killing microorganisms: a minireview. ChemNanoMat 8(1):e202100369. https://doi.org/10.1002/cnma.202100369
Tian F, Li J, Nazir A, Tong Y (2021) Bacteriophage-a promising alternative measure for bacterial biofilm control. Infect Drug Resist 14:205. https://doi.org/10.2147/IDR.S290093
Di Domenico EG, Oliva A, Guembe M (2022) The current knowledge on the pathogenesis of tissue and medical device-related biofilm infections. Microorganisms 10(7):1259. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10071259
Xiu W, Shan J, Yang K, Xiao H, Yuwen L, Wang L (2021) Recent development of nanomedicine for the treatment of bacterial biofilm infections. View 2(1):20200065. https://doi.org/10.1002/VIW.20200065
Wang T, Rong F, Tang Y, Li M, Feng T, Zhou Q, Li P, Huang W (2021) Targeted polymer-based antibiotic delivery system: a promising option for treating bacterial infections via macromolecular approaches. Prog Polym Sci 116:101389. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2021.101389
Tan P, Fu H, Ma X (2021) Design, optimization, and nanotechnology of antimicrobial peptides: from exploration to applications. Nano Today 39:101229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nantod.2021.101229
Modi S, Inwati GK, Gacem A, Saquib Abullais S, Prajapati R, Yadav VK, Syed R, Alqahtani MS, Yadav KK, Islam S, Ahn Y, Jeon BH (2022) Nanostructured antibiotics and their emerging medicinal applications: an overview of nanoantibiotics. Antibiotics 11(6):708. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11060708
Sacher E, Yelon A (2021) A pragmatic perspective of the antibacterial properties of metal-based nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 11(12):3214. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11123214
Li P, Sun L, Xue S, Qu D, An L, Wang X, Sun Z (2022) Recent advances of carbon dots as new antimicrobial agents. SmartMat 3(2):226–248. https://doi.org/10.1002/smm2.1131
Alavi M, Jabari E, Jabbari E (2021) Functionalized carbon-based nanomaterials and quantum dots with antibacterial activity: a review. Expert Rev Anti-Infect Ther 19(1):35–44. https://doi.org/10.1080/14787210.2020.1810569
Qaisa FA, Shafiqab A, Ahmada I, Husainc FM, Khand RA, Hassane I (2020) Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Carum copticum: assessment of its quorum sensing and biofilm inhibitory potential against gram negative bacterial pathogens. Microb Pathog 144:104172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micpath.2020.104172
Qin D, Yang G, Wang Y, Zhou Y, Zhang L (2019) Green synthesis of biocompatible trypsin-conjugated Ag nanocomposite with antibacterial activity. Appl Surf Sci 469:528–536. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.11.057
Wang YF, Pan MM, Song YL, Li Z, Wang L, Jiang M, Yu X, Xu L (2022) Beyond the fluorescence labelling of novel nitrogen-doped silicon quantum dots: the reducing agent and stabilizer for preparing hybrid nanoparticles and antibacterial applications. J Mater Chem B 10(36):7003–7013. https://doi.org/10.1039/d2tb01304e
Roy S, Ezati P, Rhim JW, Molaei R (2022) Preparation of turmeric-derived sulfur-functionalized carbon dots: antibacterial and antioxidant activity. J Mater Sci 57(4):2941–2952. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-021-06804-2
Zhao D, Zhang R, Liu X, Li X, Xu M, Huang X, Xiao X (2022) Screening of chitosan derivatives-carbon dots based on antibacterial activity and application in anti-staphylococcus aureus biofilm. Int J Nanomed 17:937. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S350739
Liu W, Gu H, Ran B, Liu W, Sun W, Wang D, Du J, Fan J, Peng X (2022) Accelerated antibacterial red-carbon dots with photodynamic therapy against multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Sci China Mater 65(3):845–854. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40843-021-1770-0
Gao Z, Yang D, Wan Y, Yang Y (2020) One-step synthesis of carbon dots for selective bacterial inactivation and bacterial differentiation. Anal Bioanal 412(4):871–880. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-019-02293-0
Xu Y, Huang T, Wang S, Meng M, Yan Y (2022) SiO2-coated molecularly imprinted sensor based on Si quantum dots for selective detection of catechol in river water. J Environ Chem Eng 10(1):106850. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2021.106850
Tiwari A, Sherpa YL, Pathak AP, Singh LS, Gupta A, Tripathi A (2019) One-pot green synthesis of highly luminescent silicon nanoparticles using Citrus limon (L.) and their applications in luminescent cell imaging and antimicrobial efficacy. Mater Today Commun 19:62–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2018.12.005
Zhao D, Liu H, Zhang Z, Xiao X, Li J (2022) Preparation of green luminescent silicon quantum dots by synergistic method for VB12 detection and antimicrobial property research application. Colloids Surf B 220:112868. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2022.112868
Zhao D, Zhang R, Xu M, Li X, Jiao Y, Xiao X (2022) A novel quaternized carbon dot-papain complex for the double-target anti-biofilm activity and visualization-ratio fluorescence dual-mode detection of H2O2. Mater Chem Front 6(19):2848–2858. https://doi.org/10.1039/d2qm00347c
Mandal S, Prasad SR, Mandal D, Das P (2019) Bovine serum albumin amplified reactive oxygen species generation from anthrarufin-derived carbon dot and concomitant nanoassembly for combination antibiotic-photodynamic therapy application. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 11(36):33273–33284. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b12455
Ahmady IM, Hameed MK, Almehdi AM, Arooj M, Workie B, Sahle-Demessie E, Han C, Mohamed AA (2019) Green and cytocompatible carboxyl modified gold-lysozyme nanoantibacterial for combating multidrug-resistant superbugs. Biomater Sci 7(12):5016–5026. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9bm00935c
Zhu H, Li J, Wang J, Wang E (2019) Lighting up the gold nanoclusters via host-guest recognition for high-efficiency antibacterial performance and imaging. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 11(40):36831–36838. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b11026
Zhang Z, Wei C, Ma W, Li J, Xiao X, Zhao D (2019) One-step hydrothermal synthesis of yellow and green emitting silicon quantum dots with synergistic effect. Nanomaterials 9(3):466. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9030466
Mitra SD, Shailaja S, Harshitha N, Mitra J (2023) Essential oil and phytoconstituent Linalool from Homalomena aromatica Schott Rhizomes exhibit antibacterial and synergistic effects with beta-lactam antibiotics against Carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae CRE and methicillin resistant S aureus MRSA pathogens. Ind Crops Prod 198:116666. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2023.116666
Hao K, Xu B, Zhang G, Lv F, Wang Y, Ma M, Si H (2021) Antibacterial activity and mechanism of Litsea cubeba L. essential oil against Acinetobacter baumannii. Nat Prod Commun. https://doi.org/10.1177/1934578X21999146
Zhong L, Gao X, Qiao J, Chen Y, Zhang X, Xiao Z, Chen P (2023) Formation of blue-emitting colloidal Si quantum dots through pulsed discharge of Si strips in distilled water medium. J Phys Chem C 127(8):4168–4175. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.2c07272
Alessi B, Macias-Montero M, Maddi C, Maguire P, Svrcek V, Mariotti D (2020) Bridging energy bands to the crystalline and amorphous states of Si QDs. Faraday Discuss 222:390–404. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9fd00103d
Angeles DM, Scheffers DJ (2021) The cell wall of Bacillus subtilis. Issues Mol Biol 41(1):539–596. https://doi.org/10.21775/cimb.041.539
Ezati P, Rhim JW, Molaei R, Priyadarshi R, Roy S, Min S, Kim YH, Lee SG, Han S (2022) Preparation and characterization of B, S, and N-doped glucose carbon dots: antibacterial, antifungal, and antioxidant activity. Sustain Mater Technol 32:e00397. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.susmat.2022.e00397
Wang Y, Zhou J, Gu H, Jia X, Su K, Zhang B, Zhang Q (2019) Preparation of anti-nonspecific adsorption chitosan-based bovine serum albumin imprinted polymers with outstanding adsorption capacity and selective recognition ability based on magnetic microspheres. Macromol Mater Eng 304(4):1800731. https://doi.org/10.1002/mame.201800731
Li Y, Yuan Z, Gao Y, Bao Z, Sun N, Lin S (2022) Mechanism of trypsin activation by pulsed electric field treatment revealed based on chemical experiments and molecular dynamics simulations. Food Chem 394:133477. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.133477
Fanaei Pirlar R, Emaneini M, Beigverdi R, Banar M, van Leeuwen WB, Jabalameli F (2020) Combinatorial effects of antibiotics and enzymes against dual-species Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms in the wound-like medium. PLoS ONE 15(6):e0235093. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0235093
Ng IS, Song CP, Ooi CW, Tey BT, Lee YH, Chang YK (2019) Purification of lysozyme from chicken egg white using nanofiber membrane immobilized with reactive orange 4 dye. Int J Biol Macromo 134:458–468. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.05.054
Xu W, Dai Q, Wang Y, Hu X, Xu P, Ni R, Meng J (2018) Creating magnetic ionic liquid-molecularly imprinted polymers for selective extraction of lysozyme. RSC Adv 8(39):21850–21856. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8ra03818j
Swaidan A, Ghayyem S, Barras A, Addad A, Szunerits S, Boukherroub R (2021) Enhanced antibacterial activity of Cus-BSA/lysozyme under near infrared light irradiation. Nanomaterials 11(9):2156. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11092156
Tamara FR, Lin C, Mi FL, Ho YC (2018) Antibacterial effects of chitosan/cationic peptide nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 8(2):88. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8020088
Naassaoui I, Aschi A (2019) Evaluation of properties and structural transitions of poly-L-lysine: effects of pH and temperature. J Macromol Sci Part B 58(8):673–688. https://doi.org/10.1080/00222348.2019.1638593
Nicolas M, Beito B, Oliveira M, Tudela Martins M, Gallas B, Salmain M, Boujday S, Humblot V (2021) Strategies for antimicrobial peptides immobilization on surfaces to prevent biofilm growth on biomedical devices. Antibiotics 11(1):13. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11010013
Brzeski J, Wyrzykowski D, Chylewska A, Makowski M, Papini AM, Makowska J (2022) Metal-ion interactions with dodecapeptide fragments of human cationic antimicrobial protein LL-37 [hCAP (134–170)]. J Phys Chem B 126(36):6911–6921. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcb.2c05200
Sánchez-López E, Gomes D, Esteruelas G, Bonilla L, Lopez-Machado AL, Galindo R, Cano A, Espina M, Ettcheto M, Camins A, Silva AM, Durazzo A, Santini A, Garcia ML, Souto EB (2020) Metal-based nanoparticles as antimicrobial agents: an overview. Nanomaterials 10(2):292. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10020292
Wang Y, Wang W, You Z, Liu X (2022) Observation of synergistic antibacterial properties of prodigiosin from Serratia marcescens jx-1 with metal ions in clinical isolates of Staphylococcus aureus. Prep Biochem Biotechnol 52(3):344–350. https://doi.org/10.1080/10826068.2021.1944201
Xie Y, Gao M, Liu Y, Fu Q, Wang G, Dai Y, Jia S (2019) Interaction of Zn (II) and Cu (II) with ε-poly-L-lysine and properties of the complexes//E3S Web of conferences. EDP Sci 131:01003. https://doi.org/10.1051/e3sconf/201913101003
Lv Y, Yan T, Zhou S, Xu Y (2023) Like stars falling down from the sky: resins effectively assist in and facilitate centrifugal separation and recycling of tiny microbial cells. Green Chem 25(18):7234–7242. https://doi.org/10.1039/D3GC00909B
Funding
This work was funded by the Fundamental Research Funds for South-Central Minzu University (CZY22003), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (2197832), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81703464).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Dan Zhao was involved in writing—original draft, writing—review & editing. Yan Jiao helped in formal analysis, investigation, data curation. Huan Liu contributed to investigation. Xiaoyun Li assisted in investigation. Mengyu Xu assisted in investigation. Xincai Xiao and Haiyan Zhao helped in conceptualization and validation.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Handling Editor: David Ju.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, D., Jiao, Y., Liu, H. et al. Preparation of silicon quantum dot–protein complex and application in antibacterial, antibiofilm, and bacterial cell imaging. J Mater Sci 59, 6946–6964 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-024-09622-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-024-09622-4