Abstract
Purpose
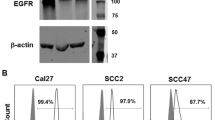
NKG2A, an inhibitory receptor expressed on NK cells and T cells, leads to immune evasion by binding to HLA-E expressed on cancer cells. Here, we investigated the relationship between HLA-E surface expression on head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) cell lines and the efficacy of monalizumab, an NKG2A inhibitor, in promoting NK cell activity.
Methods
Six HNSCC cell lines were used as target cells. After exposure to IFN- γ, HLA-E surface expression on HNSCC cell lines was measured by flow cytometry. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) from healthy donors and isolated NK cells were used as effector cells. NK cells were stimulated by treatment with IL-2 and IL-15 for 5 days, and NK cell-induced cytotoxicity was analyzed by CD107a degranulation and 51Cr release assays.
Results
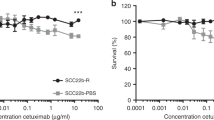
We confirmed that HLA-E expression was increased by IFN-γ secreted by NK cells and that HLA-E expression was different for each cell line upon exposure to IFN-γ. Cell lines with high HLA-E expression showed stronger inhibition of NK cell cytotoxicity, and efficacy of monalizumab was high. Combination with cetuximab increased the efficacy of monalizumab. In addition, stimulation of isolated NK cells with IL-2 and IL-15 increased the efficacy of monalizumab, even in the HLA-E low groups.
Conclusion
Monalizumab efficacy was correlated with HLA-E surface expression and was enhanced when NK cell activity was increased by cetuximab or cytokines. These results suggest that monalizumab may be potent against HLA-E-positive tumors and that monalizumab efficacy could be improved by promoting NK cell activity.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data are available upon reasonable request. Contact email: bhumsuk@snu.ac.kr.
References
André P, Denis C et al (2018) Anti-NKG2A mAb is a checkpoint inhibitor that promotes anti-tumor immunity by unleashing both T and NK cells. Cell 175(7):1731–43.e13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2018.10.014
Battin C, Kaufmann G et al (2022) NKG2A-checkpoint inhibition and its blockade critically depends on peptides presented by its ligand HLA-E. Immunology 166(4):507–521. https://doi.org/10.1111/imm.13515
Benevolo M, Mottolese M et al (2011) High expression of HLA-E in colorectal carcinoma is associated with a favorable prognosis. J Transl Med 9:184. https://doi.org/10.1186/1479-5876-9-184
Braud VM, Allan DS et al (1998) TAP- and tapasin-dependent HLA-E surface expression correlates with the binding of an MHC class I leader peptide. Curr Biol 8(1):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0960-9822(98)70014-4
Capuano C, Pighi C et al (2021) Harnessing CD16-mediated NK cell functions to enhance therapeutic efficacy of tumor-targeting mAbs. Cancers (basel) 13(10):2500. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13102500
Charap AJ, Enokida T et al (2020) Landscape of natural killer cell activity in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. J Immunother Cancer 8(2):e001523. https://doi.org/10.1136/jitc-2020-001523
Chen Q, Li T et al (2018) Drug response to PD-1/PD-L1 blockade: based on biomarkers. Onco Targets Ther 11:4673–4683. https://doi.org/10.2147/ott.S168313
Cichocki F, Miller JS (2019) Setting traps for NKG2A gives NK cell immunotherapy a fighting chance. J Clin Investig 129(5):1839–1841. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci128480
Cohen RB, Bauman JR et al (2020) Combination of monalizumab and cetuximab in recurrent or metastatic head and neck cancer patients previously treated with platinum-based chemotherapy and PD-(L)1 inhibitors. J Clin Oncol 38(15_suppl):6516. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2020.38.15_suppl.6516
Croxatto D, Martini S et al (2017) IL15 induces a potent antitumor activity in NK cells isolated from malignant pleural effusions and overcomes the inhibitory effect of pleural fluid. Oncoimmunology 6(4):e1293210. https://doi.org/10.1080/2162402x.2017.1293210
de Kruijf EM, Sajet A et al (2010) HLA-E and HLA-G expression in classical HLA class I-negative tumors is of prognostic value for clinical outcome of early breast cancer patients. J Immunol 185(12):7452–7459. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1002629
Derré L, Corvaisier M et al (2006) Expression and release of HLA-E by melanoma cells and melanocytes: potential impact on the response of cytotoxic effector cells. J Immunol 177(5):3100–3107. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.177.5.3100
Ducoin K, Oger R et al (2022) Targeting NKG2A to boost anti-tumor CD8 T-cell responses in human colorectal cancer. Oncoimmunology 11(1):2046931. https://doi.org/10.1080/2162402x.2022.2046931
Ehlers FAI, Beelen NA et al (2021) ADCC-inducing antibody trastuzumab and selection of KIR-HLA ligand mismatched donors enhance the NK cell anti-breast cancer response. Cancers (basel) 13(13):3232. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13133232
Elmusrati A, Wang J et al (2021) Tumor microenvironment and immune evasion in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Oral Sci 13(1):24. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41368-021-00131-7
Galot R, Le Tourneau C et al (2021) A phase II study of monalizumab in patients with recurrent/metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck: the I1 cohort of the EORTC-HNCG-1559 UPSTREAM trial. Eur J Cancer 158:17–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2021.09.003
Gooden M, Lampen M et al (2011) HLA-E expression by gynecological cancers restrains tumor-infiltrating CD8+ T lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108(26):10656–10661. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1100354108
Gotwals P, Cameron S et al (2017) Prospects for combining targeted and conventional cancer therapy with immunotherapy. Nat Rev Cancer 17(5):286–301. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc.2017.17
Herbst RS, Soria J-C et al (2014) Predictive correlates of response to the anti-PD-L1 antibody MPDL3280A in cancer patients. Nature 515(7528):563–567. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature14011
Herbst RS, Majem M et al (2022) COAST: an open-label, phase II, multidrug platform study of durvalumab alone or in combination with oleclumab or monalizumab in patients with unresectable, stage III non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 40:3383–3393. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.22.00227
Horng T, Bezbradica JS et al (2007) NKG2D signaling is coupled to the interleukin 15 receptor signaling pathway. Nat Immunol 8(12):1345–1352. https://doi.org/10.1038/ni1524
Hromadnikova I, Pirkova P et al (2013) Influence of in vitro IL-2 or IL-15 alone or in combination with Hsp-70-derived 14-mer peptide (TKD) on the expression of NK cell activatory and inhibitory receptors. Mediat Inflamm 2013:405295. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/405295
Iwaszko M, Bogunia-Kubik K (2011) Clinical significance of the HLA-E and CD94/NKG2 interaction. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (warsz) 59(5):353–367. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00005-011-0137-y
Johnson DE, Burtness B et al (2020) Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Nat Rev Dis Primers 6(1):92. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41572-020-00224-3
Kamiya T, Seow SV et al (2019) Blocking expression of inhibitory receptor NKG2A overcomes tumor resistance to NK cells. J Clin Investig 129(5):2094–2106. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci123955
Koehl U, Brehm C et al (2013) Clinical grade purification and expansion of NK cell products for an optimized manufacturing protocol. Front Oncol 3:118. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2013.00118
Lauterbach N, Wieten L et al (2015) Peptide-induced HLA-E expression in human PBMCs is dependent on peptide sequence and the HLA-E genotype. Tissue Antigens 85(4):242–251. https://doi.org/10.1111/tan.12525
Lee YJ, Benveniste EN (1996) Stat1 alpha expression is involved in IFN-gamma induction of the class II transactivator and class II MHC genes. J Immunol 157(4):1559–1568
Lee N, Goodlett DR et al (1998) HLA-E surface expression depends on binding of TAP-dependent peptides derived from certain HLA class I signal sequences. J Immunol 160(10):4951–4960
Lee J, Park KH et al (2017) Natural killer cell activity for IFN-gamma production as a supportive diagnostic marker for gastric cancer. Oncotarget 8(41):70431–70440. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.19712
Lehmann C, Zeis M et al (2001) Activation of natural killer cells with interleukin 2 (IL-2) and IL-12 increases perforin binding and subsequent lysis of tumour cells. Br J Haematol 114(3):660–665. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2141.2001.02995.x
Leibson PJ (1998) Cytotoxic lymphocyte recognition of HLA-E: utilizing a nonclassical window to peer into classical MHC. Immunity 9(3):289–294. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1074-7613(00)80611-1
Levy EM, Sycz G et al (2009) Cetuximab-mediated cellular cytotoxicity is inhibited by HLA-E membrane expression in colon cancer cells. Innate Immun 15(2):91–100. https://doi.org/10.1177/1753425908101404
Li D, Brackenridge S et al (2022) Mouse and human antibodies bind HLA-E-leader peptide complexes and enhance NK cell cytotoxicity. Communications Biology 5(1):271. https://doi.org/10.1038/s42003-022-03183-5
Liu S, Galat V et al (2021) NK cell-based cancer immunotherapy: from basic biology to clinical development. J Hematol Oncol 14(1):7. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-020-01014-w
Lo Monaco E, Sibilio L et al (2008) HLA-E: strong association with β2-microglobulin and surface expression in the absence of HLA class I signal sequence-derived peptides. J Immunol 181(8):5442. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.181.8.5442
Lo Monaco E, Tremante E et al (2011) Human leukocyte antigen E contributes to protect tumor cells from lysis by natural killer cells. Neoplasia 13(9):822–830. https://doi.org/10.1593/neo.101684
Mahaweni NM, Ehlers FAI et al (2018) NKG2A expression is not per se detrimental for the anti-multiple myeloma activity of activated natural killer cells in an in vitro system mimicking the tumor microenvironment. Front Immunol 9:1415. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2018.01415
Mandal R, Şenbabaoğlu Y et al (2016) The head and neck cancer immune landscape and its immunotherapeutic implications. JCI Insight 1(17):e89829. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.89829
Matsunami K, Miyagawa S et al (2002) Modulation of the leader peptide sequence of the HLA-E gene up-regulates its expression and down-regulates natural killer cell-mediated swine endothelial cell lysis. Transplantation 73(10):1582–1589. https://doi.org/10.1097/00007890-200205270-00010
Miller JS, Soignier Y et al (2005) Successful adoptive transfer and in vivo expansion of human haploidentical NK cells in patients with cancer. Blood 105(8):3051–3057. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2004-07-2974
Morinaga T, Iwatsuki M et al (2022) Evaluation of HLA-E expression combined with natural killer cell status as a prognostic factor for advanced gastric cancer. Ann Surg Oncol 29(8):4951–4960. https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-022-11665-3
Nguyen S, Beziat V et al (2009) HLA-E upregulation on IFN-gamma-activated AML blasts impairs CD94/NKG2A-dependent NK cytolysis after haplo-mismatched hematopoietic SCT. Bone Marrow Transplant 43(9):693–699. https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2008.380
Park HR, Ahn YO et al (2019) NK92-CD16 cells are cytotoxic to non-small cell lung cancer cell lines that have acquired resistance to tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Cytotherapy 21(6):603–611. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcyt.2019.03.312
Park J-E, Kim S-E et al (2020) Anti-tumor effects of NK cells and anti-PD-L1 antibody with antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity in PD-L1-positive cancer cell lines. J Immunother Cancer 8(2):e000873. https://doi.org/10.1136/jitc-2020-000873
Paul S, Lal G (2017) The molecular mechanism of natural killer cells function and its importance in cancer immunotherapy. Front Immunol 8:1124. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2017.01124
Powles T, Eder JP et al (2014) MPDL3280A (anti-PD-L1) treatment leads to clinical activity in metastatic bladder cancer. Nature 515(7528):558–562. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature13904
Rautela J, Huntington ND (2017) IL-15 signaling in NK cell cancer immunotherapy. Curr Opin Immunol 44:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coi.2016.10.004
Ruggeri L, Urbani E et al (2016) Effects of anti-NKG2A antibody administration on leukemia and normal hematopoietic cells. Haematologica 101(5):626–633. https://doi.org/10.3324/haematol.2015.135301
Salomé B, Sfakianos JP et al (2022) NKG2A and HLA-E define an alternative immune checkpoint axis in bladder cancer. Cancer Cell 40(9):1027–43.e9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccell.2022.08.005
Sanchez-Correa B, Bergua JM et al (2017) In vitro culture with interleukin-15 leads to expression of activating receptors and recovery of natural killer cell function in acute myeloid leukemia patients. Front Immunol 8:931. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2017.00931
Sentman CL, Barber MA et al (2006) NK cell receptors as tools in cancer immunotherapy. Adv Cancer Res 95:249–292. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0065-230x(06)95007-6
Sheffer M, Lowry E et al (2021) Genome-scale screens identify factors regulating tumor cell responses to natural killer cells. Nat Genet 53(8):1196–1206. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41588-021-00889-w
Sordo-Bahamonde C, Vitale M et al (2020) Mechanisms of resistance to NK cell immunotherapy. Cancers (basel) 12(4):893. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12040893
van Hall T, André P et al (2019) Monalizumab: inhibiting the novel immune checkpoint NKG2A. J Immunother Cancer 7(1):263. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40425-019-0761-3
Wang KS, Frank DA et al (2000) Interleukin-2 enhances the response of natural killer cells to interleukin-12 through up-regulation of the interleukin-12 receptor and STAT4. Blood 95(10):3183–3190
Ward JP, Bonaparte MI et al (2004) HLA-C and HLA-E reduce antibody-dependent natural killer cell-mediated cytotoxicity of HIV-infected primary T cell blasts. AIDS 18(13):1769–1779. https://doi.org/10.1097/00002030-200409030-00005
Xu YP, Wieten L et al (2019) Clinical significance of HLA-E genotype and surface/soluble expression levels between healthy individuals and patients with acute leukemia. Leuk Lymphoma 60(1):208–215. https://doi.org/10.1080/10428194.2018.1474521
Zaghi E, Calvi M et al (2019) Targeting NKG2A to elucidate natural killer cell ontogenesis and to develop novel immune-therapeutic strategies in cancer therapy. J Leukoc Biol 105(6):1243–1251. https://doi.org/10.1002/jlb.Mr0718-300r
Zhou F (2009) Molecular mechanisms of IFN-gamma to up-regulate MHC class I antigen processing and presentation. Int Rev Immunol 28(3–4):239–260. https://doi.org/10.1080/08830180902978120
Acknowledgements
We used BioRender software (Biorender.com) to create an illustrative diagram, and thank Soomin Kim for helping with the figure design.
Funding
This study was supported by a grant from the Korea Health Industry Development Institute (KHIDI) [grant number: HI14C1277] and the National R&D Program for Cancer Control [grant number: HA16C0015], funded by Ministry of Health and Welfare (MHW), Republic of Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conception and design: JL and BK. Development of methodology: JL, BK, H-RP, J-EP, SK, and TMK. Acquisition of data (e.g., provided cells and provided facilities, etc.): JL, H-RP, J-EP, and SK. Analysis and interpretation of data: JL, BK, SK, and TMK. Study supervision: BK, SK, MK, TMK, D-WK, and DSH. Writing, review and/or revision of the manuscript: all authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Conflict of interest
None declared.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, J., Keam, B., Park, HR. et al. Monalizumab efficacy correlates with HLA-E surface expression and NK cell activity in head and neck squamous carcinoma cell lines. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 149, 5705–5715 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-022-04532-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-022-04532-x