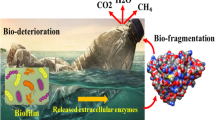
Abstract
For decades, plastic waste management has been one of the major ecological challenges of our society. Despite the introduction of biodegradable alternatives such as polylactic acid (PLA), their beneficial environmental impact is limited by the requirement of specific compost facility as biodegradation of PLA in natural environment occurs at a very slow rate. In this work, a plastic-degrading enzyme was utilized to facilitate degradation process. Genomic and proteomic tools were employed to identify a new biodegradable plastic-degrading enzyme from Cryptococcus nemorosus TBRC2959. The new enzyme, Cr14CLE, functions optimally under mild conditions with temperature range of 30 to 40 °C and suffers no significant loss of enzymatic activity at pH ranging from 6 to 8. In addition to PLA, Cr14CLE is capable to degrade other types of biodegradable plastic such as polybutylene succinate (PBS) and polybutylene adipate terephthalate (PBAT) as well as composite bioplastic. Applications of Cr14CLE have been demonstrated through the preparation of enzyme-coated PLA film and laminated PLA film with enzyme layer. PLA films prepared by both approaches exhibited capability to self-degrade in water.
Key points
• Novel plastic-degrading enzyme (Cr14CLE) was identified and characterized.
• Cr14CLE can degrade multiple types of biodegradable plastics under mild conditions.
• Applications of Cr14CLE on self-degradable plastic were demonstrated.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The genomic sequences analyzed during the current study are available in NCBI Sequence Read Archive (SRA) under the accession number PRJNA923129. The codon-optimized sequences for the expression of Cr14CLE and CLE-sp2 are available under GenBank accession numbers OR094865 and OR094866.
References
Allen K, Cohen D, Culver A, Cummins A, Curtis S, Eriksen M, Gordon M, Howe A, Jackson S, Lapis N (2018) Better alternatives now BAN LIST 2.0. The Circulate Initiative. https://www.thecirculateinitiative.org/projects/Better-Alternatives-Now-B.A.N.-List-2.0. Accessed 24 Nov 2022
Almagro Armenteros JJ, Tsirigos KD, Sønderby CK, Petersen TN, Winther O, Brunak S, von Heijne G, Nielsen H (2019) SignalP 5.0 improves signal peptide predictions using deep neural networks. Nat Biotechnol 37:420–423. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41587-019-0036-z
Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ (1990) Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 215:403–410. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2
Bagheri AR, Laforsch C, Greiner A, Agarwal S (2017) Fate of so-called biodegradable polymers in seawater and freshwater. Global Chall 1:1700048. https://doi.org/10.1002/gch2.201700048
Bankevich A, Nurk S, Antipov D, Gurevich AA, Dvorkin M, Kulikov AS, Lesin VM, Nikolenko SI, Pham S, Prjibelski AD, Pyshkin AV, Sirotkin AV, Vyahhi N, Tesler G, Alekseyev MA, Pevzner PA (2012) SPAdes: a new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J Comput Biol 19:455–477. https://doi.org/10.1089/cmb.2012.0021
Bolger AM, Lohse M, Usadel B (2014) Trimmomatic: a flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 30:2114–2120. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btu170
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254. https://doi.org/10.1006/abio.1976.9999
Chamas A, Moon H, Zheng J, Qiu Y, Tabassum T, Jang JH, Abu-Omar M, Scott SL, Suh S (2020) Degradation rates of plastics in the environment. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 8:3494–3511. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.9b06635
Chateau M, Rousselle J-P (2020) Masterbatch composition comprising a high concentration of biological entities (U.S. Patent No. 10,723,848). U.S. Patent and Trademark Office. https://patents.google.com/patent/US10723848B2/en
Chen S, Zhou Y, Chen Y, Gu J (2018) fastp: an ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 34:i884–i890. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bty560
Dauvergne P (2018) Why is the global governance of plastic failing the oceans? Glob Environ Chang 51:22–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2018.05.002
Flynn JM, Hubley R, Goubert C, Rosen J, Clark AG, Feschotte C, Smit AF (2020) RepeatModeler2 for automated genomic discovery of transposable element families. Proc Natl Acad Sci 117:9451–9457. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1921046117
Greene J, California. Department of Resources Recycling and Recovery, CSU CRF (2012) Report topic: PLA and PHA biodegradation in the marine environment: contractor’s report. Dept Resour Recycl Recover. https://www2.calrecycle.ca.gov/Publications/Details/1435. Accessed 24 Nov 2022
Guemard E, Dalibey M (2022) Liquid composition comprising biological entities and uses thereof (U.S. Patent No. 11,384,218). U.S. Patent and Trademark Office. https://patents.google.com/patent/US11384218B2/en
Guemard E, Chateau M, Marty A (2021) Process for preparing a biodegradable plastic composition (U.S. Patent No. 11,198,767). U.S. Patent and Trademark Office. https://patents.google.com/patent/US11198767B2/en
Gurevich A, Saveliev V, Vyahhi N, Tesler G (2013) QUAST: quality assessment tool for genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 29:1072–1075. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btt086
Haider TP, Völker C, Kramm J, Landfester K, Wurm FR (2019) Plastics of the future? The impact of biodegradable polymers on the environment and on society. Angew Chem Int Ed 58:50–62. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201805766
Harwood CR, Cutting SM (1990) Molecular biological methods for Bacillus. Wiley
Hoshino A, Isono Y (2002) Degradation of aliphatic polyester films by commercially available lipases with special reference to rapid and complete degradation of poly(L-lactide) film by lipase PL derived from Alcaligenes sp. Biodegradation 13:141–147. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1020450326301
Hu X, Gao Z, Wang Z, Su T, Yang L, Li P (2016) Enzymatic degradation of poly(butylene succinate) by cutinase cloned from Fusarium solani. Polym Degrad Stab 134:211–219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2016.10.012
Huang Q, Hiyama M, Kabe T, Kimura S, Iwata T (2020) Enzymatic self-biodegradation of poly(l-lactic acid) films by embedded heat-treated and immobilized proteinase K. Biomacromol 21:3301–3307. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biomac.0c00759
Jambeck JR, Geyer R, Wilcox C, Siegler TR, Perryman M, Andrady A, Narayan R, Law KL (2015) Plastic waste inputs from land into the ocean. Science 347:768–771. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1260352
Jamshidian M, Tehrany EA, Imran M, Jacquot M, Desobry S (2010) Poly-lactic acid: production, applications, nanocomposites, and release studies. Comprehensive Rev Food Sci Food Saf 9:552–571. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1541-4337.2010.00126.x
Kawai F, Nakadai K, Nishioka E, Nakajima H, Ohara H, Masaki K, Iefuji H (2011) Different enantioselectivity of two types of poly(lactic acid) depolymerases toward poly(l-lactic acid) and poly(d-lactic acid). Polym Degrad Stab 96:1342–1348. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2011.03.022
Kodama Y, Masaki K, Kondo H, Suzuki M, Tsuda S, Nagura T, Shimba N, Suzuki E, Iefuji H (2009) Crystal structure and enhanced activity of a cutinase-like enzyme from Cryptococcus sp. strain S-2. Proteins: structure, function, and bioinformatics 77:710–717. https://doi.org/10.1002/prot.22484
Koitabashi M, Noguchi MT, Sameshima-Yamashita Y, Hiradate S, Suzuki K, Yoshida S, Watanabe T, Shinozaki Y, Tsushima S, Kitamoto HK (2012) Degradation of biodegradable plastic mulch films in soil environment by phylloplane fungi isolated from gramineous plants. AMB Express 2:40. https://doi.org/10.1186/2191-0855-2-40
Lunt J (1998) Large-scale production, properties and commercial applications of polylactic acid polymers. Polym Degrad Stab 59:145–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0141-3910(97)00148-1
Masaki K, Kamini NR, Ikeda H, Iefuji H (2005) Cutinase-like enzyme from the yeast Cryptococcus sp. strain S-2 hydrolyzes polylactic acid and other biodegradable plastics. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:7548–7550. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.71.11.7548-7550.2005
Oda Y, Yonetsu A, Urakami T, Tonomura K (2000) Degradation of polylactide by commercial proteases. J Polym Environ 8:29–32. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010120128048
Prema S, Palempalli UMD (2015) Degradation of polylactide plastic by PLA depolymerase isolated from Thermophilic Bacillus. Int J Curr Microbiol App Sci 4:645–654
Rudnik E, Briassoulis D (2011) Degradation behaviour of poly(lactic acid) films and fibres in soil under Mediterranean field conditions and laboratory simulations testing. Ind Crops Prod 33:648–658. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2010.12.031
Simão FA, Waterhouse RM, Ioannidis P, Kriventseva EV, Zdobnov EM (2015) BUSCO: assessing genome assembly and annotation completeness with single-copy orthologs. Bioinformatics 31:3210–3212. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btv351
Stanke M, Morgenstern B (2005) AUGUSTUS: a web server for gene prediction in eukaryotes that allows user-defined constraints. Nucleic Acids Res 33:W465–W467. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gki458
Sulaiman S, Yamato S, Kanaya E, Kim J-J, Koga Y, Takano K, Kanaya S (2012) Isolation of a novel cutinase homolog with polyethylene terephthalate-degrading activity from leaf-branch compost by using a metagenomic approach. Appl Environ Microbiol 78:1556–1562. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.06725-11
Suzuki K, Sakamoto H, Shinozaki Y, Tabata J, Watanabe T, Mochizuki A, Koitabashi M, Fujii T, Tsushima S, Kitamoto HK (2013) Affinity purification and characterization of a biodegradable plastic-degrading enzyme from a yeast isolated from the larval midgut of a stag beetle, Aegus laevicollis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97:7679–7688. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-012-4595-x
Wang G-X, Huang D, Ji J-H, Völker C, Wurm FR (2021) Seawater-degradable polymers—fighting the marine plastic pollution. Adv Sci 8:2001121. https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202001121
Watanabe T, Suzuki K, Shinozaki Y, Yarimizu T, Yoshida S, Sameshima-Yamashita Y, Koitabashi M, Kitamoto HK (2015) A UV-induced mutant of Cryptococcus flavus GB-1 with increased production of a biodegradable plastic-degrading enzyme. Process Biochem 50:1718–1724. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2015.07.005
Weng Y-X, Jin Y-J, Meng Q-Y, Wang L, Zhang M, Wang Y-Z (2013) Biodegradation behavior of poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) (PBAT), poly(lactic acid) (PLA), and their blend under soil conditions. Polym Test 32:918–926. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymertesting.2013.05.001
Funding
This work was financially supported by the National Science and Technology Development Agency (Grant No. P18-52705).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
N.A. and V.C. conceptualized and designed the study. N.A. identified and characterized protein. W.M., A.P., and O.R. performed bioinformatics analysis. N.A. and B.H. designed and prepared testing samples. N.A. analyzed the data and wrote the original draft of the manuscript. All authors reviewed and edited the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Arunrattanamook, N., Mhuantong, W., Paemanee, A. et al. Identification of a plastic-degrading enzyme from Cryptococcus nemorosus and its use in self-degradable plastics. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 107, 7439–7450 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-023-12816-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-023-12816-6