Abstract
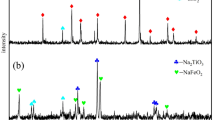
As part of a U.S. Bureau of Mines program to develop a more continuous titanium metal process that exploits domestic resources, a study was made of the kinetics of hydrofluoric acid (HF) leaching of New York rock ilmenite. The effects of leach temperature, HF concentration, and particle size on leach rate were investigated. The data fit a shrinking core model with the rate controlled by the chemical reaction step. The rate of reaction is related to temperature by the Arrhenius relationship with the activation energy being 52.6 kJ/mol for titanium and 48.4 kJ/mol for iron. The rate is linearly dependent on the HF concentration and inversely proportional to the average starting diameter of the particle. Generalized rate expressions were developed for titanium and iron. Using 19.33M HF at 45°C, 99% of the titanium and 100% of the iron in New York rock ilmenite were leached in 40 minutes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
D.E. Traut, “Induction Slag Reduction Process for Making Titanium,” Patent Application 907, 341 (1986).
D.E. Traut, D.A. Hansen and J.I. Paige, “Calcium Fluorotitanate/Induction Slag Furnace Route to Titanium Metal,” presented at AIME Annual Meeting, Phoenix, Arizona (1988), and Sixth World Conference on Titanium, Cannes, France (June 6–9, 1988).
L.E. Lynd, “Titanium” in Mineral Facts and Problems, BuMines B 675 (1985), pp. 859–879.
H.C. Kawecki and E.J. Bielecki, “Production of Potassium Titanium Fluoride,” U.S. Pat 2,568,341 (1951).
J. Kamlet, “Titanium-Aluminum Alloys,” U.S. Pat 2,781,261 (1957).
R.B. Jackson, D.H. Kelly and R.V. Townsend, “Anhydrous Titanium Tetrafluoride,” U.S. Patent 2,900,234 (1959).
B. Peskin et al., “Verfahren zur Herstellung von Fluotitansaure und Hexafluotitanaten (Method for the Manufacture of Fluorotitanic Acid and Hexafluorotitanates),” German Patent 1,222,026 (1966).
Chemical and Phosphates, Ltd., “Process for the Production of Fluotitanic Acid and of Fluotitanates,” British Patent 1,044,025 (1966).
K. Nagasubramanian and K.J. Liu, “Recovery of TiO2 from Ilmenite-Type Ore Using an Organophosphoric Acid Extractant for Impurity Iron Removal,” U.S. Patent 4,168,297 (1979).
V.N. Plakhotnik, I.L. Gulivets and N.V. Krivenko, “Sposob polucheniya geksaftortitanata Kaliya (Potassium Hexafluorotitanate),” U.S.S.R. Patent 819,062 (1981).
R.K. Biswas and M.G.K. Mondai, “A Study on the Dissolution of Ilmenite Sand,” Hydrometallurgy, 17 (1987), pp. 385–390.
G.W. Elger et al., “Producing Chlorination-Grade Feedstock from Domestic Ilmenite-Laboratory and Pilot Plant Studies,” BuMines RI 9002 (1986), pp. 4–5
O. Levenspiel, Chemical Reaction Engineering, 2nd ed. (New York: John Wiley and Sons, 1972), pp. 359–368.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hansen, D.A., Traut, D.E. The kinetics of leaching rock ilmenite with hydrofluoric acid. JOM 41, 34–36 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03220221
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03220221