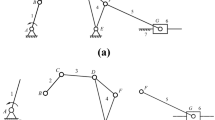
Abstract
In order to obtain a simple way for the force analysis of metamorphic mechanisms, the systematic method to unify the force analysis approach of metamorphic mechanisms as that of conventional planar mechanisms is proposed. A force analysis method of metamorphic mechanisms is developed by transforming the augmented Assur groups into Assur groups, so that the force analysis problem of metamorphic mechanisms is converted into the force analysis problems of conventional planar mechanisms. The constraint force change rules and values of metamorphic joints are obtained by the proposed method, and the constraint force analysis equations of revolute metamorphic joints in augmented Assur group RRRR and prismatic metamorphic joints in augmented Assur group RRPR are deduced. The constraint force analysis is illustrated by the constrained spring force design of paper folding metamorphic mechanism, and its metamorphic working process is controlled by the spring force and geometric constraints of metamorphic joints. The results of spring force show that developped design method and approach are feasible and practical. By transforming augmented Assur groups into Assur groups, a new method for the constraint force analysis of metamorphic joints is proposed firstly to provide the basis for dynamic analysis of metamorphic mechanism.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
DAI J S, REES J J. Mobility in metamorphic mechanisms of foldable/erectable kinds[J]. Transactions of the ASME: Journal of Mechanical Design, 1999, 121(3): 375–382.
YAN H S, KUO C H. Topological representations and characteristics of variable kinematic joints[J]. Transactions of the ASME Journal of Mechanical Design, 2006, 128(2): 384–391.
LI D L, DAI J S, ZHANG Q X, et al. Structure synthesis of metamorphic mechanisms based on the configuration transformations[J]. Chinese J. Mech. Eng., 2002, 38(7): 12–6. (in Chinese)
LIU C H, YANG T L. Essence and characteristics of metamorphic mechanisms and their metamorphic ways[C]//Proceedings of 11th World Congress in Mechanism and Machine Science,Tianjing, China, April 1–4, 2004: 1285–1288.
DING X L, YANG Y. Investigation of reconfiguration theory based on an assembly-circles artifact[C]//ASME/IFToMM International Conference on Reconfigurable Mechanisms and Robots, London, United Kingdom, June 22–24, 2009: 456–463.
WANG D L, DAI J S. Theoretical foundation of metamorphic mechanisms and its synthesis[J]. Chinese J. Mech. Eng., 2007, 43(8): 32–42. (in Chinese)
LI S J, DAI J S. Structure synthesis of single-driven metamorphic mechanisms based on the augmented Assur groups[J]. Transactions of ASME Journal of Mechanisms and Robotics, 2012, 4(3): 031004.
LI S J, DAI J S. The equivalent resistance gradient model of metamorphic mechanisms and the design approach[C]//the ASME/IFToMM International Conference on Reconfigurable Mechanisms and Robots, Tianjin, China, July 9–11, 2012: 53–62.
ASSUR L V. Investigation of plane hinged mechanisms with lower pairs from the point of view of their structure and classification: Part I, Bull[J]. Petrograd Polytech. Inst., 1913, 20: 329–386. (in Russian)
MANOLESCU N I. For a united point of view in the study of the structural analysis of kinematic chains and mechanisms[J]. Journal of Mechanisms, 1968, 3(3): 149–169.
VERHO A. An extension of the concept of the group[J]. Mech. and Mach. Theory, 1973, 8(2): 249–256.
MRRUTHYUNJAYS T S. Structural synthesis by transformation of binary chains[J]. Mech. and Mach. Theory, 1979, 14(4): 221–231.
SOHN W J, FREUDENSTEIN F. An application of dual graphs to the automatic generation of the kinematic structure of mechanisms [J]. Trans. of ASME J. of Mech. Trans. and Auto. in Design, 1986, 108(8): 392–398.
GALLETTI C U. A note on modular approach to planar linkage kinematic analysis[J]. Mechanism and Machine Theory, 1986, 21(5): 385–391.
LI S, HONG C. A new method for computer identifying and modeling of planar linkages[C]//Proc. of Ninth World Congress on The Theory of Machine and Mechanisms, Milano, Italy, May, 1995: 278–281.
CHUENCHOM T, KOTA S. Synthesis of programmable mechanisms using adjustable dyads[J]. Transactions of the ASME Journal of Mechanical Design, 1997, 11(6): 232–237.
CHU J K, CAO W Q. Systemics of Assur groups with multiple joints[J]. Mechanism and Machine Theory, 1998, 33(8): 1127–1133.
CHU J K, CAO W Q. Type synthesis of 6-bar one-DOF linkage with with R and P pairs[J]. Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology for Aerospace Engineering, 1991, 10(2): 8–23.
CAO W Q, CHU J K. Type synthesis of 8-bar one-DOF multiple joint linkage[J]. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. Aerosp. Eng., 1990, 9(4): 1–7.
VEEGER H E J. The position of the rotation center of the glenohumeral joint[J]. Journal of Biomechanics, 2000, 12: 1711–1715.
TANG L, SUN X. Method and realization of computer-aided combination of Assur groups in conceptual design of planar linkage mechanisms[C]//ASME/IFToMM International Conference on Reconfigurable Mechanisms and Robots, London, United Kingdom, June 22–24, 2009: 123–128.
SHAI O. Topological synthesis of all 2D mechanisms through Assur graphs[C]//Proceedings of the ASME International Design Engineering Technical Conferences & Computers and Information in Engineering Conference IDETC/CIE, Montreal, Quebec, Canada, August,2010: 15–18.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China(Grant Nos. 51175069, 51205052), State Key Laboratory of Robotics of China(Grant No. 2012-O16), and Basic Science and Research Project of Chinese National University, China(Grant No. N140304004)
LI Shujun, born in 1955, is currently a professor at School of Mechanical Engineering & Automation, Northeastern University, China. His current research interests include theory of mechanisms, robot mechanisms, metamorphic mechanisms, and mechanical design theory and method.
WANG Hongguang, born in 1965, is currently a professor at State Key Laboratory of Robotics, Shenyang Institute of Automation, Chinese Academy of Sciences, China. His current research interests include the analysis and synthesis of robot mechanism, the mechanics of serial and parallel manipulators, the modular reconfigurable robots and autonomous mobile robots.
YANG Qiang, born in 1980, is currently a lecturer at School of Mechanical Engineering & Automation, Northeastern University, China. His current research interests include theory of mechanisms, metamorphic mechanisms, parallel mechanisms, and kinematic reliability of mechanisms.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, S., Wang, H. & Yang, Q. Constraint force analysis of metamorphic joints based on the augmented Assur groups. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 28, 747–755 (2015). https://doi.org/10.3901/CJME.2015.0216.056
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3901/CJME.2015.0216.056