Abstract
Chlorites are petrogenetically important minerals, exercise controls on petroleum reservoir qualities, are common in alteration zones during hydrothermal ore mineralization, and may form during carbon sequestration in sedimentary formations. Chlorite thermochemistry and structure have been investigated, in the present study, to facilitate an improved understanding of chlorite equilibria.
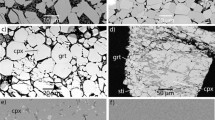
Three natural IIb chlorites were studied by powder diffraction and calorimetric methods (low-temperature relaxation calorimetry using a Physical Properties Measurement System [PPMS] and differential scanning calorimetry [DSC]). The samples include a low-Fe clinochlore [Mg-Chl] and two Fe-rich chlorites from Windsor [Fe-Chl(W)] and Michigan [Fe-Chl(M)]. The structure of each chlorite was refined in the ideal C2/m symmetry using Rietveld techniques. Lattice parameters for theWindsor chlorite are a = 5.3786(6) Å, b = 9.3176(9) Å, c = 14.2187(6) Å, β = 96.98(10)°. The Michigan chlorite returned a = 5.3897(3) Å, b = 9.3300(3) Å, c = 14.2376(2) Å, β = 97.043(5)° whereas the low-Fe clinochlore yielded a = 5.3301(3) Å, b = 9.2231(8) Å, c = 14.2912(4) Å, β= 97.03(10)°.
Heat capacities (Cp) for the three natural chlorites were measured using both PPMS (2–303 K) and DSC (282–564 K). Employing a combination of Debye-Einstein-Schottky functions, the lattice dynamics component of the Cp at lower temperature was evaluated allowing a separation of the magnetic spin ordering component of Cp from the lattice vibrational part. For Mg-Chl, Fe-Chl(W), and Fe-Chl(M), the polynomials defining the temperature dependencies of the heat capacities between 280 and 570 K are:
Cp = 1185.44(±68.93) − 9753.21(±186.85)T−0.5 − 1.9094(±1.0288)·107T−2 + 3.3013(±1.5363)·109T−3
Cp = 1006.06(±48.46) − 4134.83 (±1515.16)T−0.5 − 40.0949(±6.9413)·106T−2 + 5.9386(±1.0287)·109T−3
and
Cp = 1268.60(±67.16) − 11983.09(±2107.07)T−0.5 − 7.6037(±9.6417)·106T−2 + 1.5398(±1.4187)·109T−3, respectively.
Standard state molar thermodynamic functions, CP, ST, (HT−H0)/T, and φ were evaluated for the samples. S298.15 for Fe-Chl(W), Mg-Chl, and Fe-Chl(M) were found to be 499.14 ± 3.40, 437.81 ± 3.00 and 515.06 ± 3.60 J mol−1K−1, respectively, whereas S° for Fe-Chl(W) and Mg-Chl were determined to be 578.24 ± 3.76 and 503.21 ± 3.60 J mol−1K−1, −1
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aja, S.U. (2002) The stability of Fe-Mg chlorites in hydrothermal solutions: II. Thermodynamic properties. Clays and Clay Minerals, 50, 591–600.
Aja, S.U. and Dyar, M.D. (2002) The stability of Fe-Mg chlorites in hydrothermal solutions I. Results of experimental investigations. Applied Geochemistry, 17, 1219–1239.
Aja, S.U. and Small, J.S. (1999) The solubility of a low-Fe clinochlore between 25 and 175°C and Pv = PH2O. European Journal of Mineralogy, 11, 829–842
Anderson, G.M. and Crerar, D.A. (1993) Thermodynamics in Geochemistry: The Equilibrium Model. Oxford University Press, Oxford, UK.
Armstrong, J.T. (1982) New ZAF and a-factor correction procedures for the quantitative analysis of individual microparticles. Pp. 175–180 in: Microbeam Analysis (K.F.J. Heinrich, editor). San Francisco Press, San Francisco, California, USA.
Armstrong, J.T. (1995) CITZAF: A package of correction programs for the quantitative electron microbeam X-ray analyses of thick polished materials, thin films and particles. Microbeam Analyses, 4, 177–200.
Bailey, S.W. (1980) Summary of recommendations of AIPEA nomenclature committee on clay minerals. American Mineralogist, 65, 1–7.
Ballet, O., Coey, J.M.D., and Burke, K.J. (1985) Magnetic properties of sheet silicates: 2:1:1 layer minerals. Physics and Chemistry of Minerals, 12, 370–378.
Behrens, H. and Stuke, A. (2003) Quantification of H2O contents in silicate glasses using IR spectroscopy — a calibration based on hydrous glasses analyzed by Karl- Fischer titration. Glass Science and Technology, 76, 176–189.
Benisek, A. and Dachs, E. (2011) On the nature of the excess heat capacity of mixing. Physics and Chemistry of Minerals, 38, 185–191.
Benisek, A. and Dachs, E. (2012) A relationship to estimate the excess entropy of mixing: Application in silicate solid solutions and binary alloys. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 527, 127–131.
Benisek, A., Dachs, E., and Kroll, H. (2009) Excess heat capacity and entropy of mixing in high structural state plagioclase. American Mineralogist, 94, 1153–1161.
Berger, A., Gier, S., and Krois, P. (2009) Porosity — preserving chlorite cements in shallow-marine volcaniclastic sandstones: evidence from Cretaceous sandstones of the Sawan gas field, Pakistan. American Association of Petroleum Geology Bulletin, 93, 595–615.
Berman, R.G. (1988) Internally consistent thermodynamic data for stoichiometric minerals in the system Na2O-K2O-CaOMgO-FeO-Fe2O3-Al2O3-SiO2-TiO2-H2O-CO2. Journal of Petrology, 29, 445–522.
Berman, R.G. and Brown, T.H. (1985) Heat capacity of minerals in the system Na2O-K2O-CaO-MgO-FeO-Fe2O3-Al2O3-SiO2-TiO2-H2O-CO2: representation, estimation, and high temperature extrapolation. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 89, 168–183.
Bertoldi, C., Benisek, A., Čemic, L., and Dachs, E. (2001) The heat capacity of two natural chlorite group minerals derived from differential scanning calorimetry. Physics and Chemistry of Minerals, 28, 332–336.
Bertoldi, C., Dachs, E., and Appel, P. (2007) Heat pulse calorimetry on natural chlorite-group minerals. American Mineralogist, 92, 553–559.
Black, J.R. and Haese, R.R. (2014) Chlorite dissolution rates under CO2 saturated conditions from 50 to 120°C and 120 to 200 bar CO2. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 125, 225–240.
Boerio-Goates, J., Stevens, R., Hom, B.K., Woodfield, B.F., Piccione, P.M., Davis, M.E., and Navrotsky A. (2002) Heat capacities, third-law entropies and thermodynamic functions of SiO2 molecular sieves from T = 0 K to 400 K. Journal of Chemical Thermodynamics, 34, 205–227.
Brandt, F., Bosbach, D., Krawczyk-Bärsch, E., Arnold, T., and Bernhard, G. (2003) Chlorite dissolution in the acid pHrange: a combined microscopic and macroscopic approach. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 67, 1451–1461.
Brown, B.E. and Bailey, S.W. (1962) Chlorite polytypism: I. Regular and semi-random one-layer structure. American Mineralogist, 47, 819–850.
Dachs, E. and Benisek, A. (2011) A sample-saving method for heat capacity measurements on powders using relaxation calorimetry. Cryogenics, 51, 460–464.
Dachs, E. and Bertoldi, C. (2005) Precision and accuracy of the heat-pulse calorimetric technique: Low-temperature heat capacities of milligram-sized synthetic mineral samples. European Journal of Mineralogy, 17, 251–259.
Dachs, E., Harlov, D., and Benisek, A. (2010) Excess heat capacity and entropy of mixing along the chlorapatite—fluorapatite binary join. Physics and Chemistry of Minerals, 37, 1–12.
Dachs, E., Geiger, C.A., Benisek, A., and Grevel, K.D. (2012a) Thermodynamic properties of grossular garnet: Heat capacity behavior, standard entropy and selected petrologic applications. American Mineralogist, 97, 1299–1313.
Dachs, E., Geiger, C.A., and Benisek, A. (2012b) Almandine: Lattice and non-lattice heat capacity behavior and standard thermodynamic properties. American Mineralogist, 97, 1171–1182.
De Haller, A. and Fontboté, L. (2009) The Raúl-Condenstable iron oxide copper-gold deposit, Central Coast of Peru: Ore and related hydrothermal alteration, sulfur isotopes, and thermodynamic constraints. Economic Geology, 104, 365–384.
Foster, M.D. (1962) Interpretation of the composition and classification of chlorites. Geological Survey Profesional Paper, 414-A, 1–33.
Gailhanou, H., Rogez, J., van Miltenburg, J.C., van Genderen, A.C.G., Greńche, J.M., Gilles, C., Jalabert, D., Michau, N., Gaucher, E.C., and Blanc, P. (2009) Thermodynamic properties of chlorite CCa-2. Heat capacities, heat contents and entropies. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 73, 4738–4749.
Gopal, E.S.R. (1966) Specific Heats at Low Temperatures. Heywood Books, London.
Gould, K., Pe-piper, G., and Piper, D.J.W. (2010) Relationship of diagenetic chlorite rims to depositional facies in lower Cretaceous reservoir sandstones of the Scotian Basin. Sedimentology, 57, 587–610.
Grevel, K.D., Kahl, W.A., Majzlan, J., Navrotsky, A., Lathe, C., and Flockenberg, T. (2005) Thermodynamic properties of magnesium chloritoid. European Journal of Mineralogy, 17, 587–598.
Guilbert, J.M. and Park, Jr, C.F. (1986) The Geology of Ore Deposits. W. H. Freeman, New York.
Haszeldine, R.S., Quinn, O., England, G., Wilkinson, M., Shipton, Z.K., Evans, J.P., Heath, J., Crossey, L., Ballentine, C.J., and Graham, C.M. (2005) Natural geochemical analogues for carbon dioxide storage in deep geological porous reservoirs, a United Kingdom perspective. Oil & Gas Science and Technology — Revue d’IFP Energies Nouvelle, 60, 33–49.
Hemingway, B.S., Kittrick, J.A., Grew, E.S., Nelen, J.A., and London, D. (1984) The heat capacity of osumilite from 298.15 to 1000 K, the thermodynamic properties of natural chlorites to 500 K, and the thermodynamic properties of petalite to 1800 K. American Mineralogist, 69, 701–710.
Henderson, C.E., Essene, E.J., Anovitz, L.M., Westrum, E.F., Hemingway, B.S., and Bowman, J.R. (1983) Thermodynamic and phase equilibria of clinochlore, (Mg5Al)[Si3AlO10](OH)8. Transactions of the American Geophysical Union, 64, 466.
Holland, T.J.B. and Powell, R. (1998) An internally consistent thermodynamic dataset for phases of petrological interest. Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 16, 309–343.
Holland, T.J.B. and Powell, R. (2011) An improved and extended internally consistent thermodynamic dataset for phases of petrological interest, involving a new equation of state for solids. Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 29, 333–383.
Holland, T.J.B., Baker, J., and Powell, R. (1998) Mixing properties and activity-composition relationships of chlorites in the system MgO-FeO-Al2O3-SiO2-H2O. European Journal of Mineralogy, 10, 395–406.
Hutcheon, I. (1990) Clay—carbonate reactions in the Venture area, Scotian Shelf, Nova Scotia, Canada Pp. 199–212 in: Fluid-Mineral Interactions: A tribute to H. P. Eugster (R.J. Spencer and I.-M. Chou, editors). Special Publication, 2, Geochemical Society, St. Louis, Missouri, USA.
Jarosewich, E., Nelen, J.A., and Norberg, J.A. (1980) Reference samples for electron microprobe analysis. Geostandards Newsletters, 4, 43–47.
Joswig, W. and Fuess, H. (1990) Refinement of a one-layer triclinic chlorite. Clays and Clay Minerals, 38, 216–218.
Kittrick, J.A. (1982) Solubility of two high-Mg and two high-Fe chlorites using multiple equilibria. Clays and Clay Minerals, 30, 167–179.
Lai, S.K. and Yih, T.S. (1986) Excess entropy and resistivity of Mg-based alloys. Physica, 141B, 191–198.
Lanari, P., Wagner, T., and Vidal, O. (2014) A thermodynamic model for di-trioctahedral chlorite from experimental and natural data in the system MgO-FeO-Al2O3-SiO2-H2O: applications to P-T sections and geothermometry. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 167, 968–976.
Lougear, A., Grodzicki, M., Bertoldi, C., Trautwein, A.X., Steiner, K., and Amthauer, G. (2000) Mössbauer and molecular orbital study of chlorites. Physics and Chemistry of Minerals, 27, 258–269.
Lowson, R.T., Comarmond, M.-C.J., Rajaratnam, G., and Brown, P. (2005) The kinetics of dissolution of chlorite as a function of pH and at 25°C. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 69, 1687–1699.
Lowson, R.T., Brown, P.L., Comarmond, M.-C.J., and Rajaratnam, G. (2007) The kinetics of chlorite dissolution. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 71, 1431–1447.
Lu, J., Kharaka, Y.K., Thorsden, J.J., Horita, J., Karamalidis, A., Grifith, C., Hakala, J.A., Ambats, G., Cole, D.R., Phelps, T.J., Manning, M.A., Cook, P.J., and Hovorka, S.D. (2012) CO2-rock-brine interactions in Lower Tuscaloosa Formation at Cranfield CO2 sequestration site, Mississippi, USA. Chemical Geology, 291, 269–277.
Post, J.L. and Plummer, C.C. (1972) The chlorite series of Flagstaff Hill Area, California: A preliminary investigation. Clays and Clay Minerals, 20, 271–283.
Robie, R.A., Hemingway, B.S., and Takei, H. (1982) Heat capacities and entropies of Mg2SiO4, Mn2SiO4, and Co2SiO4 between 5 and 380 K. American Mineralogist, 67, 470–482.
Rose, A.W. and Burt, D.M. (1979) Hydrothermal alteration. Pp. 173–235 in: Geochemistry of Hydrothermal Ore Deposits (H.L. Barnes, editor). Wiley-Interscience, New Jersey, USA.
Rule, A.C. and Bailey, S.W. (1987) Refinement of the crystal structure of a monoclinic ferroan clinochlore. Clays and Clay Minerals, 35, 129–138.
Saccocia, P.J. and Seyfried, W.E. Jr. (1993) A resolution of discrepant thermodynamic properties for chamosite retrieved from experimental and empirical techniques. American Mineralogist, 78, 607–611.
Smith, J.T. and Ehrenberg, S.N. (1989) Correlation of carbon dioxide abundance with temperature in clastic hydrocarbon reservoirs. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 6, 129–135.
Smith, M.M., Wolery, T.J., and Carroll, S.A. (2013) Kinetics of chlorite dissolution at elevated temperatures and CO2 conditions. Chemical Geology, 347, 1–8.
Townsend, M.G., Longworth, G., and Kodama, H. (1986) Magnetic interaction at low temperature in chlorite and its products of oxidation: A Mössbauer investigation. The Canadian Mineralogist, 24, 105–115.
Ulbrich, H.H. and Waldbaum, D.R. (1976) Structural and other contributions to the third-law entropies of silicates. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 40, 1–24.
Vidal, O., Parra, T., and Vieillard, P. (2005) Thermodynamic properties of the Tschermak solid solution in Fe-chlorite: Application to natural examples and possible role of oxidation. American Mineralogist, 90, 347–358.
Welch, M.D., Barris, J., and Klinowski, J. (1995) A multinuclear NMR study of clinochlore. American Mineralogist, 80, 441–447.
Zazzi, A., Hirsch, T.K., Leonova, E., Kaikkonen, A., Grins, J., Annersten, H., and Eded, M. (2006) Structural investigations of natural and synthetic chlorite minerals by X-ray diffraction, Mössbauer spectroscopy and solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance. Clays and Clay Minerals, 54, 252–265.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aja, S., Omotoso, O., Bertoldi, C. et al. The Structure and Thermochemistry of Three Fe-Mg Chlorites. Clays Clay Miner. 63, 351–367 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1346/CCMN.2015.0630502
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1346/CCMN.2015.0630502