Abstract
Background
Polyethylene wear is one of the major concerns of orthopedic surgeons. However, there is no standardized calculation method for the wear rate following radiographic measurement. The purpose of this study was to propose a novel method of wear calculation and to compare its accuracy with a representative conventional method.
Methods
Relative position of the center of the femoral head to that of the cup progresses in one direction following arthroplasty surgery because of bedding-in and wear. We predetermined the amount of bedding-in, wear rate, and random error in measuring the head center position in a 2-dimensional plane. We calculated the wear rate using the head center coordinates over a certain number of measurement periods using a representative conventional method and our novel method. The conventional method consisted of transforming vector data into scalars and conducting a least-squares method. The least-squares method was directly applied to each component of the vector in the novel method. We evaluated the accuracy of these methods by comparing the expected value for the wear rate with their predetermined true values.
Results
If the error were limited to being random, the novel method could provide the predetermined wear rate as the calculation result. However, the conventional method could not.
Conclusion
We recommend using the novel method for the wear calculation rather than the conventional method because of its mathematical accuracy.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
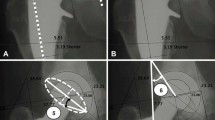
Progress of polyethylene wear significantly influences the long-term durability of the total hip prosthesis [1, 2]. In vivo wear can be observed as the femoral head penetration on postoperative radiographs, and numerous papers of wear analysis have been published [3,4,5,6,7]. There are several techniques to measure the penetration of the femoral head on radiographs after total hip arthroplasty, such as Livermore’s, the dual circle technique, and radiostereometric analysis [8, 9]. Modern measurement applications, such as Hip Analysis Suite (University of Chicago Medical Center, Chicago, Il, USA) and PolyWare (Draftware Developers, Vevay, IN, USA), measure the relative position of head center to that of cup center on radiographs [10, 11]. They then provide the head center penetration data in a scalar format, after transformation from vector (Fig. 1).
Summary of the conventional method to calculate penetration. a Radiographs taken immediately following the operation and at the follow-up period. b Detection of circular edges of the cup and head and calculation of their center positions (circle and cross) are semi-automatically performed by the measurement application. c Relative positions of the head center to the cup center are calculated for each radiograph (\(\overrightarrow{{H}_{0}}\) and \(\overrightarrow{{H}_{k}}\)). d The head penetration during the follow-up period can be calculated as \(\left|\overrightarrow{{H}_{k}}-\overrightarrow{{H}_{0}}\right|\) or \(-\left|\overrightarrow{{H}_{k}}-\overrightarrow{{H}_{0}}\right|\)
Relative position of the center of the femoral head to that of the cup is considered to progress in one direction after the arthroplasty surgery as result of bedding-in and wear. The bedding-in is considered to occur during the first several years after the operation as the result of the creep deformation of polyethylene, and the wear continues at a steady pace throughout the postoperative period as a result of friction between the head and liner [8]. Random and systematic errors are inevitable in measuring the position of the head and cup center [12,13,14,15,16]. Therefore, it is common in wear calculations to apply the least-squares method to multiple measured values of penetration after the bedding-in period [17]. Although the head penetration theoretically directs upward, measured penetration sometimes directs downward, due to measurement error. In this case, measurement applications provide the measurement result of penetration as \(-\left|\overrightarrow{{H}_{k}}-\overrightarrow{{H}_{0}}\right|\), and such penetration is called negative wear. However, how the negative wear should be treated in the following wear calculations has not been standardized. There are several options for treating the negative wear, as used in previous papers: using it intact, ignoring, and assuming zero [18,19,20,21]. However, no study has yet evaluated the validity of each option or recommended which option is to be used.
This study had two purposes. The first was to evaluate the accuracy of the conventional method of the wear calculation. The second was to propose a new method for the wear calculation and evaluate its accuracy.
Methods
Predetermined conditions and notations about the head and cup center measurement
For the purpose of evaluating the accuracy of the wear calculations, a set of generalized data of the wear measurement of a single hip was prepared in this study. It was assumed that the head center penetrated postoperatively in accordance with the principle of polyethylene wear.
The horizontal and vertical lines were defined as the x- and y-axes, respectively, and the coordinates of the head center relative to the cup center immediately after surgery was defined as (0, 0). The medial and proximal directions were defined as positive, and the lateral and distal directions as negative. Bedding-in was defined as \(\overrightarrow{b}=\left({b}_{x},{b}_{y}\right)\) and presumed to occur until the first postoperative follow-up (t1). Wear was defined to progress steadily after surgery at a rate of \(\overrightarrow{w}=\left({w}_{x},{w}_{y}\right)\) per year (\(\overrightarrow{b}\) and \(\overrightarrow{w}\) were parallel, and \({b}_{y}>0, {w}_{y}>0\)). According to these definitions, the coordinates of the head center at postoperative period tk (year) could be calculated as
where measurements of the head center positions are presumed to be performed n + 1 times in this study (k = 0, 1, 2, …, n, t0 = 0) (Fig. 2).
Mathematical notations about the true positions of the femoral head center. Head center coordinates relative to the cup center immediately after the operation were defined as \(\left({x}_{0}, {y}_{0}\right)=(0, 0)\). Penetration of the head center by the bedding-in \(\overrightarrow{b}=\left({b}_{x}, {b}_{y}\right)\) starts immediately after the operation and was presumed not to end until the first measurement period (t1). Penetration by wear starts immediately after the operation and continues at a steady pace throughout the follow-up period: \(\overrightarrow{w}=\left({w}_{x}, {w}_{y}\right)\) per year
Errors in measuring \(\left({x}_{k},{y}_{k}\right)\) were defined as \(\left({x}_k^{\prime },{y}_k^{\prime}\right)\). Then, \(\left({x}_k+{x}_k^{\prime },{y}_k+{y}_k^{\prime}\right)\) could be used as the coordinates measured at postoperative period tk. For accurate evaluation of the following wear calculations, the systematic error was presumed to be eliminated from \(\left({x}_k^{\prime },{y}_k^{\prime}\right)\). Then \(\left({x}_k^{\prime },{y}_k^{\prime}\right)\) represent random errors in measuring \(\left({x}_{k},{y}_{k}\right)\), and
where E is the expected value. The bedding-in and steady-state wear rate were calculated using the conventional and novel methods based on these definitions. Both calculation methods start after the penetration vector, and the measurement errors at each follow-up period were provided (Fig. 3).
Mathematical notations about the head center positions with measurement errors. Measurement errors at postoperative period tk were defined as \(\left({x}_k^{\prime },{y}_k^{\prime}\right)\) (k = 0, 1, …, n), then the measured coordinates of the head center at postoperative period tk were \(\left({x}_k+{x}_k^{\prime },{y}_k+{y}_k^{\prime}\right)\). Penetration vector during tk years was notated as \(\left({X}_{k},{Y}_{k}\right)\), which were calculated as \(\left({x}_k+{x}_k^{\prime }-{x}_0^{\prime },{y}_k+{y}_k^{\prime }-{y}_0^{\prime}\right)\)
Accuracy evaluation of the wear calculations using the predetermined measurement values
The accuracy of the wear calculation method was evaluated by comparing the predetermined true values of the bedding-in (\(\overrightarrow{b}\)) and wear rate (\(\overrightarrow{w}\)) with their expected values of the calculated results using \(\left({X}_{k},{Y}_{k}\right)\) (k = 0, 1, 2, …, n). The calculation method could be claimed as accurate when they were consistent [22].
Meanwhile, the best-fit line for multiple points \(\left({u}_{k},{v}_{k}\right)\) (k = 1, 2, …, n) is \(y=ax+b\), a and b can be calculated as follows using the least-squares method [17, 23].
These formulae can be represented more simply as follows:
where \({M}_{k}=\frac{n{u}_{k}-\sum_{l=1}^{n}{u}_{l}}{C}, {N}_{k}=\frac{\sum_{l=1}^{n}{\left({u}_{l}\right)}^{2}-{u}_{k}\sum_{l=1}^{n}{u}_{l}}{C}.\)
Conventional method
Conventional wear calculations start by transforming the penetration vectors with measurement errors into scalar. Negative wear was used intact in this study because it seemed the most popular option in previous studies [18,19,20,21]. Therefore, the penetration at tk years \(({P}_{k})\) was calculated as:
where \(sgn\left({Y}_{k}\right)=1\) when \({Y}_{k}\geqq 0\), and \(sgn\left({Y}_{k}\right)=-1\) when \({Y}_{k}<0.\) Using the least-squares method for linear regression (Eqs. (4) and (5)), the steady-state wear rate and bedding-in (\({W}_{c}\) and \({B}_{c}\)) were calculated as follows (Fig. 4).
The conventional method to calculate the bedding-in and wear rate. Pk was calculated for each postoperative period (tk) using Eq. (6). The best-fit line for multiple penetration data (tk, Pk) was identified using the least-squares method. The wear rate and bedding-in were indicated by the slope (Wc) and y-intercept (Bc) of the line, respectively
Therefore, we were able to conclude that the conventional method was accurate when the following equations were satisfied.
When all measurements were performed without an error, that is, \({P}_{k}=\left|\overrightarrow{b}+{t}_{k}\overrightarrow{w}\right|=\sqrt{{\left({x}_{k}\right)}^{2}+{\left({y}_{k}\right)}^{2}},\) the calculated results were consistent with the true values (\({W}_{c}=\left|\overrightarrow{w}\right|, {B}_{c}=\left|\overrightarrow{b}\right|\)). Thus,
Because \({M}_{k}\) and \({N}_{k}\) could take any real values depending on the measurement period
was necessary and sufficient for Eqs. (7) and (8) to be satisfied.
Novel method
We propose a novel calculation method in which penetration vectors are used without the transformation before the linear regression. In this method, the x and y components of the wear rate and bedding-in (Wx, Bx, Wy, and By) were calculated separately. Best-fit lines for \(\left({t}_{k},{X}_{k}\right)\) and \(\left({t}_{k},{Y}_{k}\right)\) (k = 1, 2, …, n) were respectively defined as
where \({W}_{x}\), \({B}_{x}\), \({W}_{y}\), and \({B}_{y}\) could be calculated using Eqs. (4) and (5), as follows (Fig. 5).
The novel method to calculate the bedding-in and wear rate. The x and y components of the penetration vector (Xk and Yk) were independently calculated for each postoperative period (tk). Best-fit lines for \(\left({t}_{k}, {X}_{k}\right)\) and \(\left({t}_{k}, {Y}_{k}\right)\) were identified separately using the least-squares method (lower left and upper right). The x and y components of the wear rate and bedding-in were indicated by the slope (Wx, Wy) and y-intercept (Bx, By) of the lines, respectively
Their expected values were as follows.
Therefore, we could conclude that the novel method was accurate when these expected values were consistent with the predetermined true values, wx, bx, wy, and by, respectively.
Results
Conventional method
Because \(\sqrt{{\left({X}_{k}\right)}^{2}+{\left({Y}_{k}\right)}^{2}}\) cannot be directly presented by a formula using \(\sqrt{{\left({x}_{k}\right)}^{2}+{\left({y}_{k}\right)}^{2}}\) [4], we used the Taylor expansion to find the relationship between them. When f was defined as \(f\left(x,y\right)=\sqrt{{x}^{2}+{y}^{2}}\), it could be Taylor-expanded around \({x}_{k}\) and \({y}_{k}\) as.
When the expected values were considered,
When Eq. (2) was assigned, \(x'_k\) and \(y'_k\) were independent and \(E\left({R}_{n}\right)\) was approximated as zero:
Because the variance of \(x'_k\) and could be considered equivalent (\(\left({\sigma}_{x_k^{\prime }}={\sigma}_{y_k^{\prime }}={\sigma}_e\right)\), where \(\sigma\) denotes the standard deviation),
(See Additional file 1: Appendix (1).)
Because \(E\left(sgn\left({Y}_{k}\right)\right)\) can vary between 0 and 1 according to the value of \({y}_{k}\), \({y}_k^{\prime}\), and \({y}_0^{\prime }\), \(E\left({P}_{k}\right)\) could vary between 0 and \(\sqrt{{\left({x}_{k}\right)}^{2}+{\left({y}_{k}\right)}^{2}}+\frac{{\left({\sigma }_{e}\right)}^{2}}{\sqrt{{\left({x}_{k}\right)}^{2}+{\left({y}_{k}\right)}^{2}}}\). Therefore, Eq. (9) could not always be satisfied.
Novel method
According to the definitions of \({X}_{k}\) and \({Y}_{k}\) (Eq. (3)),
Therefore, Eqs. (14)–(17) could be transformed into
From the combination of Eqs. (19) and (20), we know that the best-fit line for points \(\left({t}_{k},{x}_{k}\right)\) (k = 1, 2, …, n) is.
When Eq. (1) is taken into account,
From the combination of Eqs. (21) and (22), we know that the best-fit line for points \(\left({t}_{k},{y}_{k}\right)\) (k = 1, 2, …, n) is.
Similarly,
These results demonstrate the accuracy of the novel method.
Discussion
This study mathematically demonstrates both the insufficient accuracy of the conventional method and the sufficient accuracy of the novel method for wear calculation. Insufficient accuracy of the conventional method was proved by the fact that Eq. (9) was not always satisfied. Given the same reason, the conventional calculation could not be sufficiently accurate even if the other option to treat the negative wear (assuming zero or neglecting) was adopted. Discrepancy between the average vector (\(\sqrt{{\left({x}_{k}\right)}^{2}+{\left({y}_{k}\right)}^{2}}\)) and the average scalar (\(E\left(\sqrt{{\left({X}_{k}\right)}^{2}+{\left({Y}_{k}\right)}^{2}}\right)\)) was also discussed in other fields of study. Ranacher et al. demonstrated that the distance between two points recorded with the Global Positioning System (GPS) is, on average, larger than the true distance [24]. This discrepancy is due in part to the uncertainty in location measurement by the GPS and results in a difference between the average vector and scalar lengths. Similar findings have been reported in the field of wind speed measurement [25]. Thus, transformation of vector measurement data into scalar before averaging has a potential to lead to wrong calculation results.
The latest measurement techniques, such as dual circle and radiostereometric analysis, provides penetration data in vector format, but they have been then usually transformed into scalar by wear measurement applications for the purpose of applying the conventional calculation method. However, we demonstrated more accuracy with the novel method, which uses vector penetration data intact. We recommend wear researchers to adopt the novel method in the wear analysis, and, simultaneously, manufacturers of the wear measurement application to provide the penetration data in the vector format as the result of measurement.
The accuracy of the novel method was evaluated in the situation of wear calculation of a single hip. Practically, we can use spreadsheet software, such as Excel (Microsoft Corp., Redmond, WA, USA), for the calculation using the novel method. There are several ways to perform the calculation on Excel after collecting all head center penetration vector data throughout the postoperative period. We can enter the formulae (Eqs. (10)–(13)) into a spreadsheet for direct calculations, generate an approximate straight line in a scatterplot, or use “Solver” functions to calculate \(\left({B}_{x},{B}_{y}\right)\) and \(\left({W}_{x},{W}_{y}\right).\) For better comprehending the novel method, an example for calculating the bedding-in and wear rate are presented in Additional file 1: Appendix (2). Furthermore, we can use the mean and standard deviation of each component to statistically summarize the data of a group of hips as: \(\left(\overline{{B }_{x}}\pm {\sigma }_{{B}_{x}},\overline{{B }_{y}}\pm {\sigma }_{{B}_{y}}\right)\) and \(\left(\overline{{W }_{x}}\pm {\sigma }_{{W}_{x}},\overline{{W }_{y}}\pm {\sigma }_{{W}_{y}}\right).\) Regarding the clinical significance of wear data, using average penetration \(\sqrt{{\left(\overline{{W }_{x}}\right)}^{2}+{\left(\overline{{W }_{y}}\right)}^{2}}\pm \sqrt{\frac{{\left(\overline{{W }_{x}}\right)}^{2}{\left({\sigma }_{{W}_{x}}\right)}^{2}+{\left(\overline{{W }_{y}}\right)}^{2}{\left({\sigma }_{{W}_{y}}\right)}^{2}}{{\left(\overline{{W }_{x}}\right)}^{2}+{\left(\overline{{W }_{y}}\right)}^{2}}}\) (Additional file 1: Appendix (3) [26]) may also be suitable to compare between groups.
When the linear wear rate was provided in the vector format, how should the volumetric wear rate be calculated? There are several popular methods for the volumetric wear approximate calculation [27, 28]. Wear depth (d) and wear angle (β) are unexceptionally necessary for them, and the former is a scalar value transformed from the penetration vector. Therefore, it should be avoided to average or apply the least-squares method to values of the volumetric wear if possible. We consider that it is more accurate to calculate the volumetric wear rate of a single hip using the linear wear rate vector obtained by the novel method than by applying the least-squares method to multiple values of the volumetric wear obtained for each follow-up period. We also consider that to use the average wear vector to calculate the average volumetric wear of a group of hips would be more accurate than to average values of volumetric wear obtained for multiple cases. When W′x and W′y were defined as the components of the wear vector calibrated by the cup inclination angle, \(\sqrt{{\left(\overline{{W }_{x}}\right)}^{2}+{\left(\overline{{W }_{y}}\right)}^{2}}\left(=\sqrt{\left({\overline{W^\prime_x}}\right)^2+\left({\overline{W^\prime_y}}\right)^2}\right)\) can be used for average d. When \(\overline{W^\prime_x}\ge0\), \({\tan}^{-1}\frac{\overline{W^\prime_y}}{\overline{W^\prime_x}}\) can be used for β, and when \(\overline{W^\prime_x}<0\), \({\tan}^{-1}\frac{\overline{W^\prime_y}}{\overline{W^\prime_x}}+\pi\) can be used [29].
There is a limitation to this study. The wear progresses 3-dimensionally in vivo, although this study evaluated the accuracy of only 2-dimensional wear calculations. We consider that the conventional method would also be less accurate, and the novel method would be more accurate when they were applied to 3-dimensional wear calculations because a z component could be added to the formulae without impairing solvability. These were simply testified in Additional file 1: Appendix (4).
Availability of data and materials
The datasets generated and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Sochart DH. Relationship of acetabular wear to osteolysis and loosening in total hip arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1999;363:135–50.
Dowd JE, Sychterz CJ, Young AM, Engh CA. Characterization of long-term femoral head- penetration rates. Association with and prediction of osteolysis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2000;82:1102–7.
So K, Goto K, Kuroda Y, Matsuda S. Minimum 10-Year Wear Analysis of Highly Cross-Linked Polyethylene in Cementless Total Hip Arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2015;30:2224–6.
Ise K, Kawanabe K, Tamura J, Akiyama H, Goto K, Nakamura T. Clinical results of the wear performance of cross-linked polyethylene in total hip arthroplasty: prospective randomized trial. J Arthroplasty. 2009;24:1216–20.
Okutani Y, Goto K, Kawata T, Okuzu Y, So K, Kuroda Y, Matsuda S. A long-term comparative study between two different designs of cemented stems: Distal-cylindrical versus distal-taper. J Orthop. 2018;15:190–5.
Kawata T, Goto K, So K, Kuroda Y, Matsuda S. Polyethylene and highly cross-linked polyethylene for cemented total hip arthroplasty: A comparison of over ten-year clinical and radiographic results. J Orthop. 2017;14:520–4.
Goto K, Kuroda Y, Kawai T, Kawanabe K, Matsuda S. The use of a bioactive bone cement containing apatite-wollastonite glass-ceramic filler and bisphenol-a-glycidyl methacrylate resin for acetabular fixation in total hip arthroplasty: long-term follow-up results of a clinical trial. Bone Joint J. 2019;101-B:787–92.
Martell JM. Clinical wear assessment. In: Callaghan JJ, Rosenberg AG, Rubash HE, editors. The Adult Hip. 2nd ed. Pennsylvania: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2007. p. 238–47.
McCalden RW, Naudie DD, Yuan X, Bourne RB. Radiographic methods for the assessment of polyethylene wear after total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005;87:2323–34.
Devane PA, Horne JG. Assessment of polyethylene wear in total hip replacement. Clin Orthop. 1999;369:59–72.
Martell JM, Berdia S. Determination of polyethylene wear in total hip replacements with use of digital radiographs. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1997;79:1635–41.
Bragdon CR, Estok DM, Malchau H, Kärrholm J, Yuan X, Bourne R, Veldhoven J, Harris WH. Comparison of two digital radiostereometric analysis methods in the determination of femoral head penetration in a total hip replacement phantom. J Orthop Res. 2004;22:659–64.
Ebramzadeh E, Sangiorgio SN, Lattuada F, Kang JS, Chiesa R, McKellop HA, Dorr LD. Accuracy of measurement of polyethylene wear with use of radiographs of total hip replacements. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003;85:2378–84.
Maruyama M, Tensho K, Wakabayashi S, Hisa K. Standing versus supine radiographs to evaluate femoral head penetration in the polyethylene liner after total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2014;29:2415–9.
Sychterz CJ, Young AM, Engh CA. Effect of radiographic quality on computer-assisted head penetration measurements. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2001;386:150–8.
Wan Z, Boutary M, Dorr LD. Precision and limitation of measuring two-dimensional wear on clinical radiographs. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2006;449:267–74.
Sychterz CJ, Engh CA Jr, Yang A, Engh CA. Analysis of temporal wear patterns of porous-coated acetabular components: Distinguishing between true wear and so-called bedding-in. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1999;81:821–30.
Smith PN, Ling RS, Taylor R. The influence of weight-bearing on the measurement of polyethylene wear in THA. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1999;81:259–65.
Babovic N, Trousdale RT. Total hip arthroplasty using highly cross-linked polyethylene in patients younger than 50 years with minimum 10-year follow-up. J Arthroplasty. 2013;28:815–7.
Dorr LD, Wan Z, Shahrdar C, Sirianni L, Boutary M, Yun A. Clinical performance of a Durasul highly cross-linked polyethylene acetabular liner for total hip arthroplasty at five years. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005;87:1816–21.
Ranawat AS, Tsailis P, Meftah M, Koob TW, Rodriguez JA, Ranawat CS. Minimum 5-year wear analysis of first-generation highly cross-linked polyethylene in patients 65 years and younger. J Arthroplasty. 2012;27:354–7.
Taylor JR. Statistical Analysis of Random Uncertainties. In: Taylor JR, editor. An introduction to error analysis. 2nd ed. California: University Science Books; 1997. p. 93–120.
Taylor JR. Statistical Least-Squares Fitting. In: Taylor JR, editor. An introduction to error analysis. 2nd ed. California: University Science Books; 1997. p. 181–208.
Ranacher P, Brunauer R, Trutschnig W, Van der Spek S, Reich S. Why GPS makes distances bigger than they are. Int J Geogr Inf Sci. 2016;30:316–33.
Frenkiel FN. Frequency distributions of velocities in turbulent flow. J Meteorology. 1951;8:316–20.
Taylor JR. Propagation of Uncertainties. In: Taylor JR, editor. An introduction to error analysis. 2nd ed. California: University Science Books; 1997. p. 45–92.
Sychterz CJ, Moon KH, Hashimoto Y, Terefenko KM, Engh CA, Bauer TW. Wear of polyethylene cups in total hip arthroplasty. a study of specimens retrieved post mortem. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1996;78:1193–200.
Uddin MS, Mak CYE, Callary SA. Evaluating hip implant wear measurements by CMM technique. Wear. 2016;364–365:193–200.
Mardia KV, Jupp PE. Directional Statistics. England: Wiley; 2000. p. 15.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
This research received no specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors reviewed and approved the manuscript. Drafting the manuscript: Kazutaka So. Study concept and design: Koji Goto, Yutaka Kuroda. Supervision: Atsushi Kawaguchi, Shuichi Matsuda.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
So, K., Goto, K., Kawaguchi, A. et al. The superior accuracy of a novel method in total hip wear calculations following radiographic measurement. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 23, 130 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12891-021-04964-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12891-021-04964-5