Abstract
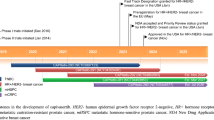
Alpelisib (Piqray™)—an orally available phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) inhibitor with specific activity against PI3K alpha (PI3Kα)—is being developed by Novartis for the treatment of breast cancer. Alpelisib has demonstrated efficacy in combination with fulvestrant as treatment for hormone receptor (HR)-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor-2 (HER2)-negative breast cancer in patients with a PIK3CA mutation and was recently approved for this indication in the USA. This article summarizes the milestones in the development of alpelisib leading to this first approval.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
An oral phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) inhibitor being developed by Novartis for the treatment of breast cancer |
Received its first global approval on May 24th 2019 in the USA |
Approved for use in combination with fulvestrant to treat postmenopausal women, and men, with HR-positive, HER2-negative, PIK3CA-mutated, advanced or metastatic breast cancer following progression on or after treatment with an endocrine-based regimen |

1 Introduction
Alpelisib (Piqray™), a phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) inhibitor with specific activity against PI3K alpha (PI3Kα), is being developed by Novartis Oncology (previously Novartis) for the treatment of breast cancer. Mutation or amplification of the PIK3CA gene, which encodes the catalytic (p110α) subunit of PI3K, is frequently observed in solid tumours including approximately 40% of breast cancers and is thus a logical target for therapeutic intervention [1, 2]. Alpelisib in combination with fulvestrant is approved in the USA for the treatment of postmenopausal women and men with hormone receptor (HR) positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor-2 (HER2)-negative, PIK3CA-mutated, advanced or metastatic breast cancer [3]. Alpelisib is also under development for use in triple negative breast cancer and HER2-positive advanced breast cancer in several countries worldwide [4].
The recommended dose of alpelisib is 300 mg once daily taken with food. In the event of adverse reactions requiring a reduction in dose the dose of alpelisib should be reduced first to 250 mg once daily and then to 200 mg once daily. If dosage reduction below 200 mg/day is required alpelisib should be discontinued [5].
1.1 Company Agreements
In January 2016 Novartis entered into a worldwide clinical collaboration with Radius Health to conduct preclinical trials to study the effects of alpelisib in combination with elacestrant (RAD 1901), an oral estrogen receptor degrader being developed by Radius Health. Under the terms of the non-exclusive agreement, both companies will contribute resources and supply compound material necessary for the planned studies and will share third party out-of-pocket research and development expenses. Each party will solely own all rights to any invention related to its respective product, and the parties will jointly own all data and inventions related to the combination use of elacestrant with alpelisib or another compound arising under the collaboration [6].
2 Scientific Summary
2.1 Pharmacodynamics
Alpelisib had an IC50 of 4.6 nmol/L against wild-type PI3Kα but had considerably less activity against PI3Kδ (IC50 290 nmol/L), PI3Kγ (IC50 250 nmol/L) and PI3Kβ (IC50 1,156 nmol/L) in vitro. The drug potently inhibited the most common PIK3CA somatic mutations (H1047R and E545 K) with an IC50 of ≈ 4 nmol/L. Alpelisib had low activity against the distinct lipid kinase PIK4β (IC50 581 nmol/L) and no discernible activity against the class III family member Vps34 and the related class IV PIKK protein kinases mTOR, DNA-PK, and ATR (IC50s > 9100 nmol/L). In Rat1 cells transformed using activated PI3Ks, alpelisib potently inhibited Akt phosphorylation in cells transformed with PI3Kα (IC50 74 nmol/L) but had ≥ 15-fold lower activity in cells transformed with PI3Kβ and PI3Kδ [7].
In vivo in mice bearing Rat1-myr-p110α tumours, single or repeated oral doses of alpelisib 12.5, 25 or 50 mg/kg were associated with dose and time-dependent inhibition of the PI3K/Akt pathway that paralleled drug exposure in tumour and plasma. In a further study using the same model, oral administration of alpelisib 12.5, 25 or 50 mg/kg for ≤ 8 consecutive days was associated with a dose-dependent antitumor effect with a treatment/control ratio (T/C) of 14.1% and regressions of 9.6% and 65.2%, respectively [7].
2.2 Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetic profile of alpelisib has been studied in a phase Ib dose-escalation study (NCT01219699) in patients with tumours harbouring PIK3CA mutation and/or amplification (n = 134). Alpelisib was administered orally at a dose of 30 to 450 mg once daily or 120 to 200 mg twice daily on a continuous schedule in 28 day cycles until disease progression, unacceptable toxicity, withdrawal of consent, or investigator’s decision, with 400 mg once daily (achieved by 65 patients) and 150 mg twice daily (achieved by 15 patients) established as the maximum tolerated doses. Median tmax on cycle 1 day 1 was ≈ 2 hours at both maximum tolerated doses and median t½ was 7.6 hours with the 400 mg once daily dose. The pharmacokinetic profile and exposure were similar on cycle 1 day 1, cycle 1 day 8, and cycle 2 day 1, indicating minimal accumulation. Inter-patient variability at steady state was moderate in patients treated with the once-daily regimen (mean coefficient of variation 17 to 43% for Cmax and 16 to 41% for AUC0-24h) but was higher in patients receiving the drug twice-daily (mean coefficient of variation 37 to 54% for Cmax and 26 to 40% for AUC0-12h) [1]. A population pharmacokinetic analysis in patients (n = 60) participating in this trial found that the pharmacokinetic profile of alpelisib was best described by a one compartment model with typical population oral clearance and volume of distribution estimates of 10 L/h (between subject variability 26%) and 108 L (between subject variability 28%), respectively. The optimal number of transit compartments was estimated to be 8.1, with a mean transit time to the absorption compartment of 1.28 hours (between subject variability 32%) and between-occasion variability in the rate and extent of absorption of 46% and 26%, respectively [8].

Administration of a single 400 mg oral dose of [14C]alpelisib (2.78 MBq of 14C) to male volunteers (n = 4) produced a maximum radioactivity of 2320 and 1890 (mean) ng-equivalents/mL in blood and plasma, respectively, after 2 hours. Levels declined in a biphasic manner with Tlast values of 36 and 60 h, respectively. The t½ of radioactivity was 11.1 and 18.0 h, respectively. Alpelisib plasma concentrations had a similar profile to radioactivity, peaking at 1320 ng/ml after 2 h then declining in a biphasic manner with a mean t½ of 13.7 h. The mean apparent oral clearance and apparent terminal volume of distribution were 39.0 L/h and 838 L, respectively, with the pharmacokinetic profiles of alpelisib and radioactivity decaying largely in parallel indicating the presence of formation rate-limited metabolites. According to the ratio of AUCINF of radioactivity and alpelisib in plasma, the relative exposure to alpelisib was 60.0% of total radioactivity. Inter-individual variability in pharmacokinetic parameters was high (coefficients of variance 30.8 to 69.2%). 38.2 and 39.5% of alpelisib was excreted as unchanged drug or the primary (inactive) metabolite (M4), respectively, 79.8% in faeces and 13.1% in urine [9].
2.3 Therapeutic Trials
2.3.1 Hormone Receptor-Positive, Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2-Negative Breast Cancer
2.3.1.1 Phase III
Treatment with alpelisib plus fulvestrant was associated with prolonged progression-free survival compared to placebo plus fulvestrant in patients with advanced PIK3CA-mutated, HR-positive, HER2-negative breast cancer previously treated with endocrine-based therapy in the phase III SOLAR-1 trial (NCT02437318). Patients were divided according tumour-tissue PIK3CA mutation status and randomized to treatment with alpelisib 300 mg/day plus fulvestrant 500 mg every 28 days and once on day 15 (n = 169 with and 115 without PIK3CA mutations) or placebo plus fulvestrant (n = 172 with and 116 without PIK3CA mutations). The primary endpoint was progression-free survival, as assessed by the investigator, in the cohort with PIK3CA-mutated cancer; progression-free survival was also analysed in the cohort without PIK3CA-mutated cancer. In patients with PIK3CA mutation, progression-free survival after 20 months’ (median) follow up was 11.0 months in the alpelisib plus fulvestrant group and 5.7 months in the placebo plus fulvestrant group (hazard ratio for progression or death 0.65, p < 0.001). In patients without PIK3CA mutation progression free survival was 7.4 months in the alpelisib plus fulvestrant group and 5.6 months in the placebo plus fulvestrant group (hazard ratio for progression or death 0.85). Overall response (complete or partial response) in patients with PIK3CA-mutated cancer was 26.6 and 12.8% in the alpelisib and placebo groups, respectively [10].
2.3.1.2 Phase II
Addition of alpelisib to 24-weeks’ neoadjuvant letrozole treatment did not improve response in patients with HR-positive, HER2-negative early breast cancer in the phase II NEO-ORB trial (NCT01923168). Postmenopausal women with HR-positive, HER2-negative, T1c-T3 breast cancer were divided according to tumour-tissue PIK3CA mutation status and randomized to 24 weeks’ treatment with alpelisib 300 mg/day plus letrozole 2.5 mg/day (n = 60 with and 71 without PIK3CA mutations) or placebo plus letrozole 2.5 mg/day (n = 67 with and 59 without PIK3CA mutations). In patients with PIK3CA mutations the objective response rate (complete or partial response) was 43.3% in those given alpelisib plus letrozole compared with 44.8% in the placebo plus letrozole group. In patients without PIK3CA mutations the overall response rate was 63.4% in those given alpelisib plus letrozole compared with 61.0% in the placebo plus letrozole group. Pathologic complete response rates were 3% or less in all groups [11].
2.3.2 Adverse Events
Adverse reactions (all grades) occurring in ≥ 35% of patients in the alpelisib vs placebo arms in the SOLAR-1 trial were hyperglycaemia (64% of alpelisib plus fulvestrant vs. 10% of placebo plus fulvestrant recipients), diarrhoea (58% vs. 16%), nausea (45 vs. 22%), stomatitis (30 vs. 6%), fatigue (42 vs. 29%), decreased appetite (36 vs. 10%) and rash (52 vs. 7%) [5, 10]. Laboratory abnormalities occurring in ≥ 10% of patients included decreased lymphocyte count (52 vs. 40%), decreased haemoglobin (42 vs. 29%), prolonged activated partial thromboplastin time (21 vs. 16%), decreased platelet count (14 vs. 6%), increased glucose (79 vs. 34%), increased creatinine (67 vs. 25%), increased gamma glutamyl transferase (52 vs. 44%), increased alanine aminotransferase (44 vs. 34%), increased lipase (42 vs. 25%), decreased calcium (27 vs. 20%), decreased glucose (26 vs. 14%), decreased potassium (14 vs. 2.8%), decreased albumin (14 vs. 8%) and decreased magnesium (11 vs. 4.2%) [5].
Thirty five percent of patients receiving alpelisib plus fulvestrant experienced serious adverse reactions. The most frequent were hyperglycaemia (10%), rash (3.5%), diarrhoea (2.8%), acute kidney injury (2.5%), abdominal pain (2.1%), and anaemia (2.1%). Two patients died while receiving alpelisib plus fulvestrant from causes other than the underlying malignancy, one as a result of cardio-respiratory arrest and the other because of a second primary malignancy [5].
Permanent discontinuation of alpelisib plus fulvestrant and alpelisib only because of adverse events was required in 4.6 and 21% of patients, respectively. The most frequent adverse events leading to treatment discontinuation were hyperglycaemia (6%), rash (4.2%), diarrhoea (2.8%), and fatigue (2.5%). Fifty five percent of patients receiving alpelisib plus fulvestrant required dose reductions because of adverse reactions, most frequently hyperglycaemia (29%), rash (9%), diarrhoea (6%), stomatitis (3.5%) and mucosal inflammation (2.1%) [5].
2.4 Companion Diagnostic
The therascreen® PIK3CA RGC PCR kit developed by QIAGEN has been approved by the US FDA as a companion diagnostic to aid in identifying patients eligible for treatment with alpelisib [12]. A second companion diagnostic is being developed by Foundation Medicine (a subsidiary of Roche) [13].
2.5 Ongoing Clinical Trials
The phase III SOLAR-1 trial described above is ongoing. Further trials evaluating alpelisib-containing regimens are pending or ongoing in patients with HR-positive, HER2-negative breast cancer (NCT03056755 [BYLieve]) [14], locally recurrent or metastatic HER-2-negative breast cancer (NCT02379247), HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer (NCT01300962, NCT02038010, NCT02167854), advanced or metastatic estrogen receptor (ER)-positive breast cancer (NCT01872260, NCT02734615), recurrent triple negative breast cancer or high grade serous ovarian cancer (NCT01623349), metastatic androgen receptor-positive and PTEN-positive breast cancer (NCT03207529).
3 Current Status
Alpelisib received its first global approval on May 24th 2019 in the USA for use in combination with fulvestrant to treat postmenopausal women, and men, with HR-positive, HER2-negative, PIK3CA-mutated, advanced or metastatic breast cancer—as detected by an FDA-approved test—following progression on or after treatment with an endocrine-based regimen.
References
Juric D, Rodon J, Tabernero J, et al. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase alpha-selective inhibition with alpelisib (BYL719) in PIK3CA-altered solid tumors: results from the first-in-human study. J Clin Oncol. 2018;36(13):1291–9.
Pereira B, Chin SF, Rueda OM, et al. The somatic mutation profiles of 2,433 breast cancers refines their genomic and transcriptomic landscapes. Nat Commun. 2016;7:11479.
Novartis. FDA approves Novartis Piqray®; the first and only treatment specifically for patients with a PIK3CA mutation in HR +/HER2− advanced breast cancer. 2019. [media release]. 28 May 2019.
Novartis. Novartis global pipeline. 2019. https://www.novartis.com/our-science/novartis-global-pipeline. Accessed 6 June 2019
Novartis. Piqray® (alpelisib) US prescribing information. 2019. https://www.pharma.us.novartis.com. Accessed 28 May 2019.
Radius. Radius health announces clinical collaboration with a leading pharmaceutical company to evaluate RAD1901 combination regimens in advanced breast cancer. [media release]. 27 Jan 2016. http://www.radiuspharm.com.
Fritsch C, Huang A, Chatenay-Rivauday C, et al. Characterization of the novel and specific PI3Kalpha inhibitor NVP-BYL719 and development of the patient stratification strategy for clinical trials. Mol Cancer Ther. 2014;13(5):1117–29.
De Buck SS, Jakab A, Boehm M, et al. Population pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of BYL719, a phosphoinositide 3-kinase antagonist, in adult patients with advanced solid malignancies. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2014;78(3):543–55.
James A, Blumenstein L, Glaenzel U, et al. Absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion of [14C] BYL719 (alpelisib) in healthy male volunteers. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2015;76(4):751–60.
Andre F, Ciruelos E, Rubovszky G, et al. Alpelisib for PIK3CA-mutated, hormone receptor-positive advanced breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2019;380(20):1929–40.
Mayer IA, Prat A, Egle D, et al. A phase II randomized study of neoadjuvant letrozole plus alpelisib for hormone receptor-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative breast cancer (NEO-ORB). Clin Cancer Res. 2019;25(10):2975–87.
Qiagen. QIAGEN launches first FDA-approved companion diagnostic for PIK3CA biomarkers to enhance precision medicine in breast cancer. [media release]. 28 May 2019. https://corporate.qiagen.com.
Foundation Medicine Inc. Foundation Medicine announces strategic collaboration with major pharmaceutical company [media release]. 17 Oct 2018. http://investors.foundationmedicine.com.
Rugo HS, Bianchi GV, Chia SKL, et al. BYLieve: A phase II study of alpelisib (ALP) with fulvestrant (FUL) or letrozole (LET) for treatment of PIK3CA mutant, hormone receptor-positive (HR +), human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative (HER2-) advanced breast cancer (aBC) progressing on/after cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibitor (CDK4/6i) therapy [abstract no. TPS1107]. J Clin Oncol. 2018;36(15 Suppl).
Funding
The preparation of this review was not supported by any external funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
During the peer review process the manufacturer of the agent under review was offered an opportunity to comment on the article. Changes resulting from any comments received were made by the authors on the basis of scientific completeness and accuracy. A. Markham, a contracted employee of Adis International Ltd/Springer Nature, is responsible for the article content and declares no relevant conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Additional information for this AdisInsight Report can be found at https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.8317130.
This profile has been extracted and modified from the AdisInsight database. AdisInsight tracks drug development worldwide through the entire development process, from discovery, through pre-clinical and clinical studies to market launch and beyond.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Markham, A. Alpelisib: First Global Approval. Drugs 79, 1249–1253 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40265-019-01161-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40265-019-01161-6