Summary
Two new species of Eriocaulon (Eriocaulaceae) from Bokor National Park, Kampot province, southwest Cambodia are described and illustrated: E. bokorense Soulad. & Praj. and E. cambodianum Soulad. & Praj. Information regarding the habitat and an IUCN provisional conservation assessment of each species are provided.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Eriocaulon L. (Eriocaulaceae) consists of over 450 species and is widely distributed in Africa, Asia and America (Larridon et al. 2019). The genus is characterised by its habitat in aquatic and wetland areas, by its short stems and basal rosettes of leaves, and solitary heads of many small unisexual flowers at the apices of the scapes (Stützel 1998; Prajaksood et al. 2017; Leach 2017). The species of Eriocaulon are widely distributed from lowlands to high mountains in subtropical to tropical areas of the world (Stützel 1998). In Asia, the highest number of species is in India with 109 species (Ansari & Balakrishnan 2009; Darshetkar et al. 2017; Darshetkar et al. 2019; Francis et al. 2020; Anoop & Robi 2021), followed by Thailand with 36 species (19 endemics, Prajaksood & Chantaranothai 2002; Prajaksood et al. 2012; Prajaksood et al. 2017; Khorngton et al. 2020), China with 35 species (13 endemics, Ma et al. 2000) and Japan with 34 species (8 endemics, Satake 1940).
The flora of Cambodia is poorly known and has one of the lowest estimated collecting densities in Southeast Asia (Middleton et al. 2019). Eriocaulon in Cambodia was initially represented by three species (of 27 species in total) in the Flore générale de l’Indo-Chine (Lecomte 1912) but only one species in the monograph by Zhang (1999). The most up-to-date checklist of Cambodia by Cho et al. (2016) and floristic surveys in Cambodia (Rundel & Middleton 2017; Khorngton et al. 2020) raised the number of species to 14, with one variety.
Critical examination of Eriocaulon specimens collected in Cambodia, Laos and Vietnam has been under way since 2013, during which time lectotypes have been designated (Souladeth et al. 2017) and species new to science published (Khorngton et al. 2020; Souladeth et al. 2020) in preparation of a revision for the Flora of Cambodia, Laos and Vietnam. In the present study, two new species, Eriocaulon bokorense Soulad. & Praj. and E. cambodianum Soulad. & Praj. are described from Cambodia. Consequently, the number of Eriocaulon species known in Cambodia has increased to 16, with one variety also recognised (Table 1).
Materials and Methods
Field collections were made in Cambodia by the first author from August to September 2017. More than 1100 herbarium collections, including type specimens, have been consulted in the following herbaria: BKF, BM, E, FOF, FU, HHU, HNL, K, KAG, KEP, KKU, KYO, L, LINN, M, NY, P, QBG, RUPP and VNM. The new species were compared with morphologically similar species in published descriptions (Lecomte 1912; Moldenke 1950; Royen 1959; Zhang 1999; Ma et al. 2000; Ansari & Balakrishnan 2009; Prajaksood et al. 2012; Cho et al. 2016; Leach 2017; Prajaksood et al. 2017; Leach 2018; Khorngton et al. 2020; Souladeth et al. 2020; Anoop & Robi 2021). The descriptions are based on dried herbarium specimens using standard terms for taxonomic description. Seed coat morphology follows the terminology of Nair (1987) and Zona et al. (2012). The conservation assessments were evaluated using the IUCN Red List Categories and Criteria (IUCN 2020). The area of occupancy (AOO, grid resolution = 2 km), the number of sub-populations (radius 5 km), the number of localities (grid resolution = 10 km) and the extent of occurrence (EOO) were calculated using R version 4.1.0 (RStudio Team 2021) with four packages, namely (1) Computation of Parameters Used in Preliminary Assessment of Conservation Status (ConR), (2) Geographic Data Analysis and Modelling (raster), (3) Classes and Methods for Spatial Data (sp), and (4) World Vector Map Data from Natural Earth Used in 'rnaturalearth' (rnaturalearthdata).
Taxonomic Treatment
Eriocaulon bokorense Soulad. & Praj., sp. nov. Type: Cambodia, Kampot Province, Bokor National Park, 1000 m alt., 4 Dec. 1993, E. Poilane 23061 (holotype P! [P01762557]).
http://www.ipni.org/urn:lsid:ipni.org:names:77234371-1
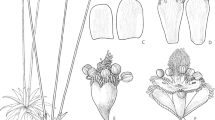
Annual herbs. Leaves rosulate, linear, 0.8 – 2 cm long, 0.2 mm wide, glabrous, apex acute. Scapes 1 – 30, 5 – 7 cm long, 0.5 – 0.8 mm in diam., 3-ridged, twisted, glabrous. Sheaths 1 – 1.8 cm long, glabrous, apex acute. Heads globose, 2 – 3 × 3 – 3.5 mm, white. Receptacles convex, pilose. Involucral bracts incurved, obovate, 1.5 – 1.8 × 1.2 – 1.4 mm, brown, chartaceous, glabrous, apex obtuse. Floral bracts oblanceolate, 1.3 – 1.4 × 0.8 – 1 mm, light brown, dark brown in middle, chartaceous, hoary towards apex, apex acute. Male flowers: pedicellate, c. 0.2 mm long; sepals 3, free, obovate, boat-shaped, 1 – 1.2 × 1 – 1.2 mm, light brown, chartaceous, hoary dorsally towards apex, apex acute; petals 3, fused basally, lobes ovate to triangular, 0.3 – 0.5 mm long, light brown, chartaceous, hoary at margin, with a minute black gland, apex acute; stamens 6, filaments 0.2 – 0.3 mm long; anthers black. Female flowers: pedicellate, c. 0.2 mm long; sepals 3, free, obovate, boat-shaped, 2 – 2.5 × 1 – 1.2 mm, light brown, chartaceous, hoary dorsally towards apex, apex acute; petals 3, free, subequal, broadly elliptic, attenuate, 2 – 2.3 × 1.5 – 1.8 mm, brown, coriaceous, hoary at apex with a black gland, apex acute; ovary sessile, trilocular; style to 1 mm long; stigmas 3, 0.5 mm long. Seeds ovoid to ellipsoid, obtuse at both ends, 0.5 – 0.8 mm long, 0.5 – 0.7 mm in diam., reddish-brown; cells of seed coat transversely elongate, aligned in vertical rows; scale-like appendages present, solitary from the middle of transverse wall. Figs 1 & 2.
Eriocaulon bokorense. A – B habit; C – D heads (C front view & D back view showing involucral bracts); E involucral bract; F floral bract; G – H male flowers (G deciduous anther & H with anthers); J female sepals; K female petals; L female flower; M seeds with scale-like appendages. A – B & H from Fuse et al. 6353 (FU!); C – G, J – M from E. Poilane 23061 (holotype P! [P01762557]). photos: a – b s. tagane; c – m p. souladeth.
recognition. Eriocaulon bokorense is morphologically similar to E. laosense Moldenke (Moldenke 1950; Prajaksood et al. 2017; type specimens, Poilane 15468, holotype NY102707!; isotype, P00224174!) in its small (up to 7 cm long), glabrous leaves, scape and involucral bracts, but differs in the shape of the heads (globose in E. bokorense vs hemispherical in E. laosense), involucral bracts (obovate vs elliptic), floral bracts (oblanceolate vs linear to oblong), male sepals (obovate, boat-shaped with acute apex vs obovate, uncurved with obtuse apex), female petals (broadly elliptic, coriaceous vs lanceolate, chartaceous), and the presence of appendages (presence vs absence). A comparison of these two taxa is shown in Table 2.
distribution. Asia: Cambodia (Map 1).
SPECIMENS EXAMINED. CAMBODIA. Kampot Province, Bokor National Park, at alt. 1000 m, 4 Dec. 1993, E. Poilane 23061 (holotype P! [P01762557]); ibid., 15 Dec. 1954, M. Schmid s.n. (P! [P01721448]); ibid., 20 Nov. 1999, S. Hul, L. Yok, S. Lim & C. Seng 742 (P! [P06172806]); ibid., 10°39'16.88"N, 104°03'25.1"E, alt. 992 m, 22 Dec. 2011, Toyama et al. 2518 (FU!; TNS; Herbarium of the Forest Administration of Cambodia); ibid., 10°39'15.1"N, 104°00'16.4"E, alt. 1013 m, 19 Nov. 2013, Cho et al. CB-2736 (HHU!); ibid., near transect line 5, edge of bog evergreen forest, on the plateau, 10°39'09.06"N, 104°03'38.68"E, alt. 935 m, 12 Dec. 2013, Fuse et al. 6353 (FU!; TNS; Herbarium of the Forest Administration of Cambodia).
HABITAT. In open areas in montane evergreen forest, at 935 – 1013 m altitude.
CONSERVATION STATUS. Critically Endangered (CR B1a+B2a, IUCN 2020). This species has an area of occupancy (AOO) of 12 km2. It is known from only one sub-population in one locality (Bokor Plateau, Bokor National Park, Kampot Province), with an estimate of less than 1000 mature individuals. The extent of occurrence (EOO) is 12 km2. The summit of the plateau is characterised by well-developed sphagnum bog (known as Popokvil bog; Fig. 3). This type of bog is relatively rare in mainland Southeast Asia (Tagane et al. 2017; Rundel & Middleton 2017). Since this plateau is a well-known tourist attraction, the presence of people may increase disturbance in the area and affect the future survival chances of this species.
PHENOLOGY. Flowering and fruiting from November to December.
ETYMOLOGY. The epithet “bokorense” refers to Bokor National Park, Kampot Province, south-eastern Cambodia.
NOTE. This species is characterised by its small size, white globose heads and female petals broadly elliptic, attenuate and coriaceous. Material from Toyama et al. 2518, Cho et al. CB-2736 and Fuse et al. 6353 (TD4997, CB2736 and TD5003 in Fig. 2 of Larridon et al. 2019, respectively) was used for phylogenetic analyses of Eriocaulon using chloroplast DNA (matK, rbcL, rpoB and rpoC1) and PHYC (Larridon et al. 2019). The results support the recognition of this species as new to science.
Eriocaulon cambodianum Soulad. & Praj., sp. nov. Type: Cambodia. Kampot, 800 m alt., 5 Feb. 1928, E. Poilane 14702 (holotype P! [P01762571]).
http://www.ipni.org/urn:lsid:ipni.org:names:77234372-1
Perennial herbs, stems shortly rhizomatous, 1 – 3 cm long. Leaves rosulate, linear, (3 –) 20 – 30 cm × 3 – 4 mm, glabrous, apex obtuse to acute. Scapes few, to 50 cm long, 1 – 1.8 mm in diam., strongly 8-ridged, not twisted, glabrous. Sheaths 10 – 15 cm long, glabrous, apex acute. Heads globose, 5 – 6 × 6 – 7 mm, greyish-brown. Receptacles concave, pilose. Involucral bracts incurved, broadly ovate, 3 – 3.2 × 2 – 2.1 mm, yellowish-brown, coriaceous, glabrous, apex acute. Floral bracts elliptic, keeled, 3 – 4 × 1.5 – 2 mm, greyish-brown at base, blackish-brown from middle towards apex, coriaceous, long brown hairs dorsally towards apex, apex acute. Male flowers: pedicellate, c. 0.3 mm long; sepals 3, free, obovate, boat-shaped, keeled, 2 – 2.7 × 0.6 – 0.8 mm, greyish-brown at base, blackish-brown from middle towards apex, coriaceous, hoary dorsally towards apex, apex obtuse; petals 3, fused basally, lobes triangular, 1 – 1.2 × 0.5 mm, brown, hoary towards apex, with a black gland, apex acute; stamens 6, filaments c. 0.5 mm long; anthers black. Female flowers: pedicellate, c. 0.3 mm long; sepals 3, free, dissimilar, the middle one broadly elliptic, slightly curved, the two laterals boat-shaped, keeled, 2 – 2.5 × 1.1 – 1.5 (– 1.8) mm, greyish-brown at base, blackish-brown from middle towards apex, coriaceous, hoary dorsally towards apex, apex acute; petals 3, free, subequal, elliptic, 3.5 – 3.7 × 0.8 – 1.2 mm, coriaceous, brown, dense long brown hairs, short white hairs ventrally towards apex, with a black gland, apex acute; ovary sessile, trilocular; style 0.6 mm long; stigmas 3, 1.2 mm long. Seeds ellipsoid, obtuse at both ends, 0.4 – 0.5 × 0.3 – 0.4 mm, light brown; cells of seed coat transversely elongate, aligned in vertical rows; minute appendages present. Figs 4 & 5.
Eriocaulon cambodianum. A type specimen showing the habit; B – C heads (B young head & C mature head); D scape; E involucral bract; F floral bract; G male flower; H female sepals; J female petals; K pistil and petals; L seed. A, C – L from E. Poilane 14702 (holotype P! [P01762571]); B from Kira et al. 158 (KYO!). photos: P. SOULADETH.
recognition. Eriocaulon cambodianum resembles E. fluviatile Trimen (Ansari & Balakrishnan 2009; Prajaksood et al. 2017); type specimen of E. tonkinense Ruhland [synonym of E. fluviatile (Balansa 247, K000873549!)] in having a rhizomatous stem, leaves to 30 cm long; globose and greyish-brown heads, the similar shape of the female sepals, and the blackish-brown colouring of the floral bracts, male and female sepals but differs in the nature of the receptacles (concave and pilose in E. cambodianum vs elongate and glabrous in E. fluviatile), colour of the anthers (black vs white or pale yellow), the nature of the female sepals (dissimilar, the middle one broadly elliptic, the two laterals boat-shaped, keeled and coriaceous vs similar, oblanceolate, shallowly curved and chartaceous), and the presence of appendages (presence vs absence). Additional characters are shown in Table 3.
distribution. Asia: Cambodia (Map 1).
specimens examined. cambodia. Kampot, 800 m alt., 5 Feb. 1928, E. Poilane 14702 (holotype P! [P01762571]); Kampot, Bokor National Park, Popokvil, 4 Dec. 1964, T. Kira, K. Hozumi, K. Yoda & S. Kokawa 158 (KYO!); ibid., 10°37'36"N, 104°01'39"E, at alt. 1014 m, 22 Nov. 2007, V. D. Nguyen & Rattana CB-VN 179 (K!); Kampong Speu, Kirirom, Mt Sral [Schral], at alt. 1000 m, 18 Feb. 1960, T. Smitinand & E. C. Abbe 6450 (K!).
habitat. On sandy soil mixed with rocks near streams in montane evergreen forest, at 800 – 1014 m altitude.
conservation status. The preliminary assessment of this species is Endangered (EN), B1a+B2a (IUCN 2020). This species has an area of occupancy (AOO) of 16 km2. It is known from three sub-populations in three localities (Bokor National Park in Kampot Province and Mt Sral in Kampong Speu Province). The extent of occurrence (EOO) is 650 km2.
phenology. Flowering and fruiting from November to February.
etymology. The species epithet “cambodianum” refers to the country of the type locality.
note. This species is characterised by its shortly rhizomatous stem, greyish-brown heads, the female sepals dissimilar, the middle one broadly elliptic, the two laterals boat-shaped, keeled and coriaceous and anther black.
References
Anoop, P. B. & Robi, A. J. (2021). Eriocaulon meenachilense, a new tuberous species of Eriocaulaceae from the southern western Ghats, India. Edinburgh J. Bot. 78: 336. https://doi.org/10.24823/EJB.2021.336
Ansari, R. & Balakrishnan, N. P. (2009). The family Eriocaulaceae in India (Rev. ed.). Bishen Singh Mahendra Pal Singh, Dehra Dun.
Cho, S.-H., Chhang, P. & Kim, Y.-D. (2016). A checklist for the seed plants of Cambodia. National Institution of Biological Resources, Environmental Research Complex, Incheon.
Darshetkar, A. M., Datar, M. N., Tamhankar, S. & Choudhary, R. K. (2017). Eriocaulon parvicephalum (Eriocaulaceae), a new species from Western Ghats, India. Phytotaxa 303: 233 – 242. https://doi.org/10.11646/phytotaxa.303.3.3
Darshetkar, A. M., Datar, M. N., Rao, G. R., Tamhankar, S., Prabhukumar, K. M. & Choudhary, R. K. (2019). Eriocaulon karaavalense (Eriocaulaceae), a New Species from India Based on Morphological and Molecular Evidence. Ann. Bot. Fenn. 56 (4 – 6): 305 – 316. https://doi.org/10.5735/085.056.0417
Francis, D., Mohan, V., Venugopal, D. K. & Nampy, S. (2020). A new species of Eriocaulon (Eriocaulaceae) from the Southern western Ghats of Kerala, India. Edinburgh J. Bot. 77 (2): 281 – 290. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0960428620000013
IUCN (2020). IUCN Red List Categories and Criteria, Version 2020-1. http://www.iucnredlist.org. (Accessed 10 Dec. 2020).
Khorngton, S., Souladeth, P. & Prajaksood, A. (2020). Eriocaulon longibracteatum (Eriocaulaceae), a new species from Thailand and Cambodia. Kew Bull. 75: 20. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12225-020-9879-1
Larridon, I., Tanaka, N., Liang, Y., Phillips, S. M., Barfod, A. S., Cho, S., Gale, S. W., Jobson, R. W., Kim, Y., Li, J., Muasya, A. M., Parnell, J. A. N., Prajaksood, A., Shutoh, K., Souladeth, P., Tagane, S., Tanaka, N., Yano, O., Mesterházy, A., Newman, M. F. & Ito, Y. (2019). First molecular phylogenetic insights into the evolution of Eriocaulon (Eriocaulaceae, Poales). J. Pl. Res. 132: 589 – 600. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10265-019-01129-3
Leach, J. G. (2017). A revision of Australian Eriocaulon (Eriocaulaceae). Telopea 20: 205 – 259.
Leach, J. G. (2018). Synopsis of the genus Eriocaulon (Eriocaulaceae) for New Guinea. Austral. Syst. Bot. 31: 420 – 432.
Lecomte, H. (1912). Eriocaulonacées. In: H. Lecomte (ed.), Flore Générale de l’Indo-Chine 7: 1 – 18. Masson, Paris.
Ma, W. L., Zhang, Z. X. & Stützel, T. (2000). Eriocaulaceae. In: C. Y. Wu, P. H. Raven & D. Y. Hong (eds), Flora of China 24: 7 – 17. Science Press & Missouri Botanical Garden Press, Beijing & St. Louis.
Middleton, D. J., Armstrong, K., Baba, Y., Balslev, H., Chayamarit, K., Chung, R. C. K., Conn, B. J., Fernando, E. S., Fujikawa, K., Kiew, R., Luu, H. T., Aung, M. M., Newman, M. F., Tagane, S., Tanaka, N., Thomas, D. C., Tran, T. B., Utteridge, T. M. A., van Welzen, P. C., Widyatmoko, D., Yahara, T. & Wong, K. M. (2019). Progress on Southeast Asia’s Flora projects. Gard. Bull. Singapore 71 (2): 267 – 319. https://doi.org/10.26492/gbs71(2).2019-02
Moldenke, H. N. (1950). Notes on New and Noteworthy Plants 11. Phytologia 3: 307 – 320.
Nair, R. V. (1987). Taxonomic significance of seed coat morphology in Eriocaulon Linn. (Eriocaulaceae). Seed Sci. Technol. 15: 197 – 310.
Prajaksood, A. & Chantaranothai, P. (2002). A New Species of Eriocaulon (Eriocaulaceae) from Thailand. Kew Bull. 57: 499 – 501.
Prajaksood, A., Parnell, J. A. N. & Chantaranothai, P. (2012). New taxa and new combinations of Eriocaulaceae from Thailand. Kew Bull. 67: 655 – 685.
Prajaksood, A., Chantaranothai, P. & Parnell, J. A. N. (2017). Eriocaulaceae. In: T. Santisuk & H. Balslev (eds), Flora of Thailand 13 (3): 434 – 511. Prachachon Co. Ltd., Bangkok.
Royen, P. van (1959). Eriocaulaceae. In: H. J. Lam, Nova Guinea 10: 21 – 44.
RStudio Team (2021). RStudio: Integrated Development Environment for R. RStudio, PBC, Boston, MA. http://www.rstudio.com/. [Accessed 10 July 2021].
Rundel, P. W. & Middleton, D. J. (2017). The flora of the Bokor Plateau. southeastern Cambodia: a homage to Pauline Dy Phon. Cambodian J. Nat. Hist. 1: 17 – 37.
Satake, Y. (1940). Eriocaulaceae. In: T. Nakai & M. Honda (eds), Nova Flora Japonica. Sanseido, Tokyo [in Japanese].
Souladeth, P., Prajaksood, A., Parnell, J. A. N. & Newman, M. F. (2017). Typification of names in Eriocaulon in The Flora of Thailand and Flora of Cambodia, Laos and Vietnam. Edinburgh J. Bot. 74: 5 – 13.
Souladeth, P., Tagane, S., Newman, M. F. & Prajaksood, A. (2020). Two new species of Eriocaulon (Eriocaulaceae) from Laos. Kew Bull. 75 (4): 56. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12225-020-09909-0
Stützel, T. (1998). Eriocaulaceae. In: K. Kubitzki (ed.), The Families and Genera of Vascular Plants, Volume IV. Flowering Plants. Monocotyledons. Alismatanae and Commelinanae (except Gramineae), pp. 197 – 207. Springer-Verlag, Heidelberg.
Tagane, S., Toyama, H., Fuse, K., Chhang, P., Naiki, A., Nagamasu, H. & Yahara, T. (2017). A picture guide of forest trees in Cambodia IV: Bokor National Park. Published by Center for Asian Conservation Ecology, Kyushu University.
Zhang, Z. (1999). Monographie der Gattung Eriocaulon in Ostasien. In: U. Kück (ed.), Dissertationes Botanicae (313). J. Cramer, Berlin.
Zona, S., Davis, P., Gunathilake, L. A. A. H., Prince, J. & Horn, J. W. (2012). Seeds of Eriocaulaceae of the United States and Canada. Castanea 77 (1): 37 – 45.
Acknowledgements
We should like to thank the curators and staff of BKF, BM, E, FOF, FU, HHU, HNL, K, KAG, KEP, KKU, KYO, L, LINN, M, NY, P, QBG, RUPP, and VNM herbaria for loans of specimens and access to the material studied. We thank Dr Sovanmoly Hul (P) and Mrs Peou Youleang (RUPP) for their help during field expeditions in Cambodia, Dr Shuichiro Tagane (KAG) for sharing photos and specimens from his work in Cambodia, Dr Sirinan Khorngton (KKU) for preparing the drawing and Mr Sangmany Boutthavong (Faculty of Forest Science, National University of Laos) for providing a distribution map. We are grateful to the Franklinia Foundation who contributed to the fieldwork through a grant to the Muséum national d’histoire naturelle for the Flora of Cambodia, Laos and Vietnam. This project was financially supported by the U.K. Darwin Initiative (grant no. EIDPS033), the Sud Expert Plantes Développement Durable (SEP2D): Botanical study of the Eriocaulaceae, Bambusoideae (Gramineae) and Zingiberaceae in Indochina (Cambodia, Laos and Vietnam), and a Khon Kaen University Scholarship for ASEAN and GMS Countries’ Personnel. The FOF herbarium in Laos is supported by the the Lancang-Mekong Cooperation Special Fund (Second Batch). The Royal Botanic Garden Edinburgh is supported by the Scottish Government’s Rural and Environmental Science and Analytical Services Division.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Souladeth, P., Newman, M.F. & Prajaksood, A. Two new species of Eriocaulon (Eriocaulaceae) from Cambodia. Kew Bull 77, 127–137 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12225-022-10005-8
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12225-022-10005-8