Abstract
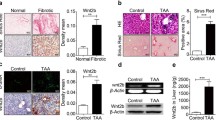
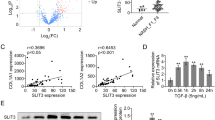
Liver fibrosis is an aberrant wound healing response to tissue injury characterized by excessive extracellular matrix deposition and loss of normal liver architecture. Hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) activation is regards to be the major process in liver fibrogenesis which is dynamic and reversible. Both Hippo signaling core factor Yap and Hedgehog (Hh) signaling promote HSCs transdifferentiation thereby regulating the repair process of liver injury. However, the molecular function of YAP and the regulation between Yap and Hh during fibrogenesis remain uncertain. In this study, the essential roles of Yap in liver fibrosis were investigated. Yap was detected to be increased in liver fibrotic tissue by the thioacetamide (TAA)-induced zebrafish embryonic and adult models. Inhibition of Yap by both embryonic morpholino interference and adult’s inhibitor treatment was proved to alleviate TAA-induced liver lesions by and histology and gene expression examination. Transcriptomic analysis and gene expression detection showed that Yap and Hh signaling pathway have a cross talking upon TAA-induced liver fibrosis. In addition, TAA induction promoted the nuclear colocalization of YAP and Hh signaling factor GLI2α. This study demonstrates that Yap and Hh play synergistic protective roles in liver fibrotic response and provides new theoretical insight concerning the mechanisms of fibrosis progression.
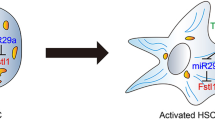
Graphical abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akladios B, Mendoza Reinoso V, Cain JE, Wang T, Lambie DL, Watkins DN, Beverdam A (2017) Positive regulatory interactions between YAP and Hedgehog signalling in skin homeostasis and BCC development in mouse skin in vivo. PLoS ONE 12(8):e0183178
Alsamman S, Christenson SA, Yu A, Ayad NM, Mooring MS, Segal JM, Hu JK-H, Schaub JR, Ho SS, Rao V (2020) Targeting acid ceramidase inhibits YAP/TAZ signaling to reduce fibrosis in mice. Sci Transl Med 12(557):1–14
Amali AA, Rekha RD, Lin CJ-F, Wang W-L, Gong H-Y, Her G-M, Wu J-L (2006a) Thioacetamide induced liver damage in zebrafish embryo as a disease model for steatohepatitis. J Biomed Sci 13(2):225–232
Amali AA, Rekha RD, Lin CJ-F, Wang W-L, Gong H-Y, Her G-M, Wu J-L (2006b) Thioacetamide induced liver damage in zebrafish embryo as a disease model for steatohepatitis. J Biomed Sci 13:2
Ballestri S, Nascimbeni F, Romagnoli D, Lonardo A (2016) The independent predictors of non‐alcoholic steatohepatitis and its individual histological features. Insulin resistance, serum uric acid, metabolic syndrome, alanine aminotransferase and serum total cholesterol are a clue to pathogenesis and candidate targets for treatment. Hepatol Res 46(11):1074–1087
Brunt EM (2010) Pathology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 7(4):195–203
Bruschi FV, Tardelli M, Einwallner E, Claudel T, Trauner M (2020) PNPLA3 I148M up-regulates hedgehog and yap signaling in human hepatic stellate cells. Int J Mol Sci 21(22):8711
Cai X, Wang J, Wang J, Zhou Q, Yang B, He Q, Weng Q (2020) Intercellular crosstalk of hepatic stellate cells in liver fibrosis: new insights into therapy. Pharmacol Res 155:104720
Choi SS, Omenetti A, Witek RP, Moylan CA, Syn W-K, Jung Y, Yang L, Sudan DL, Sicklick JK, Michelotti GA (2009) Hedgehog pathway activation and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transitions during myofibroblastic transformation of rat hepatic cells in culture and cirrhosis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 297(6):G1093–G1106
Chuang H-M, Su H-L, Li C, Lin S-Z, Yen S-Y, Huang M-H, Ho L-I, Chiou T-W, Harn H-J (2016) The role of butylidenephthalide in targeting the microenvironment which contributes to liver fibrosis amelioration. Front Pharmacol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2016.00112
Cotton JL, Li Q, Ma L, Park J-S, Wang J, Ou J, Zhu LJ, Ip YT, Johnson RL, Mao J (2017) YAP/TAZ and hedgehog coordinate growth and patterning in gastrointestinal mesenchyme. Dev Cell 43(1):35-47.e34
Dechêne A, Sowa JP, Gieseler RK, Jochum C, Bechmann LP, El Fouly A, Schlattjan M, Saner F, Baba HA, Paul A (2010) Acute liver failure is associated with elevated liver stiffness and hepatic stellate cell activation. Hepatology 52(3):1008–1016
Du K, Hyun J, Premont RT, Choi SS, Michelotti GA, Swiderska-Syn M, Dalton GD, Thelen E, Rizi BS, Jung Y (2018) Hedgehog-YAP signaling pathway regulates glutaminolysis to control activation of hepatic stellate cells. Gastroenterology 154(5):1465–1479
Ellis EL, Mann DA (2012) Clinical evidence for the regression of liver fibrosis. J Hepatol 56(5):1171–1180
Fang Y, Liu C, Shu B, Zhai M, Deng C, He C, Luo M, Han T, Zheng W, Zhang J, Liu S (2018) Axis of serotonin-pERK-YAP in liver regeneration. Life Sci 209:490–497
Friedman SL (2008) Hepatic stellate cells: protean, multifunctional, and enigmatic cells of the liver. Physiol Rev 88(1):125–172
Gao H, Bu Y, Wu Q, Wang X, Chang N, Lei L, Chen S, Liu D, Zhu X, Hu K (2015) Mecp2 regulates neural cell differentiation by suppressing the Id1 to Her2 axis in zebrafish. J Cell Sci 128(12):2340–2350
Gao W, Sun J, Wang F, Lu Y, Wen C, Bian Q, Wu H (2019) Deoxyelephantopin suppresses hepatic stellate cells activation associated with inhibition of aerobic glycolysis via hedgehog pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 516(4):1222–1228
George SM, Lu F, Rao M, Leach LL, Gross JM (2021) The retinal pigment epithelium: Development, injury responses, and regenerative potential in mammalian and non-mammalian systems. Prog Retin Eye Res 85:100969
Ghuloum FI, Johnson CA, Riobo-Del Galdo NA, Amer MH (2022) From mesenchymal niches to engineered in vitro model systems: exploring and exploiting biomechanical regulation of vertebrate hedgehog signalling. Mater Today Bio 17:100502
Halder G, Johnson RL (2011) Hippo signaling: growth control and beyond. Development (cambridge, England) 138(1):9–22
Hammes TO, Pedroso GL, Hartmann CR, Escobar TDC, Fracasso LB, da Rosa DP, Marroni NP, Porawski M, da Silveira TR (2012) The effect of taurine on hepatic steatosis induced by thioacetamide in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Dig Dis Sci 57(3):675–682
Han S, Bai E, Jin G, He C, Guo X, Wang L, Li M, Ying X, Zhu Q (2014) Expression and clinical significance of YAP, TAZ, and AREG in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Immunol Res 2014:1–10
Henderson JM, Polak N, Chen J, Roediger B, Weninger W, Kench JG, McCaughan GW, Zhang HE, Gorrell MD (2018) Multiple liver insults synergize to accelerate experimental hepatocellular carcinoma. Sci Rep 8(1):1–12
Hinz B, Celetta G, Tomasek JJ, Gabbiani G, Chaponnier C (2001) Alpha-smooth muscle actin expression upregulates fibroblast contractile activity. Mol Biol Cell 12(9):2730–2741
Hu J, Sun S, Jiang Q, Sun S, Wang W, Gui Y, Song H (2013) Yes-associated protein (yap) is required for early embryonic development in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Int J Biol Sci 9(3):267–278
Huo X, Li H, Li Z, Yan C, Mathavan S, Liu J, Gong Z (2019a) Transcriptomic analyses of oncogenic hepatocytes reveal common and different molecular pathways of hepatocarcinogenesis in different developmental stages and genders in krasG12V transgenic zebrafish. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 510(4):558–564
Huo X, Li H, Li Z, Yan C, Agrawal I, Mathavan S, Liu J, Gong Z (2019b) Transcriptomic profiles of tumor-associated neutrophils reveal prominent roles in enhancing angiogenesis in liver tumorigenesis in zebrafish. Sci Rep 9(1):1–11
Jiang Q, Liu D, Gong Y, Wang Y, Sun S, Gui Y, Song H (2009) yap is required for the development of brain, eyes, and neural crest in zebrafish. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 384(1):114–119
Jin L, Huang H, Ni J, Shen J, Liu Z, Li L, Fu S, Yan J, Hu B (2021) Shh-Yap signaling controls hepatic ductular reactions in CCl4-induced liver injury. Environ Toxicol 36(2):194–203
Johnson RL (2019) Hippo signaling and epithelial cell plasticity in mammalian liver development, homeostasis, injury and disease. Sci China Life Sci 62(12):1609–1616
Katoch S, Patial V (2021) Zebrafish: an emerging model system to study liver diseases and related drug discovery. J Appl Toxicol 41(1):33–51
Kinkel MD, Eames SC, Philipson LH, Prince VE (2010) Intraperitoneal injection into adult zebrafish. JoVE 42:e2126
Kisseleva T, Brenner DA (2008) Mechanisms of fibrogenesis. Exp Biol Med 233(2):109–122
Kojic S, Radojkovic D, Faulkner G (2011) Muscle ankyrin repeat proteins: their role in striated muscle function in health and disease. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci 48(5–6):269–294
Kumar V, Dong Y, Kumar V, Almawash S, Mahato RI (2019) The use of micelles to deliver potential hedgehog pathway inhibitor for the treatment of liver fibrosis. Theranostics 9(25):7537–7555
Lam SH, Wu YL, Vega VB, Miller LD, Spitsbergen J, Tong Y, Zhan H, Govindarajan KR, Lee S, Mathavan S (2006) Conservation of gene expression signatures between zebrafish and human liver tumors and tumor progression. Nat Biotechnol 24(1):73–75
Lau LF (2016) Cell surface receptors for CCN proteins. J Cell Commun Signal 10(2):121–127
Lee EH, Park KI, Kim KY, Lee JH, Jang EJ, Ku SK, Kim SC, Suk HY, Park JY, Baek SY, Kim YW (2019) Liquiritigenin inhibits hepatic fibrogenesis and TGF-β1/Smad with Hippo/YAP signal. Phytomedicine 62:152780
Li R, Cai L, Ding J, Hu CM, Wu TN, Hu XY (2015) Inhibition of hedgehog signal pathway by cyclopamine attenuates inflammation and articular cartilage damage in rats with adjuvant-induced arthritis. J Pharm Pharmacol 67(7):963–971
Lin Y-T, Ding J-Y, Li M-Y, Yeh T-S, Wang T-W, Yu J-Y (2012) YAP regulates neuronal differentiation through Sonic hedgehog signaling pathway. Exp Cell Res 318(15):1877–1888
Lin H, Huang Y, Tian T, Wang P, Li Y (2020) Propionate promotes vitamin D receptor expression via yes-associated protein in rats with short bowel syndrome. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 523(3):645–650
Liu Y, Lu T, Zhang C, Xu J, Xue Z, Busuttil RW, Xu N, Xia Q, Kupiec-Weglinski JW, Ji H (2019) Activation of YAP attenuates hepatic damage and fibrosis in liver ischemia-reperfusion injury. J Hepatol 71(4):719–730
Liu-Chittenden Y, Huang B, Shim JS, Chen Q, Lee S-J, Anders RA, Liu JO, Pan D (2012) Genetic and pharmacological disruption of the TEAD–YAP complex suppresses the oncogenic activity of YAP. Genes Dev 26(12):1300–1305
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 25(4):402–408
Lodyga M, Hinz B (2020) TGF-β1–a truly transforming growth factor in fibrosis and immunity. In: Proceedings of the seminars in cell and developmental biology. Elsevier, pp 123–139
Ma H-Y, Yamamoto G, Xu J, Liu X, Karin D, Kim JY, Alexandrov LB, Koyama Y, Nishio T, Benner C (2020) IL-17 signaling in steatotic hepatocytes and macrophages promotes hepatocellular carcinoma in alcohol-related liver disease. J Hepatol 72(5):946–959
Machado MV, Diehl AM (2018) Hedgehog signalling in liver pathophysiology. J Hepatol 68(3):550–562
Machado MV, Michelotti GA, Pereira TA, Xie G, Premont R, Cortez-Pinto H, Diehl AM (2015) Accumulation of duct cells with activated YAP parallels fibrosis progression in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J Hepatol 63(4):962–970
Manmadhan S, Ehmer U (2019) Hippo signaling in the liver–a long and ever-expanding story. Front Cell Dev Biol 7:33
Mannaerts I, Leite SB, Verhulst S, Claerhout S, Eysackers N, Thoen LF, Hoorens A, Reynaert H, Halder G, van Grunsven LA (2015) The Hippo pathway effector YAP controls mouse hepatic stellate cell activation. J Hepatol 63(3):679–688
Migdał M, Tralle E, Nahia KA, Bugajski Ł, Kędzierska KZ, Garbicz F, Piwocka K, Winata CL, Pawlak M (2021) Multi-omics analyses of early liver injury reveals cell-type-specific transcriptional and epigenomic shift. BMC Genom 22:1–15
Mooring M, Fowl BH, Lum SZ, Liu Y, Yao K, Softic S, Kirchner R, Bernstein A, Singhi AD, Jay DG (2020) Hepatocyte stress increases expression of yes-associated protein and transcriptional coactivator with PDZ-binding motif in hepatocytes to promote parenchymal inflammation and fibrosis. Hepatology 71(5):1813–1830
Moya IM, Halder G (2019) Hippo–YAP/TAZ signalling in organ regeneration and regenerative medicine. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 20(4):211–226
Nguyen Q, Anders RA, Alpini G, Bai H (2015) Yes-associated protein in the liver: regulation of hepatic development, repair, cell fate determination and tumorigenesis. Dig Liver Dis 47(10):826–835
Nguyen-Lefebvre AT, Selzner N, Wrana JL, Bhat M (2021) The hippo pathway: a master regulator of liver metabolism, regeneration, and disease. FASEB J 35(5):e21570
Oh SH, Swiderska-Syn M, Jewell ML, Premont RT, Diehl AM (2018) Liver regeneration requires Yap1-TGFβ-dependent epithelial-mesenchymal transition in hepatocytes. J Hepatol 69(2):359–367
Panciera T, Azzolin L, Cordenonsi M, Piccolo S (2017) Mechanobiology of YAP and TAZ in physiology and disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 18(12):758–770
Reimer MM, Kuscha V, Wyatt C, Sörensen I, Frank RE, Knüwer M, Becker T, Becker CG (2009) Sonic hedgehog is a polarized signal for motor neuron regeneration in adult zebrafish. J Neurosci 29(48):15073–15082
Rekha RD, Amali AA, Her GM, Yeh YH, Gong HY, Hu SY, Lin GH, Wu JL (2008) Thioacetamide accelerates steatohepatitis, cirrhosis and HCC by expressing HCV core protein in transgenic zebrafish Danio rerio. Toxicology 243(1–2):11–22
Rockey DC, Bell PD, Hill JA (2015) Fibrosis—a common pathway to organ injury and failure. N Engl J Med 372(12):1138–1149
Seki E, Schwabe RF (2015) Hepatic inflammation and fibrosis: functional links and key pathways. Hepatology 61(3):1066–1079
Shen X, Peng Y, Li H (2017) The injury-related activation of hedgehog signaling pathway modulates the repair-associated inflammation in liver fibrosis. Front Immunol 8:1450
Subramanian A, Tamayo P, Mootha VK, Mukherjee S, Ebert BL, Gillette MA, Paulovich A, Pomeroy SL, Golub TR, Lander ES (2005) Gene set enrichment analysis: a knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc Natl Acad Sci 102(43):15545–15550
Swiderska-Syn M, Xie G, Michelotti GA, Jewell ML, Premont RT, Syn WK, Diehl AM (2016) Hedgehog regulates yes-associated protein 1 in regenerating mouse liver. Hepatology 64(1):232–244
Turola E, Milosa F, Critelli R, di Giovanni M, Cotelli F, Villa E (2015) Overfeeding accelerates thioacetamide-induced liver damage in zebrafish
van der Helm D, Groenewoud A, de Jonge-Muller ES, Barnhoorn MC, Schoonderwoerd MJ, Coenraad MJ, Hawinkels LJ, Snaar-Jagalska BE, van Hoek B, Verspaget HW (2018) Mesenchymal stromal cells prevent progression of liver fibrosis in a novel zebrafish embryo model. Sci Rep 8(1):1–11
Varelas X (2014) The Hippo pathway effectors TAZ and YAP in development, homeostasis and disease. Development (cambridge, England) 141(8):1614–1626
Villesen IF, Daniels SJ, Leeming DJ, Karsdal MA, Nielsen MJ (2020) the signalling and functional role of the extracellular matrix in the development of liver fibrosis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 52(1):85–97
Wang Y, Chen W, Han C, Zhang J, Song K, Kwon H, Dash S, Yao L, Wu T (2018) Adult hepatocytes are hedgehog-responsive cells in the setting of liver injury: evidence for smoothened-mediated activation of NF-κB/epidermal growth factor receptor/Akt in hepatocytes that counteract Fas-induced apoptosis. Am J Pathol 188(11):2605–2616
Watt KI, Harvey KF, Gregorevic P (2017) Regulation of tissue growth by the mammalian hippo signaling pathway. Front Physiol 8:942
Wells RG, Schwabe RF (2015) Origin and function of myofibroblasts in the liver. In: Proceedings of the seminars in liver disease. Thieme Medical Publishers, pp 097–106
Xu S, Zhang H, Chong Y, Guan B, Guo P (2019) YAP promotes VEGFA expression and tumor angiogenesis though Gli2 in human renal cell carcinoma. Arch Med Res 50(4):225–233
Xu L, Wettschureck N, Bai Y, Yuan Z, Wang S (2021) Myofibroblast YAP/TAZ is dispensable for liver fibrosis in mice. J Hepatol 75:238–241
Yan J, Huang H, Liu Z, Shen J, Ni J, Han J, Wang R, Lin D, Hu B, Jin L (2020) Hedgehog signaling pathway regulates hexavalent chromium-induced liver fibrosis by activation of hepatic stellate cells. Toxicol Lett 320:1–8
Yao F, Zhou Z, Kim J, Hang Q, Xiao Z, Ton BN, Chang L, Liu N, Zeng L, Wang W (2018) SKP2-and OTUD1-regulated non-proteolytic ubiquitination of YAP promotes YAP nuclear localization and activity. Nat Commun 9(1):1–16
Yi X, Yu J, Ma C, Li L, Luo L, Li H, Ruan H, Huang H (2018) Yap1/Taz are essential for the liver development in zebrafish. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 503(1):131–137
Yu H, Yao Y, Bu F, Chen Y, Wu Y, Yang Y, Chen X, Zhu Y, Wang Q, Pan X (2019) Blockade of YAP alleviates hepatic fibrosis through accelerating apoptosis and reversion of activated hepatic stellate cells. Mol Immunol 107:29–40
Yu D, Liu H, Qin J, Huangfu M, Guan X, Li X, Zhou L, Dou T, Liu Y, Wang L, Fu M, Wang J, Chen X (2021) Curcumol inhibits the viability and invasion of colorectal cancer cells via miR-30a-5p and Hippo signaling pathway. Oncol Lett 21(4):299
Zhang Y, Zhang X, Cui L, Chen R, Zhang C, Li Y, He T, Zhu X, Shen Z, Dong L, Zhao J, Wen Y, Zheng X, Li P (2017) Salvianolic acids for injection (SAFI) promotes functional recovery and neurogenesis via sonic hedgehog pathway after stroke in mice. Neurochem Int 110:38–48
Zhao Y, Huang X, Ding TW, Gong Z (2016) Enhanced angiogenesis, hypoxia and neutrophil recruitment during Myc-induced liver tumorigenesis in zebrafish. Sci Rep 6(1):1–12
Zhao Y, Wang H-L, Li T-T, Yang F, Tzeng C-M (2020) Baicalin ameliorates dexamethasone-induced osteoporosis by regulation of the RANK/RANKL/OPG signaling pathway. Drug Des Dev Ther 14:195
Zhubanchaliyev A, Temirbekuly A, Kongrtay K, Wanshura LC, Kunz J (2016) Targeting mechanotransduction at the transcriptional level: YAP and BRD4 are novel therapeutic targets for the reversal of liver fibrosis. Front Pharmacol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2016.00462
Acknowledgements
We thank Professor Zhiyuan Gong in National University of Singapore and Professor Qingshun Zhao in Nanjing University in China for valuable discussions about this research.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31701279) and Xiamen Municipal Science and Technology Bureau-Xiamen City Division of Funding Management Project (No. 3502Z20203016).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YZ, CT conceived and designed the experiments; YZ, HW and TH performed all experiments; YZ, HW analyzed data; YZ, HW, BM, GC and CT wrote and reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
This study was approved by the ethics committee of Nanjing Tech University.
Informed consent
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, Y., Wang, H., He, T. et al. Knockdown of Yap attenuates TAA-induced hepatic fibrosis by interaction with hedgehog signals. J. Cell Commun. Signal. 17, 1335–1354 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12079-023-00775-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12079-023-00775-6