Abstract
Salivary gland tumors are rare, comprising less than 3% of all neoplasia of head and neck region. Pleomorphic adenoma is the most common salivary gland tumor, accounting for 60–80% of benign tumors of salivary glands, which predominantly affect the superficial lobe of the parotid gland. The “pleomorphic” nature of the tumor can be explained on the basis of its epithelial and connective tissue origin. Usually they are found as solitary unilateral, firm and mobile, painless, slow growing mass. The tumor has a female predilection between 30 and 50 years of age. Utmost care is to be taken to preserve the facial nerve while performing superficial or total parotidectomy. We present 10 cases of pleomorphic adenoma of parotid gland over period of 2 years, highlighting the prognosis following surgical management.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Pleomorphic adenoma is of the most common salivary gland tumour, pleomorphic adenoma accounts for about 60 to 80% of the benign tumours of the salivary glands and 60–70% of all the parotid tumours. This tumour is known as a benign mixed tumour. The incidence of parotid tumour is about 2.4 in 100,000/Year. Right side involvement is more than left side and more common in female than male (1.4:1) more commonly between fifth and sixth decades of life and its occurrence is rare in children [1].
Pleomorphic adenoma is less commonly seen in the submandibular salivary gland (10%) and is seldom encountered in the sublingual gland (1%). In minor salivary glands (5–10%), the palate and the lip are the most common sites. Other sites of minor salivary include the nose, paranasal sinuses, and the larynx. Rare or unusual sites of occurrence include ectopic salivary gland tissues (e.g.: mandible, neck lymph node, axilla) [2].
The exact etiology is unknown, however, incidence increases 15–20 years after exposure to radiation. One study suggests that the simian virus (SV40) may play an etiologic role in the development of pleomorphic adenoma [3].
Intricate Details
We present 10 patients who were diagnosed with pleomorphic adenoma of parotid gland and were managed surgically from a novitiate ENT surgeon’s point of view.
- 1.
40 years old female patient known hypertensive presented with painless swelling over the left side of the face which was diagnosed as pleomorphic adenoma of left parotid gland and was managed by performing superficial parotidectomy. Post operatively patient developed parotid fistula which recovered over a period of 6 months–1 year.
- 2.
35 years old female patient presented with swelling on the right side of the face and on evaluation it was diagnosed as pleomorphic adenoma of right parotid gland and was managed by performing superficial parotidectomy. Post operatively patient developed angular deviation of the mouth, which recovered over a period of 6 months.
- 3.
17 years old female patient presented with cystic swelling in the right parotid area, masquerading as parotid adenoma. Patient was managed by performing superficial parotidectomy. Patients post operative period was uneventful.
- 4.
45 years old female patient who is a known diabetic presented with swelling over the left side of the face. On evaluation it was diagnosed as pleomorphic adenoma of left parotid gland and was managed by performing superficial parotidectomy. Patients post operative period was uneventful.
- 5.
75 years old female patient presented with pigmented lesion in the right preauricular area and swelling over the right infra auricular area. On evaluation it was diagnosed as basal cell carcinoma with pleomorphic adenoma of right parotid gland. Patient was managed by performing excision of the lesion in the right preauricular area and superficial parotidectomy was done. Post operatively patient developed gapping of wound which recovered over a period of 2 months.
- 6.
17 years old female patient presented with swelling on the right side of the face. FNAC was performed and was diagnosed as pleomorphic adenoma of right parotid gland. Patient was managed by performing superficial parotidectomy. Immediate post operative period patient developed gapping of wound which completely healed over a period of 2 months.
- 7.
58 years old male patient presented with swelling on the right side of the face and was diagnosed as pleomorphic adenoma of right parotid gland. Patient was managed by performing superficial parotidectomy. Post operatively patient developed parotid fistula which healed spontaneously.
- 8.
48 years old female patient presented with swelling on the right side of the face. On evaluation it was diagnosed as pleomorphic adenoma of right parotid gland. Post operatively patient developed parotid fistula which is being managed by canulating the fistula with stent, result of which is further awaited.
- 9.
45 years old female patient presented with swelling on the left side of the face. Patient was managed by performing superficial parotidectomy after it was diagnosed as pleomorphic adenoma of left parotid gland. Patients post operative period was uneventful.
- 10.
42 years old male patient presented with swelling on the left side of the face. On evaluation it was diagnosed as pleomorphic adenoma of left parotid gland. Patient was managed by superficial parotidectomy. Patients post operative period was uneventful.
Results
During the period of 2 years (2013–2015) 10 patients who were diagnosed with pleomorphic adenoma of parotid gland and were operated.
In our series out of 10 patients, eight were female patients and two were male patient showing propensity for females and involvement of right side more than left side. Usually seen in fourth and fifth decade.
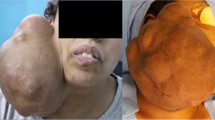
Most of the patients presented with slow growing, painless swelling which gradually increased over time. During this period a rare case of pigmented lesion in the right preauricular area with swelling of right parotid gland was documented. The swelling was firm in consistency, non-tender on palpation. It was freely mobile and skin over the swelling was pinchable. Facial and eye movements were normal on examination. Intraoral clinical examination was normal. A provisional diagnosis of benign tumor of the right parotid gland with basal cell carcinoma of right preauricular area was taken into consideration (Fig. 1). Pleomorphic adenoma, Warthin’s tumor, intraparotid cyst, basal cell carcinoma with secondaries in the neck, melanoma with secondaries, intraparotid lymphnode and neuroma of the facial nerve (nerve sheath tumor) were considered as the most probable differential diagnosis.
Fine needle aspiration cytology (FNAC) of the swelling was performed under local anesthesia and showed admixed epithelial, myoepithetial and mesenchymal tissue elements.
Patient was managed by performing superficial parotidectomy with excision of the lesion in the right preauricular area (Figs. 2 and 3).
Excised specimen of lesion in the preauricular area was 3 × 2 × 1 cm.
Histopathology—Upper and deep dermis showed malignant neoplasm with cell arranged in lobules. Nests and sheets separated by minimal fibrovascular stroma. Individual cells are basaloid with vesicular nucleus coarse chromatin,moderate eosinophilic cytoplasm, palisading cells noted suggestive of basal cell carcinoma (Fig. 4).
Excised specimen of tumor mass was 3.5 × 2 × 2 cm.
Histopathology—A well-capsulated cellular mass of sheets and islands of epithelial cells arranged in tubules, cords, trabecular in a background of chondromyxoid stroma. Foci of normal parotid gland at the periphery with few lymphoid follicles (Fig. 5).
All the patients were managed by performing superficial parotidectomy. Out of which three patients developed parotid fistula and one patient developed angular deviation of mouth and two patients developed minor complications like seroma and gapping of wound which recovered over time.
Discussion
World Health Organization (1972) defined PA as a well-defined tumor characterized by its pleomorphic or mixed appearance. There is intermixing of the clearly recognizable epithelial component with mucoid, myxoid and chondroid component [4]. Although the lesion presents several histological features due to the different compounds with a myxoid or chondroid matrix, it is generally considered to be a benign neoplasm [5].
Pleomorphic adenomas are generally discovered during routine physical examination, as an asymptomatic mass. PA has a glandular origin in the head and neck region and usually manifests as a mobile, slow progressing, asymptomatic firm swelling that does not cause ulceration of the overlying mucosa [6]. The majority of these tumors measure 2–6 cm in size when excised [7]. However, large tumor may be seen as a single, irregular nodular mass stretching the overlying skin or mucosa [8]. The tumor may weigh from several grams to more than 8 kg. Parotid gland PA is usually seen below the lobule of the ear and overlying the angle of the mandible [9]. Facial nerve weakness is an infrequent sign in parotid tumors although large neglected tumors may present with facial nerve weakness [10]. Oral retrotonsillar mass/parapharyngeal space tumor may be a presenting sign in cases of deep lobe involvement [11].
Imaging modalities such as computed tomography (CT) and Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) are essential aids in diagnosis. MRI is favored on the basis of better soft tissue delineation, detailed tumor margin description and the tumor relationship with the surrounding structures [12].
FNAC is a reliable procedure that can guide the surgeon to choose the right surgical approach [13]. The procedure is usually performed following diagnostic imaging to rule out a vascular lesion although it is not the first choice diagnostic tool [13].
As pleomorphic adenoma exhibits a varied histopathologic presentation, it may be confused histopathologically with myoepithelioma, Adenoid cystic carcinoma, mucoepidermoid carcinoma and basal cell adenoma.
Aggressiveness and extent of the tumor mass and its relation with the facial nerve form the important criteria which dictate the choice of treatment of pleomorphic adenoma of the parotid gland. Enucleation, and superficial or total parotidectomy with preservation of the facial nerve formed the mainstay of surgical treatment [14].
Pleomorphic adenomas need to be managed diligently as they have a tendency for recurrence and malignant transformation. Rupture of the capsule and subsequent tumor spillage during excision are attributable risk factors for recurrence. Up to 10% cases show malignant transformation and features predictive of malignant change include advancing age, massive tumor size, a long duration of the mass, occurrence in submandibular salivary gland, and hyalinized connective tissue [15].
Conclusion
In point of view as a novitiate ENT surgeon, It is found that pleomorphic adenoma of superficial lobe of parotid gland is found to be common with female predilection, veering towards the right lobe and with age preponderance of 45 years.
We were happy to document a very rare case of coexistence of basal cell carcinoma in preauricular area with pleomorphic adenoma of parotid gland which was adequately and aptly managed.
A learning curve of technique of superficial parotidectomy was understood and encountered common complications during postoperative period and were delt with near nill co morbidities.
The saving grace was that there was no facial palsy. But angular deviation of mouth was encountered in one case which recovered spontaneously.
A greater feeling of happiness comes as ENT surgeon does parotid surgery.
References
Gleeson M, Browning GG, Burton MJ, Clarke R, Hibbert J, Jones NS, Lund VJ, Luxon LM, Watkinson JC (2008) Scott-Brown’s otorhinolaryngology, head and neck surgery, 7th edn. Hodder Arnold, London, pp 2480–2481
Silva SJ, Costa GT, Filho ACB, Faria PR, Loyola AM (2006) Metachronous bilateral pleomorphic adenoma of the parotid gland. Oral Surg Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endodontol 101(3):333–338
Martinelli M, Martini F, Rinaldi E, Caramanico L, Magri E, Grandi E et al (2002) Simian virus 40 sequences and expression of the viral large T antigen oncoprotein in human pleomorphic adenomas of parotid glands. Am J Pathol 161(4):1127–1133
Traiger J, Rosen MB (1965) Mixed tumor of the cheek: report of a case. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 19:711–714
Berdal P, Hall JG (1969) Parapharyngeal growth of parotid tumours. Acta Otolaryngol Suppl 263:164–166
Dalati T, Hussein MR (2009) Juvenile pleomorphic adenoma of the cheek: a case report and review of literature. Diagn Pathol 4(32):1–5
Beunting JE, Smith TL, Holmes DK (1998) Giant pleomorphic adenoma of the parotid gland: case report and review of the literature. Ear Nose Throat J 77(8):643, 637–638, 640
Ellis GL, Auclair PL (1996) Tumors of the salivary glands (Atlas of Tumor Pathology) 3rd series. Fascicle 17. Armed Forces of Institute of Pathology, Washington, DC
Guerriere CN, Goff JJ, Cummings GH, Auber AE (1999) An unusually large, solid tumor of the parotid gland. Ann Plast Surg 43(5):529–532
Silva SJ, Costa GT, Filho ACB, Faria PR, Loyola AM (2006) Metachronous bilateral pleomorphic adenoma of the parotid gland. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endodontol 101(3):333–338
Takahama A Jr, Perez DEC, Magrin J, Almeida OP, Kowalski LP (2008) Giant pleomorphic adenoma of the parotid gland. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal 13(1):58–60
Sergi B, Limongelli A, Scarano E, Fetoni AR, Paludetti G (2008) Giant deep lobe parotid gland pleomorphic adenoma involving the parapharyngeal space. Report of three cases and review of the diagnostic and therapeutic approaches. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital 28:261–265
Contucci AM, Corina L, Sergi B, Fadda G, Paludetti G (2003) Correlation between fine needle aspiration biopsy and histologic findings in parotid masses. Personal experience. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital 23:314–318
Mehle ME, Krause DH, Wood BG, Benninger SM, Eliachar I, Levine HL et al (1993) Facial nerve morbidity following parotid surgery for benign disease. The Cleveland Clinic Foundation experience. Laryngoscope 103:386–388
Zarbo RJ (2002) Salivary gland neoplasia: a review for the practicing pathologist. Mod Pathol 15(3):298–323
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Dr. C.V. Srinivas and Dr. C. Shivani declared that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Srinivas, C.V., Shivani, C. Novice’s Sojourn to Parotid Surgery. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 71 (Suppl 1), 243–247 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-018-1245-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-018-1245-3