Abstract
Mediastinal cysts are usually congenital but present in adulthood. A pericardial cyst is usually localized in the right cardiophrenic region. Thymic cysts are less common and are located in the cervical region or anterior mediastinal region. While thoracoscopic excision or aspiration can be applied in pericardial cysts, excision is recommended in thymic cysts. We present a case of a thymic cyst located in the localization of the pericardial cyst and radiologically containing wall punctate calcification.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Case report
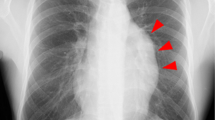
A 53-year-old female presented with chest pain. A mediastinal cystic lesion located in the right paracardiac area was detected on thorax computed tomography (Fig. 1). Radiologically, cystic lesions of the mediastinum, primarily pericardial cyst, cystic teratoma, and thymic cyst, have been considered preliminary diagnoses. The mediastinal cyst was resected thoracoscopically and histopathological examination was reported as a thymic cyst.
The calcified mediastinal cyst has been reported rarely. The best known calcified mediastinal cyst is a cystic teratoma, which is usually located anteriorly in the mediastinum [1]. In the literature, rim calcification has been reported in some cases with thymic cysts [2]. Pericardial cysts account for approximately one-third of all mediastinal cysts. They are usually detected between the ages of 30 and 50 years [3]. Pericardial cysts are mostly simple cysts, typically uniloculated, with smooth contours, and contain clear water-like fluid. Usually they are located in the right cardiophrenic angle [3]. Diffuse wall calcification has been reported, albeit very rarely, in pericardial cysts, which cannot be differentiated from hydatid cysts radiologically [4]. The presence of punctate calcification in mediastinal cystic cases matching the pericardial cyst localization may support the diagnosis of a thymic cyst.
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Eroğlu A, Aydın Y, Altuntaş B, Ulaş AB. Surgical management of primary mediastinal hydatid cysts: a 30-year experience. Turk Gogus Kalp Dama. 2016;24:495–500.
Khayata M, Alkharabsheh S, Shah NP, Klein AL. Pericardial cysts: a contemporary comprehensive review. Curr Cardiol Rep. 2019;21:64.
Sugimoto S, Misao T, Nakano H, Yamane M. Mediastinal cyst with rim calcification. Jpn J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2004;52:261–3.
Sorour AA, Maleszewski JJ, Schaff HV, Klarich KW. A symptomatic calcified pericardial cyst. Mayo Clin Proc. 2019;94:367–9.
Funding
The authors received no financial support for the research and/or authorship of this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: Y.A., S.O., A.B.U.
Study design: Y.A., S.O.
Defining the study: Y.A., S.O.
Project writing and management: Y.A., A.B.U.
Extensive literature search: Y.A., A.B.U.
Actually performing the study: viz. Y.A., S.O., A.B.U.
Data acquisition: Y.A., S.O., A.B.U., A.E.
Data analysis: Y.A., S.O., A.B.U., A.E.
Manuscript writing and repeated editing and reviewing of the manuscript: Y.A., A.E.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
N/A.
Informed consent statement
Written consent for studies and publication was obtained from the patients prior to the surgery.
Statement of human and animal rights
The study has been performed in accordance with the ethical standards as laid down in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. This article does not contain any studies with animals performed by any of the authors.
Conflict of interest
The authors declared no conflicts of interest with respect to the authorship and/or publication of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Aydin, Y., Ozmen, S., Ulas, A.B. et al. An important finding for differential diagnosis in thymic cyst mimicking pericardial cyst: punctate calcification. Indian J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 40, 502–503 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12055-024-01710-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12055-024-01710-z