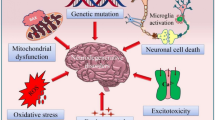
Abstract
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is characterized by progressive degeneration of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra and loss of both motor and non-motor features. Several clinical and preclinical studies have provided evidence that estrogen therapy reduces the risk of PD but have limitations in terms of adverse peripheral effects. Therefore, we examined the potential beneficial effects of the brain-selective estrogen prodrug, 10β, 17β-dihydroxyestra-1,4-dien-3-one (DHED) on nigrostriatal dopaminergic neurodegeneration and behavioral abnormalities in 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) mouse model of PD. Wild-type mice were treated with daily subcutaneous injections of DHED (50 and 100 µg/kg) or vehicle for four weeks. To produce PD-like symptoms, mice were injected with MPTP (18 mg/kg in saline; intraperitoneally) four times at 2-hr intervals for one day. After behavioral examination, mice were sacrificed, and the brains were isolated for neurochemical and morphological examinations. MPTP injected mice exhibited loss of dopaminergic neurons and fibers in substantia nigra and striatum respectively, along with impaired motor function at day 7 post MPTP injection. These phenotypes were associated with significantly increased oxidative stress and inflammatory responses in the striatum regions. DHED treatments significantly mitigated behavioral impairments and dopaminergic neurodegeneration induced by MPTP. We further observed that DHED treatment suppressed oxidative stress and inflammation in the striatum of MPTP treated mice when compared to vehicle treated mice. In conclusions, our findings suggest that DHED protects dopaminergic neurons from MPTP toxicity in mouse model of PD and support a beneficial effect of brain-selective estrogen in attenuating neurodegeneration and motor symptoms in PD-related neurological disorders.

Graphical Abstract
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disease that affects more than 10 million people worldwide. PD is characterized by the degeneration of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta (SNpc) coupled with proteinaceous inclusions composed of misfolded or aggregated form of α-synuclein (Goedert 2001; Breydo et al. 2012). This nigral neuronal loss consequently results in dopamine depletion in striatum, resulting in enervating motor function. The PD symptoms usually begin slowly and worsen over time. Despite extensive research over the past several decades, there are no effective treatments that can slow or stop the progression of the disease. The current therapeutics for PD only provide symptomatic relief and do not stop the progressive loss of the dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra of the brain. Therefore, there is a critical need to identify effective and safe drugs that provide a higher quality of life for individuals affected with PD.
Exposure to environmental neurotoxin, 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3, 6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) is known to produce parkinsonian features in humans, primates and recapitulates dopaminergic degenerations in the nigrostriatal pathway in rodents (Przedborski and Vila 2003). The active and toxic metabolite of MPTP, 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium (MPP+) is selectively taken up by the dopaminergic neurons where it causes disruption of oxidative phosphorylation and redox homeostasis along with generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and inflammatory responses, leading to dopaminergic neurotoxicity (Khan et al. 2013; Dauer and Przedborski 2003). Therefore, MPTP is widely adopted as a tool to study the molecular and neuropathological events in PD and to screen potential neuroprotective drugs.
Several studies have documented that increased oxidative stress, and overt neuroinflammation lead to impaired cellular function which in turn, exacerbates neurodegeneration in age-related neurodegenerative diseases such as PD (Hald and Lotharius 2005; Mosley et al. 2006). The human brain, besides being rich in phospholipids and polyunsaturated fatty acid, consumes a substantial amount of oxygen and is thus always under higher oxidative threat. Oxidative damage to lipids and biomolecules such as DNA and proteins alters cellular and molecular phenomenon and exacerbate the PD progression (Jenner and Olanow 2006). Analysis of the post-mortem human PD brain and experimental models of PD showed that activation of glial cells and increased oxidative stress occur where neurodegeneration occurs (Dias et al. 2013; Ouchi et al. 2009). Therefore, it can be speculated that the inhibition of sustained inflammation and oxidative stress may preserve the degeneration of dopaminergic neurons.
Biological sex is an important unequivocal risk factor for PD and potentially impacts the onset and progression of PD. Epidemiologic studies have suggested that the incidence of PD was higher in men than that in women (Van Den Eeden et al. 2003; Hirsch et al. 2016), suggesting a possible protective influence of female sex hormone estrogen. Consistent with this notion, a study by Ragonese and colleagues found an association between factors suppressing estrogen stimulation during life and the development of PD (Ragonese et al. 2006). It is well documented that 17β-estradiol has neuroprotective effects in several neurodegenerative diseases, via its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects (Butler et al. 2020; Thakkar et al. 2016; Vegeto et al. 2003; Khan et al. 2019). Several preclinical studies suggest that estradiol exerts neuroprotective effects on dopaminergic neurons and promotes dopaminergic activity in the striatum (Lee et al. 2019; Sawada et al. 1998). Consistent with rodent studies, case-control and prospective studies have indicated that estrogen treatments may alleviate PD symptoms in women (Tsang et al. 2000). However, the efficacy of estrogen therapy in PD is still under debate due to adverse peripheral side effects, such as breast cancer and cerebrovascular conditions. 10β,17β-dihydroxyestra-1,2-dien-3-one (DHED), is a brain-targeting bioprecursor prodrug of human estrogen 17β-estradiol converting to 17β-estradiol only in the brain (Prokai et al. 2015). This prodrug also possesses favorable physicochemical properties for blood-brain barrier transport compared to those of 17β-estradiol (Merchenthaler et al. 2016). Recent studies have demonstrated the neuroprotective effect of DHED in several mouse models of neurodegenerative diseases (Rajsombath et al. 2019; Tschiffely et al. 2016, 2018). Therefore, DHED may be a safe approach for delivering 17β-estradiol selectively into the brain for the potential treatment of PD. In this study, we report that DHED treatments protect dopaminergic neurons and preserve motor function by suppressing oxidative stress and neuroinflammation in MPTP-treated mouse model of PD.
Materials and Methods
Animals and Treatment
C57BL/6J wild-type (WT) mice were maintained at The University of Tennessee Health Science Center animal care facility. All mouse experiments were performed in accordance with the National Institutes of Health’s Guidelines for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals and approved by our Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee. As the endogenous female sex hormone estrogen can protect against a broad range of neurotoxic insults, we chose to use male mice in all experiments to avoid the potential complication of interpreting a neuroprotective effect of the exogenous brain-selective estrogen DHED on PD. Mice were randomly divided into four groups. The first group was vehicle-treated and served as a control group; the second group was MPTP-injected. The third and fourth groups received a daily subcutaneous injection of DHED (Millipore Sigma; # SML1642) for 3 weeks at 50 and 100 µg/kg concentration in corn oil respectively, before MPTP injections and was continued one-week post MPTP treatment. Mice received four intraperitoneal injections of MPTP (18 mg/kg body weight in saline, at 2 h intervals; Tokyo Chemical Industry Co., Ltd) as described previously (Khan et al. 2013, 2015). Mice were sacrificed on the seventh day post MPTP treatment right after behavioral assessment.
Behavioral Assessments
Mice in each group were weighed and subjected to a battery of behavioral tests as described previously (Khan et al. 2013, 2015, 2018). All behavioral tests were performed in the following order: raised beam task, rotarod, and grip strength, by investigators blinded to the treatment groups.
Raised-Beam Task
The raised-beam test was done to assess motor coordination and balance. Mice were acclimated to an 80-cm long, 20-mm wide beam elevated 50 cm above a padded base. A 60W lamp at the start served as an aversive stimulus, whereas the opposite end of the beam entered a darkened escape box. Transversal time were measured as mice traversed a 12-mm diameter square and round beam. All testing was performed in triplicate and Mean values were used for subsequent statistical analyses as previously described (Khan et al. 2018).
Rotarod
The rotarod test was done to evaluate motor coordination and balance using a rotarod apparatus. Mice were acclimated to a Rotamex-5 rotarod (Columbus Instruments) rotating at 5 revolutions per minute (rpm) for 5 min on the day prior to data acquisition. On the following day, mice were exposed to a 30 s acclimation period at 4 rpm followed by an acceleration of 4 rpm every 30 s to a target of 40 rpm at 5 min. Mice were given 3 trials at the same time. Mean values were used for statistical comparisons as previously described (Khan et al. 2013, 2018).
Grip Strength
To measure grip strength, mice were held by the scruff of the neck with one hand and the base of the tail with the other hand. Mice were then free to grasp a metal grid attached to a force meter (Columbus Instruments) with their forelimbs as they were moved along the axis of the grid. Maximal strength (g) with which mice pulled the grid was measured in triplicate trials with a minimal inter-trial interval of 5 min. Mean values were used for subsequent statistical analyses as previously described (Khan et al. 2013, 2018).
Tissue Preparation for Biochemical and Histological Analysis
After behavioral analysis, mice of each group were euthanized, the brains were removed, and striatal tissues were dissected for biochemical analysis. For immunohistochemical studies, brain tissues were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde in 0.1M phosphate buffered saline (PBS, pH 7.4) and cryoprotected with 30% sucrose in 0.1M PBS.
Immunohistology and Immunofluorescence Staining
The immunohistochemistry was performed as described by us (Khan et al. 2013, 2015). Briefly, 25 µm serial coronal sections of substantia nigra pars compacta (SNpc) and striatum of each group were cut on a cryostat (Leica). Endogenous peroxidases were quenched with 0.3% H2O2 in PBS, and sections were rinsed with PBS followed by blocking with 5% BSA for 1 h at room temperature. Sections were incubated overnight with primary antibodies rabbit anti-tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) antibody (dilution 1:500; # AB152; Chemicon) or SOD1 antibody (dilution 1:200; #ab13498, Abcam) followed by biotinylated secondary antibodies (Vector Laboratories). After rinsing three times with PBS, sections were developed using Vectastain ABC Kit from Vector Laboratories. The sections were then visualized by 3,3 diaminobenzidine (DAB; Vector laboratories) followed by cresyl violet counter staining. These sections were washed, dehydrated with gradient ethyl alcohol, cleared in xylene and mounted using DPX mounting media. The number of TH-positive neurons in four sections of the substantia nigra from each mouse was counted under light microscopy. Then, the mean number of TH-positive neurons was calculated and taken as the neuronal count of each mouse.
For immunofluorescence, the staining was done in the sections of striatum as described above except using primary antibodies for γ-H2A.X (Ser139) (1:100; monoclonal mouse, Cell Signaling), or ionized calcium binding adaptor molecule 1 (dilution 1:500; Iba1; Wako) or glial fibrillary acidic protein (dilution 1:500; GFAP; Millipore Sigma # AB5804). One of the following fluorescent secondary antibodies was used: Alexa Fluor 555 anti-rabbit, Alexa Fluor 488 anti-rabbit, Alexa Fluor 488 anti-mouse (1:500, Life technologies, Grand Island, NY). Tissue sections were then washed and mounted using 4’,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (Vector laboratories) as mounting media which provided labeling of all cell nuclei. All the counting was done under a fluorescence microscope at 400X magnifications in five non-overlapping fields per mouse and then averaged by an investigator blinded to the groups.
Assays for Oxidative Stress
A thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARS) assay kit (Cayman Chemical, # 700,870) provided a tool for the direct quantitative measurement of malondialdehyde (MDA) in biological samples. The TBARS assay kit was used according to the manufacturer’s instructions to determine the TBARS level in the striatum of mice of each group as a marker of lipid peroxidation. TBARS levels were determined by absorbance at 535 nm with a microtiter plate reader (Bio-Rad iMARK) and the results were expressed as nmol TBARS formed /mg protein.
Glutathione (GSH) was measured in striatal homogenates with a commercial enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay kit (Cayman Chemical, #703,002) in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions. Briefly, 50 µL of standards and samples were added to a reaction mixture containing nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate, glutathione reductase, glucose-6-phosphate, and 5,5′-dithiobis-2-nitrobenzoic acid. The reaction was carried out at 37 °C for 10 minutes, and then, GSH levels were determined by absorbance at 420 nm with a microtiter plate reader. The results were expressed as µmol GSH/mg protein. Protein concentrations were determined with a BCA Protein Assay Kit (ThermoFisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA).
Enzyme-linked Immunosorbent Assays
Brain tissues (striatum) from the mice of each group were collected and homogenized in tissue lysis buffer (50 mM Tris HCl, pH 8.0, 5 mM NaCl, and 1% Triton X-100) containing Halt protease and phosphatase inhibitor cocktail. Supernatants from homogenates were used for determination of IL-6, and IL-1β with commercial ELISA kits (R & D System) in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions. Briefly, the capture antibody was diluted to the working concentration in PBS and used to load a 96-well microplate with 100 µl per well. The plate was sealed and incubated overnight at room temperature. After washing, standards and samples were pipetted into the wells and incubated for 2 hrs. After washing away unbound substances, an enzyme-linked polyclonal antibody specific for IL-6 or IL-1β were added to the wells. Following a wash to remove any unbound antibody-enzyme reagent, a substrate solution was added to the wells and color developed in proportion to the amount of bound IL-6 or IL-1β. The reaction was terminated by the addition of stop solution (2N sulfuric acid). The absorbance was measured at 450 nm with a microtiter plate reader (Bio-Rad iMARK).
Statistical Analysis
One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Tukey-Kramer post-hoc test was used to calculate the statistical significance between various groups on biochemical and histological measures using GraphPad Prism software. A value of P < 0.05 was considered as statistically significant and data are expressed as mean ± SEM.
Results
DHED Treatment Attenuates Oxidative Stress in MPTP-treated Mice
Oxidative stress generally occurs by increased levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS), which can damage lipids, proteins and nucleic acids (DNA and RNA). To evaluate the effects of DHED on MPTP-induced oxidative stress, we examined TBARS, GSH and Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase (SOD1) expression levels in the brains (striatum) of mice in each group. Measuring TBARS contents proffers a convenient method of determining the relative peroxidation of lipids in tissue homogenates and their protection by DHED. We found a significant (P < 0.01) increase of TBARS contents following MPTP administration as compared to the control group. DHED treatment (100 µg/kg) followed by MPTP administration significantly inhibited (P < 0.05) the apparent increase in TBARS content as compared to the MPTP injected group (Fig. 1a). The antioxidant system including GSH and SOD play important roles in detoxification of free radicals and are commonly reduced in neurodegenerative diseases (Seaton et al. 1996; Chi et al. 2007). As expected, GSH content was reduced significantly (P < 0.01) upon MPTP treatment, as compared to the saline injected control group (Fig. 1b). The decrease in GSH content due to MPTP was significantly (P < 0.05) abolished when treated with DHED at 100 µg/kg. Similarly, MPTP significantly decreased SOD1 expression, compared with the control, while treatment with DHED with concentration of 100 µg/kg significantly (P < 0.05) rescued MPTP-induced decrease in the expression of SOD1 (Fig. 1c).
DHED treatment attenuates oxidative stress in MPTP-treated mice. TBARS level was significantly increased while GSH and SOD1 protein abundance were significantly reduced in the MPTP group as compared to the control group of mice. DHED treatment at dose of 100 µg/kg followed by MPTP injection significantly prevented both the MPTP-induced elevation of TBARS (a) as well as MPTP-induced decrease in GSH level (b) and SOD1 expression (c and d). The values are expressed as mean ± SEM *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01 (N = 5–6/group for TBARS and GSH contents; N = 3/group for SOD1 immunohistochemistry)
DHED Treatment Reduces DNA Damage in MPTP-treated Mice
Increased ROS accumulation is a major cause of DNA damage and other deleterious changes to DNA. Given the role of DNA damage in PD (Milanese et al. 2018; Gonzalez-Hunt and Sanders 2020), we sought to determine whether DHED treatment can reduce MPTP-induced DNA damage in the brains of mice. For this purpose, we investigated DNA damage in the striatum of mice of each group by examining phosphorylated H2A.X immunohistochemistry. Detection of phosphorylated H2A.X [γ-H2AX (Ser139)] serves as a sensitive and reliable molecular marker for DNA damage (Mah et al. 2010; Siddiqui et al. 2015). We found that γ-H2A.X (ser139)-immunoreactive cells (Fig. 2a and b) were more numerous (P < 0.01) in the striatum of MPTP-treated mice compared to saline treated mice. DHED treatment at dose of 100 µg/kg significantly (P < 0.05) decreased the MPTP-induced DNA damage as compared to MPTP-treated group.
DHED treatment reduces DNA damage in MPTP-treated mice. Left panel (a) shows representative confocal images of DNA DSBs (γ-H2A.X (Ser139); red) and right panel (b) shows quantitative analysis of γ-H2A.X (Ser139) positive cells in the striatum of control, MPTP and DHED + MPTP treated groups. Increased DNA damage was observed in MPTP treated mice compared to saline treated mice. In contrast, DHED treated mice reduced MPTP-induced DNA damage accumulation when compared to MPTP-treated mice. Scale bar, 50 µm. The values are expressed as mean ± SEM *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 (N = 3/group)
DHED Treatments Inhibits Glial Cells Activation in MPTP-treated Mice
Activation of microglia and astrocytes, hallmarks of neuroinflammation, has been reported in several neurodegenerative disorders (Guzman-Martinez et al. 2019). In the present study, we analyzed astrocytic (GFAP) and microglial (Iba1) activation in the brains of mice in each group (Fig. 3a-d). GFAP immunostaining exposed astroglial activation and nearly 4-fold increase in activated astrocytes in the striatum of MPTP-treated mice compared to the control group mice (Fig. 3a and b). DHED treatment at both concentrations significantly reduced the increased number of GFAP-positive cells following MPTP injection (Fig. 3a and b). Increased expression of Iba1 as an index of inflammatory response, indicates a 3-fold increase in the number and activation of microglia were observed in MPTP injected mice (Fig. 3c and d), consistent with previous reports (Khan et al. 2013; Yang et al. 2020). DHED treatment at the higher concentration significantly (P < 0.01) prevented the MPTP-induced increase in the number of microglia and their activation.
DHED treatments inhibits glial cells activation in MPTP-treated mice. The expression of microglial (Iba1) and astrocytic (GFAP) markers was determined by immunofluorescence in the brains of mice of each group. The upper panel shows representative fluorescent images of GFAP (a) and Iba1 (c) in striatum. The lower panel shows quantitative analysis of GFAP (b) and Iba1 (d) in brain. The profound expression of Iba1 and GFAP (green color) were observed in MPTP group as compared to control group, while the MPTP group treated with DHED has shown a moderate staining of Iba1 and GFAP. However, the control group has shown reduced staining. Scale bar, 50 µm. The values are expressed as mean ± SEM *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01 (N = 3/group)
Effect of DHED on MPTP-induced Inflammatory Response
The development and progression of PD are associated with a robust inflammatory response. To determine whether DHED has a beneficial effect on the MPTP-induced inflammatory response, we measured cytokines production in the striatum of mice from each group. MPTP-treated mice demonstrated significantly elevated levels of interleukin (IL)-6 (P < 0.01), and IL-1β (P < 0.01) compared with saline-treated WT mice in the supernatant fractions of brain homogenates (Fig. 5a and b). The concentration of IL-6 at 7 days post MPTP-injections was 56.59 pg/mg protein compared to 22.59 pg/mg protein in saline-injected controls (Fig. 4a). Similarly, the concentration of IL-1β at 7 days post MPTP-injections (Fig. 4b) was significantly higher (169.15 pg/mg proteins) than found in control group (56.11 pg/mg protein). In contrast, IL-6 and IL-1β cytokine production caused by MPTP treatment was significantly reduced by both concentrations of DHED treatments.
Effect of DHED on MPTP-induced inflammatory response. Quantification of interleukin (IL)-6, and IL-1β, by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay in the supernatant of brain homogenates from the striatum region from mice of each group. MPTP-treated mice demonstrated significantly elevated levels of IL-6 and IL-1β in the supernatant fraction of brain homogenates compared to control. The DHED remarkably reduced the levels of IL-6 and IL-1β in MPTP-treated mice. The values are expressed as mean ± SEM *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01 (N = 6/group)
DHED treatment protects dopaminergic neuron in mice following MPTP treatment
Tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) is the rate-limiting enzyme for dopamine synthesis, and the loss of TH-positive fibers in the striatum is considered to contribute to PD. The SNpc has dopaminergic projections to the striatum, and the degeneration of dopaminergic neurons in SNpc can lead to dopamine depletion in the striatum. To determine the neuroprotective effects of DHED on dopaminergic neurodegeneration, we performed immunohistochemistry of TH in the SNpc and striatum following MPTP injection in DHED-treated mice. In MPTP-treated mice, the number of TH-positive neurons in the SNpc and the density of TH-positive fibers in the striatum were significantly decreased compared with the saline-treated control group which are consistent with previous reports (Khan et al. 2013, 2015; Jackson-Lewis et al. 1995). DHED-treated mice show significantly reduced nigrostriatal dopaminergic neuron loss following MPTP injection (Fig. 5a and b). Additionally, DHED treatment significantly abolished the decreasing TH fibers density induced by MPTP in the striatum of mice as compared to the MPTP injected group (Fig. 5c and d). Therefore, DHED treatments attenuated the loss of dopaminergic neurons induced by MPTP in mice.
DHED treatment protects dopaminergic neuron in mice following MPTP treatment. Representative immunohistochemistry images of TH-positive neurons (a) and TH-fiber density (c) in the SNpc and striatum regions of each group, respectively and their quantifications (b and d). TH-positive neurons and TH-fiber density were significantly reduced in MPTP group as compared to control group. Interestingly, DHED treatment for four weeks attenuated TH-positive neuronal loss and TH-fibers density in the SNpc region and striatum, respectively following MPTP treatment. Scale bar, 200 µm (a) and 500 µm (c). The values are expressed as mean ± SEM *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 (N = 3/group)
DHED Treatment Improves Motor Abnormalities in MPTP-treated Mice
We determined the effects of DHED treatment on behavioral function in MPTP-treated mice using raised beam task, rotarod, and a grip strength test. Behavioral tests for each group of mice were initiated on day 7 post MPTP injection. MPTP-treated mice performed poorly on the rotarod, raised-beam task and grip strength test, which is consistent with previous reports (Zhang et al. 2019; Khan et al. 2013). DHED treatments significantly preserved motor function following MPTP treatment. Rotarod latency to fall from an accelerating rotating rod was measured in mice of each group. MPTP-injected mice had a shorter latency (P < 0.01) to fall in comparison to saline-treated WT littermates (Fig. 6a). The mice treated with DHED (100 µg/kg) significantly (P < 0.05) improved muscular coordination skill following MPTP injections as compared to MPTP injected group only. A significant decrease (P < 0.05) in motor strength as measured by the grip strength test was observed in the MPTP injected group as compared with the saline-treated WT mice. DHED treatments (100 µg/kg) significantly protected mice from the MPTP-induced decline in motor strength (Fig. 6b). Raised-beam tasks assessed the ability of mice to traverse narrow horizontal beams to reach a dark box. There was a significant effect (P < 0.01) of MPTP treatment on traversal times on the both 12-mm square and round horizontal beam. Mice from the MPTP injected group moved slower than the saline-treated control group mice (Fig. 6c). The latency to cross the 12-mm square beam was improved (P < 0.05) in mice treated with DHED at a concentration of 100 µg/kg when compared with the MPTP injected group. On the 12-mm round beam, DHED at higher concentrations (100 µg/kg) were effective to improve the latency to cross.
DHED treatment protects against MPTP-induced behavioral impairments. Mice (C57BL/6; WT) were assessed on a battery of behavioral tests to assess motor function. a Rotarod latency to fall from an accelerating rotating rod was measured in saline-injected mice, MPTP-injected mice, MPTP-injected mice treated with 50 and 100 µg/kg DHED. In each trial, n = 6 mice for each condition; 3 trials conducted. MPTP treated WT mice had a shorter latency to fall in comparison to saline-treated WT mice and significantly recovered in DHED treated mice (100 µg/kg) as compared to only MPTP treated mice. b The grip strength decreased significantly in the MPTP injected animals as compared to control animals. Treating the animals with DHED followed by MPTP injections has improved motor deficit as compared with MPTP only injected group. c Raised-beam tasks assessed the ability of mice to traverse narrow beams to reach a dark box. Overall, MPTP-treated mice moved slower than saline-treated WT mice, whereas, DHED treated mice with a dose of 100 µg/kg significantly took less time to cross the traverse narrow beams to reach a dark box as compared to the MPTP treated group. Data were analyzed by one-way ANOVA analysis. The values are expressed as mean ± SEM *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01
Discussion
Several experimental studies suggest that estrogen can protect against a broad range of neurotoxic insults. However, clinical use of estrogen therapy remains controversial due to the observed peripheral side effects. Recent studies investigated the beneficial effect of DHED, a brain-selective (Prokai et al. 2015) prodrug of 17β-estradiol and found it to be effective in several preclinical models of neurological disorders (Rajsombath et al. 2019; Tschiffely et al. 2016, 2018; Prokai et al. 2015). In the present study, we demonstrate that DHED exerted protection of dopaminergic neurons and improvement of behavioral function in the MPTP-induced mouse model of PD. These neuroprotection’s by DHED include reduction of oxidative and inflammatory responses, corroborating previous studies (Rajsombath et al. 2019; Sawada et al. 1998; Yan et al. 2019; Prokai-Tatrai et al. 2018; Tschiffely et al. 2018). These data, which present the first report of brain selective estrogen treatment on dopaminergic neurons in a MPTP-induced PD mouse model, implicate the beneficial effect of estrogen in regulation of PD-like neuropathology and motor symptoms. Similar to our findings, other studies have reported estrogen to galvanize neuroprotective mechanisms in mouse models of PD (Tripanichkul et al. 2007; Rodriguez-Perez et al. 2013; Shen et al. 2017). Furthermore, estrogen treatment has been associated with reduced oxidative stress, diminished inflammation and increased TH-positive neurons in experimental models of PD (Tripanichkul et al. 2006, 2007; Rodriguez-Perez et al. 2013). Consistent with these findings, we observed a significant reduction in markers of oxidative stress along with inflammatory markers as well as protection of dopaminergic neurons in DHED-treated males.
There is growing evidence supporting the role of oxidative stress in the development and progression of several neurodegenerative disorders including PD (Dias et al. 2013; Hald and Lotharius 2005). Increased and sustained oxidative stress triggers inflammation, which subsequently fuel the degeneration of dopaminergic neurons. It has been reported that MPTP administration in mice leads to excessive generation of ROS, which can cause oxidative stress by disrupting the balance of antioxidant and prooxidant levels (Khan et al. 2013; Zhu et al. 2019). The brain is particularly susceptible to oxidative damage due to its high levels of fatty acids and relatively low antioxidant defenses (Sanders and Timothy Greenamyre 2013). Oxidative damage to macromolecules including, lipids, proteins and DNA can lead to structural and functional disruption of the cell membrane and inactivation of enzymes, which ultimately leads to cell death (Lin and Beal 2006). GSH is the most abundant intracellular non-protein thiol and plays an important role in maintaining redox balance within a cell (Dringen 2000). Depletion of GSH may impair H2O2 clearance and increases the free radical accumulation, which in turn, promotes oxidative stress and consequently disrupts homeostasis (Aquilano et al. 2014). Superoxide dismutase (SOD) is the major antioxidant defense systems against superoxide, and catalyzes the conversion of superoxide into H2O2, which may participate in cell signaling (Fukai and Ushio-Fukai 2011). The increase in H2O2 might have induced the peroxidation of fatty acids and lead to the generation of cytotoxic metabolites of lipid such as TBARS, 4-HNE, and MDA. Increased concentration of oxidized lipid can cause decreased membrane fluidity, reduced membrane potential, and altered ions transport (Gaschler and Stockwell 2017). In view of our findings, it is reasonable to speculate that the depletion of GSH triggers lipid peroxidation, which, in turn, caused oxidative damages and ultimately lead to degeneration of dopaminergic neurons. Consistent with these notions, our present study showed that MPTP administration increased the level of TBARS and decreased the expression levels of GSH and SOD in the striatum of MPTP-treated mice. Interestingly, DHED treatment inhibited the formation of TBARS complex, and suppressed the loss of GSH and SOD in the brains of Parkinsonian mice. Our data show that DHED improved antioxidant protein abundance, but we do not know if DHED altered ROS production.
DNA damage is a modification in DNA structure and has been implicated in the pathogenesis of several neurological diseases (Gonzalez-Hunt and Sanders 2020). If left unrepaired or misrepaired, they can ultimately lead to chromosome breakage and genome instability, immune system activation, and neurodegeneration. Elevated levels of DNA damage were detected in the brains of PD patients (Camins et al. 2010; Gonzalez-Hunt and Sanders 2020) and in mouse models of PD (Wang et al. 2016; Gonzalez-Hunt and Sanders 2020). Wang et al. reported that accumulation of damaged DNA preceded onset of motor phenotype and dopaminergic degeneration in α-synuclein (A53T) overexpressing transgenic mice (Wang et al. 2016). Consistent with these studies, we found that mice treated with MPTP exhibit higher levels of DNA damage, and DHED treatments inhibited the accumulation of DNA damage in the brains of MPTP-treated mice.
Inflammation is closely intertwined with pathogenesis of PD. As documented by several studies, neuroinflammation is manifested by activation of glial cells and secretion of inflammatory cytokines including IL-1β and IL-6 in the brain (Guzman-Martinez et al. 2019; Javed et al. 2020). The up-regulation of Iba1 expression following MPTP administration is an indicator of microglial activation. Human post-mortem studies as well as mouse models of PD also reveal the presence of activated microglia in the nigrostriatal regions of PD brains (Joers et al. 2017; Javed et al. 2020). This observation is consistent with increased inflammatory response correlating positively with dopaminergic neuronal loss, as documented by other studies (Yang et al. 2020; Javed et al. 2020; Khan et al. 2013). Here, through the expression analysis of GFAP, and Iba1, we show that DHED treatment suppressed the glial cell activation-induced inflammatory response and rescues dopaminergic neuron from MPTP-induced toxicity.
Behavioral functions are closely linked to the degree of neuronal dysfunction and its assessment serves as a more powerful endpoint in evaluating neuroprotection. Therefore, examining the behavioral defects in the current study provides a sensitive evaluation of the DHED’s ability to provide neuroprotection. Consistent with previous studies (Khan et al. 2013; Anandhan et al. 2010), MPTP injections caused severe motor deficits as assessed by rotarod, grip strength, and raised beam task test in mice and DHED was found to improve motor deficits in MPTP-treated mice. Our present findings are in agreement with the earlier reports that motor deficits in Parkinsonian mice have been attenuated by estrogen supplementation (Quesada and Micevych 2004; Rodriguez-Perez et al. 2013; Yadav et al. 2017). Protection of the antioxidants defense system and suppression of inflammation were further emphasized by the restoration of TH expression by the DHED. TH is a rate-limiting enzyme in the formation of dopamine, and its expression is the marker for dopaminergic neuron survival. Inhibition of the loss of dopaminergic neurons by DHED treatment further support the neuroprotective role of DHED in MPTP-induced toxicity, as observed in the present study. The marked protective effects of DHED against dopaminergic neurodegeneration observed in this study are consistent with an earlier study (Rajsombath et al. 2019). Oxidative stress and inflammation are closely intertwined pathobiological processes that may contribute to several neurodegenerative diseases including, PD. Our present study showed that MPTP administration caused oxidative stress that was concomitant with an inflammatory response, while DHED ameliorates oxidative stress and suppresses the inflammatory cascade in mice. Given that oxidative stress is an upstream event that can activate inflammation and amplify the production of cytokines, it is likely that DHED inhibited oxidative stress and inflammation, at least in part, by this demonstrated antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects. The limitation of this study is that we did not quantify the brain and peripheral estrogen level in mice treated with DHED, given that the previously published studies reported that DHED converts to estrogen in the brain but not in the periphery (Rajsombath et al. 2019; Prokai et al. 2015; Merchenthaler et al. 2020). The other limitation of this study is that we do not know whether DHED directly interferes with uptake of MPP+ by dopaminergic neurons via the dopamine transporter. These limitations encourage further studies that focus on the neuroprotective mechanism of DHED in a mouse model with progressive dopaminergic neurodegeneration, similar to human PD condition.
In conclusion, we showed that MPTP injection alters the behavioral and neuropathological parameters that characterize Parkinson-related disorders. DHED treatment attenuated these alterations by reinstating near-normal levels of markers of oxidative stress and inflammation, suggesting neuroprotective actions of DHED. Further studies are required to confirm the protective effect of DHED in another mouse model of PD, and to identify the molecular mechanisms by which DHED protects the nigrostriatal dopamine neurons.
Data Availability
The data generated and analyzed in this study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Anandhan A, Tamilselvam K, Vijayraja D, Ashokkumar N, Rajasankar S, Manivasagam T (2010) Resveratrol attenuates oxidative stress and improves behaviour in 1 -methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) challenged mice. Ann Neurosci 17:113–119. https://doi.org/10.5214/ans.0972-7531.1017304
Aquilano K, Baldelli S, Ciriolo MR (2014) Glutathione: new roles in redox signaling for an old antioxidant. Front Pharmacol 5:196. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2014.00196
Breydo L, Wu JW, Uversky VN (2012) Alpha-synuclein misfolding and Parkinson’s disease. Biochim Biophys Acta 1822:261–285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbadis.2011.10.002
Butler MJ, Perrini AA, Eckel LA (2020) Estradiol treatment attenuates high fat diet-induced microgliosis in ovariectomized rats. Horm Behav 120:104675. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yhbeh.2020.104675
Camins A, Pizarro JG, Alvira D, Gutierrez-Cuesta J, de la Torre AV, Folch J, Sureda FX, Verdaguer E, Junyent F, Jordan J, Ferrer I, Pallas M (2010) Activation of ataxia telangiectasia muted under experimental models and human Parkinson’s disease. Cell Mol Life Sci 67:3865–3882. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-010-0408-5
Chi L, Ke Y, Luo C, Gozal D, Liu R (2007) Depletion of reduced glutathione enhances motor neuron degeneration in vitro and in vivo. Neuroscience 144:991–1003. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2006.09.064
Dauer W, Przedborski S (2003) Parkinson’s disease: mechanisms. and models Neuron 39:889–909. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0896-6273(03)00568-3
Dias V, Junn E, Mouradian MM (2013) The role of oxidative stress in Parkinson’s disease. J Parkinsons Dis 3:461–491. https://doi.org/10.3233/JPD-130230
Dringen R (2000) Metabolism and functions of glutathione in brain. Prog Neurobiol 62:649–671. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0301-0082(99)00060-x
Fukai T, Ushio-Fukai M (2011) Superoxide dismutases: role in redox signaling, vascular function, and diseases. Antioxid Redox Signal 15:1583–1606. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2011.3999
Gaschler MM, Stockwell BR (2017) Lipid peroxidation in cell death. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 482:419–425. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.10.086
Goedert M (2001) Alpha-synuclein and neurodegenerative diseases. Nat Rev Neurosci 2:492–501. https://doi.org/10.1038/35081564
Gonzalez-Hunt CP, Sanders LH (2020) DNA damage and repair in Parkinson’s disease: Recent advances and new opportunities. J Neurosci Res. https://doi.org/10.1002/jnr.24592
Guzman-Martinez L, Maccioni RB, Andrade V, Navarrete LP, Pastor MG, Ramos-Escobar N (2019) Neuroinflammation as a common feature of neurodegenerative. Disorders Front Pharmacol 10:1008. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2019.01008
Hald A, Lotharius J (2005) Oxidative stress and inflammation in Parkinson’s disease: is there a causal link? Exp Neurol 193:279–290. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2005.01.013
Hirsch L, Jette N, Frolkis A, Steeves T, Pringsheim T (2016) The Incidence of Parkinson’s Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Neuroepidemiology 46:292–300. https://doi.org/10.1159/000445751
Jackson-Lewis V, Jakowec M, Burke RE, Przedborski S (1995) Time course and morphology of dopaminergic neuronal death caused by the neurotoxin 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine. Neurodegeneration 4:257–269. https://doi.org/10.1016/1055-8330(95)90015-2
Javed H, Thangavel R, Selvakumar GP, Dubova I, Schwartz N, Ahmed ME, Zaheer S, Kempuraj D, Iyer S, Zaheer A, Khan MM (2020) NLRP3 inflammasome and glia maturation factor coordinately regulate neuroinflammation and neuronal loss in MPTP mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Int Immunopharmacol 83:106441. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2020.106441
Jenner P, Olanow CW (2006) The pathogenesis of cell death in Parkinson’s disease. Neurology 66:S24-36. https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.66.10_suppl_4.s24
Joers V, Tansey MG, Mulas G, Carta AR (2017) Microglial phenotypes in Parkinson’s disease and animal models of the disease. Prog Neurobiol 155:57–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pneurobio.2016.04.006
Khan MM, Kempuraj D, Thangavel R, Zaheer A (2013) Protection of MPTP-induced neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration by. Pycnogenol Neurochem Int 62:379–388. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2013.01.029
Khan MM, Zaheer S, Thangavel R, Patel M, Kempuraj D, Zaheer A (2015) Absence of glia maturation factor protects dopaminergic neurons and improves motor behavior in mouse model of parkinsonism. Neurochem Res 40:980–990. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-015-1553-x
Khan MM, Xiao J, Patel D, LeDoux MS (2018) DNA damage and neurodegenerative phenotypes in aged Ciz1 null. mice Neurobiol Aging 62:180–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2017.10.014
Khan M, Ullah R, Rehman SU, Shah SA, Saeed K, Muhammad T, Park HY, Jo MH, Choe K, Rutten BPF, Kim MO (2019) 17beta-estradiol modulates sirt1 and halts oxidative stress-mediated cognitive impairment in a male aging mouse model. Cells 8 https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8080928
Lee YH, Cha J, Chung SJ, Yoo HS, Sohn YH, Ye BS, Lee PH (2019) Beneficial effect of estrogen on nigrostriatal dopaminergic neurons in drug-naive postmenopausal Parkinson’s disease. Sci Rep 9:10531. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-47026-6
Lin MT, Beal MF (2006) Mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in neurodegenerative diseases. Nature 443:787–795. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature05292
Mah LJ, El-Osta A, Karagiannis TC (2010) gammaH2AX: a sensitive molecular marker of DNA damage and repair. Leukemia 24:679–686. https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2010.6
Merchenthaler I, Lane M, Sabnis G, Brodie A, Nguyen V, Prokai L, Prokai-Tatrai K (2016) Treatment with an orally bioavailable prodrug of 17beta-estradiol alleviates hot flushes without hormonal effects in the periphery. Sci Rep 6:30721. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep30721
Merchenthaler I, Lane M, Stennett C, Zhan M, Nguyen V, Prokai-Tatrai K, Prokai L (2020) Brain-selective estrogen therapy prevents androgen deprivation-associated hot flushes in a rat model. Pharmaceuticals (Basel) 13 https://doi.org/10.3390/ph13060119
Milanese C, Cerri S, Ulusoy A, Gornati SV, Plat A, Gabriels S, Blandini F, Di Monte DA, Hoeijmakers JH, Mastroberardino PG (2018) Activation of the DNA damage response in vivo in synucleinopathy models of Parkinson’s disease. Cell Death Dis 9:818. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-018-0848-7
Mosley RL, Benner EJ, Kadiu I, Thomas M, Boska MD, Hasan K, Laurie C, Gendelman HE (2006) Neuroinflammation, oxidative stress and the pathogenesis of parkinson’s disease. Clin Neurosci Res 6:261–281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cnr.2006.09.006
Ouchi Y, Yagi S, Yokokura M, Sakamoto M (2009) Neuroinflammation in the living brain of Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 15(Suppl 3):S200-204. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1353-8020(09)70814-4
Prokai L, Nguyen V, Szarka S, Garg P, Sabnis G, Bimonte-Nelson HA, McLaughlin KJ, Talboom JS, Conrad CD, Shughrue PJ, Gould TD, Brodie A, Merchenthaler I, Koulen P, Prokai-Tatrai K (2015) The prodrug DHED selectively delivers 17beta-estradiol to the brain for treating estrogen-responsive disorders. Sci Transl Med 7:297ra113. https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.aab1290
Prokai-Tatrai K, Nguyen V, Prokai L (2018) 10beta,17alpha-Dihydroxyestra-1,4-dien-3-one: a bioprecursor prodrug preferentially producing 17alpha-estradiol in the brain for targeted neurotherapy. ACS Chem Neurosci 9:2528–2533. https://doi.org/10.1021/acschemneuro.8b00184
Przedborski S, Vila M (2003) The 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine mouse model: a tool to explore the pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci 991:189–198
Quesada A, Micevych PE (2004) Estrogen interacts with the IGF-1 system to protect nigrostriatal dopamine and maintain motoric behavior after 6-hydroxdopamine lesions. J Neurosci Res 75:107–116. https://doi.org/10.1002/jnr.10833
Ragonese P, D’Amelio M, Callari G, Salemi G, Morgante L, Savettieri G (2006) Age at menopause predicts age at onset of Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 21:2211–2214. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.21127
Rajsombath MM, Nam AY, Ericsson M, Nuber S (2019) Female sex and brain-selective estrogen benefit alpha-synuclein tetramerization and the PD-like motor syndrome in 3K transgenic. Mice J Neurosci 39:7628–7640. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0313-19.2019
Rodriguez-Perez AI, Dominguez-Meijide A, Lanciego JL, Guerra MJ, Labandeira-Garcia JL (2013) Inhibition of Rho kinase mediates the neuroprotective effects of estrogen in the MPTP model of Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Dis 58:209–219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2013.06.004
Sanders LH, Timothy Greenamyre J (2013) Oxidative damage to macromolecules in human Parkinson disease and the rotenone model Free. Radic Biol Med 62:111–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2013.01.003
Sawada H, Ibi M, Kihara T, Urushitani M, Akaike A, Shimohama S (1998) Estradiol protects mesencephalic dopaminergic neurons from oxidative stress-induced neuronal death J Neurosci Res 54:707–719 https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1097-4547(19981201)54:5<707::AID-JNR16>3.0.CO;2-T
Seaton TA, Jenner P, Marsden CD (1996) Mitochondrial respiratory enzyme function and superoxide dismutase activity following brain glutathione depletion in the rat. Biochem Pharmacol 52:1657–1663. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0006-2952(96)00452-2
Shen D, Tian X, Zhang B, Song R (2017) Mechanistic evaluation of neuroprotective effect of estradiol on rotenone and 6-OHDA induced Parkinson’s disease. Pharmacol Rep 69:1178–1185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharep.2017.06.008
Siddiqui MS, Francois M, Fenech MF, Leifert WR (2015) Persistent gammaH2AX: A promising molecular marker of DNA damage and aging. Mutat Res Rev Mutat Res 766:1–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mrrev.2015.07.001
Thakkar R, Wang R, Sareddy G, Wang J, Thiruvaiyaru D, Vadlamudi R, Zhang Q, Brann D (2016) NLRP3 inflammasome activation in the brain after global cerebral ischemia and regulation by 17beta-estradiol oxid. Med Cell Longev 2016:8309031. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/8309031
Tripanichkul W, Sripanichkulchai K, Finkelstein DI (2006) Estrogen down-regulates glial activation in male mice following 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine intoxication. Brain Res 1084:28–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2006.02.029
Tripanichkul W, Sripanichkulchai K, Duce JA, Finkelstein DI (2007) 17Beta-estradiol reduces nitrotyrosine immunoreactivity and increases SOD1 and SOD2 immunoreactivity in nigral neurons in male mice following MPTP insult. Brain Res 1164:24–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2007.05.076
Tsang KL, Ho SL, Lo SK (2000) Estrogen improves motor disability in parkinsonian postmenopausal women with motor fluctuations. Neurology 54:2292–2298. https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.54.12.2292
Tschiffely AE, Schuh RA, Prokai-Tatrai K, Prokai L, Ottinger MA (2016) A comparative evaluation of treatments with 17beta-estradiol and its brain-selective prodrug in a double-transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Horm Behav 83:39–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yhbeh.2016.05.009
Tschiffely AE, Schuh RA, Prokai-Tatrai K, Ottinger MA, Prokai L (2018) An exploratory investigation of brain-selective estrogen treatment in males using a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Horm Behav 98:16–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yhbeh.2017.11.015
Van Den Eeden SK, Tanner CM, Bernstein AL, Fross RD, Leimpeter A, Bloch DA, Nelson LM (2003) Incidence of Parkinson’s disease: variation by age, gender, and race/ethnicity. Am J Epidemiol 157:1015–1022. https://doi.org/10.1093/aje/kwg068
Vegeto E, Belcredito S, Etteri S, Ghisletti S, Brusadelli A, Meda C, Krust A, Dupont S, Ciana P, Chambon P, Maggi A (2003) Estrogen receptor-alpha mediates the brain antiinflammatory activity of estradiol. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100:9614–9619. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1531957100
Wang D, Yu T, Liu Y, Yan J, Guo Y, Jing Y, Yang X, Song Y, Tian Y (2016) DNA damage preceding dopamine neuron degeneration in A53T human alpha-synuclein transgenic mice Biochem. Biophys Res Commun 481:104–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.11.008
Yadav SK, Pandey S, Singh B (2017) Role of estrogen and levodopa in 1-methyl-4-pheny-l-1, 2, 3, 6-tetrahydropyridine (mptp)-induced cognitive deficit in Parkinsonian ovariectomized mice model: A comparative study. J Chem Neuroanat 85:50–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchemneu.2017.07.002
Yan W, Wu J, Song B, Luo Q, Xu Y (2019) Treatment with a brain-selective prodrug of 17beta-estradiol improves cognitive function in Alzheimer’s disease mice by regulating klf5-NF-kappaB pathway Naunyn. Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 392:879–886. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-019-01639-w
Yang Y, Kong F, Ding Q, Cai Y, Hao Y, Tang B (2020) Bruceine D elevates Nrf2 activation to restrain Parkinson’s disease in mice through suppressing oxidative stress and inflammatory response Biochem. Biophys Res Commun 526:1013–1020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.03.097
Zhang G, Yang G, Liu J (2019) Phloretin attenuates behavior deficits and neuroinflammatory response in MPTP induced Parkinson’s disease in mice. Life Sci 232:116600. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2019.116600
Zhu YL, Sun MF, Jia XB, Cheng K, Xu YD, Zhou ZL, Zhang PH, Qiao CM, Cui C, Chen X, Yang XS, Shen YQ (2019) Neuroprotective effects of Astilbin on MPTP-induced Parkinson’s disease mice: Glial reaction, alpha-synuclein expression and oxidative stress. Int Immunopharmacol 66:19–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2018.11.004
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the William and Ella Owens Medical Research Foundation, Department of Defense grant W81XWH-17-1-0062; NIH grant R03 NS114616 and the Division of Rehabilitation Sciences, College of Health Professions, University of Tennessee Health Science Center.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thadathil, N., Xiao, J., Hori, R. et al. Brain Selective Estrogen Treatment Protects Dopaminergic Neurons and Preserves Behavioral Function in MPTP-induced Mouse Model of Parkinson’s Disease. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 16, 667–678 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11481-020-09972-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11481-020-09972-1