Abstract
Young maternal age at birth has been consistently recognized as a factor contributing to externalizing behavior. However, estimates of the magnitude of this association across existing studies are inconsistent. Such inconsistencies cloud the interpretation of the literature and highlight the need for a systematic synthesis of existing empirical evidence. Further, the roles of possible moderators in the association remain to be revealed. Moderation analyses will enhance the field’s capacity to evaluate needs and locate a subgroup of children born to teen mothers with particularly heightened vulnerabilities. To address these gaps, the present study had two primary aims. First, a meta-analysis was conducted to quantify the magnitude of the association between being born to young mothers and children’s externalizing behavior across existing studies. Second, moderation meta-analyses were conducted to evaluate whether the influence of being born to teen mothers on children’s externalizing behavior is stronger during specific developmental periods, for a specific gender, for a specific race, or across contexts with varying teen pregnancy rates at a societal level. The current study followed the PRISMA guidelines. The search utilized multiple electronic databases including Web of Science, ProQuest, PubMed, and Ovid MEDLINE through July 2019. Standardized mean difference, Cohen’s d, was used as a summary estimate of effect size. A random-effects model was conducted. Moderating effects were evaluated. Twenty-one effect sizes from 18 independent samples (n = 133,585) were included in the meta-analysis. The main meta-analysis and sensitivity analysis suggested a small yet robust association between teenage motherhood and children’s externalizing behavior problems. The relevant moderation analyses detected no statistically significant moderating effect for a specific gender, for racial and ethnic minority groups, during a specific developmental period, or across varying contexts. The current meta-analysis findings suggest that the impact of young maternal age on children’s externalizing behavior is small, yet independent. Further, such impacts of young maternal age were similar for girls and boys, in different racial and ethnic groups, across developmental periods, and across different contexts with varying teen pregnancy rates. Prevention efforts seeking to curb the emergence of youth’s externalizing behavior should focus on parenting teens, regardless of their child’s gender, race, age, or contexts. Further, the current findings suggest that prevention strategies for this specific group may benefit from a hybrid approach that combines universal, selective, and indicated prevention strategies.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
In 2017, 194,377 babies were born to adolescents aged 15–19 in the United States, accounting for 5% of all births in that year (Martin et al. 2018). Most of these births (89.2%) occurred outside of marriage (Martin et al. 2018) and nearly 8 in 10 (77%) were unwanted and unplanned (Mosher et al. 2012). Being born to young mothers has been consistently noted as a key risk factor for compromised developmental outcomes for children (Coyne and D’Onofrio 2012), including externalizing behaviors among youth (McGrath et al. 2014).
Despite increasing numbers of empirical studies examining the impacts of young maternal age on children’s externalizing behavior, estimates of the existence, direction, and magnitude of this association across existing studies have not yet reached a consensus, making it hard to discern where the existing literature stands. Further, possible moderating effects by key social status markers, such as gender and race, or contextual differences, such as teen pregnancy rates at a societal level, have received limited empirical attention. Similarly, the extent to which the influences of young maternal age on children’s externalizing behaviors vary across developmental epochs is unknown, despite the inherently developmental nature of externalizing behavior. Revealing where the current literature stands in terms of the impacts of teen pregnancy on externalizing behavior among children is important to consider, including whether a shift in intervention profiles is needed to account for this specific developmental outcome. Locating a possible moderator is also important, because it would help locate a subgroup of children born to teen mothers with particularly heightened vulnerabilities. To address these critical gaps in the existing literature, the current study involved a meta-analysis of existing evidence, including the role of possible moderators.
Young Maternal Age and Offspring Externalizing Behaviors
In contrast to internalizing behavior, which reflects problems within the self taking an inward behavioral form (Achenbach and Rescorla 2001) and often dealing with affect (Mullin and Hinshaw 2007), externalizing behavior problems refer to issues evident in children’s outward behavior, representing conflicts with (Achenbach and Rescorla 2001) or negative acting on (Liu 2004) the external environment. Consistent with a dimensional conceptualization of externalizing behavior problems (Coghill and Sonuga-Barke 2012; Wakschlag et al. 2015), externalizing behavior problems have been conceptualized as inclusive of hyperactive, disruptive, and aggressive behaviors (Hinshaw 1987). They include diagnosed disorders such as attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), oppositional defiant disorder, and conduct disorder (American Psychiatric Association 2013; Mingebach et al. 2018). Externalizing behaviors are highly prevalent psychiatric diagnoses among youth. ADHD in 2016, for example, affected about 129 million worldwide (Thomas et al. 2015) and 5.7 million American school-aged children and youth (Danielson et al. 2018), representing the most commonly diagnosed childhood mental health problem in the United States (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention 2013). Earlier externalizing behavior has developmental ramifications later in life (Loth et al. 2014), including psychiatric problems, substance use disorder, and depression in young adulthood (Reef et al. 2011). This reflects the importance of understanding factors shaping externalizing behavior among youth, such as young maternal age at birth.
A sizable literature has probed the impacts of being born to teen mothers on externalizing behavior in children. However, estimates of the magnitude of this association across existing studies are inconsistent. Whereas some work has found no significant associations with maternal age (Moore et al. 1997), other studies have noted either negative (Schneider and Eisenberg 2006) or positive (Chang et al. 2014) impacts. Such inconsistencies in existing studies cloud the interpretation of the literature and highlight the need for a systematic synthesis of existing empirical evidence.
Moderating Effects: Gender, Age, Race, and Teen Pregnancy Rates
Some conceptual discussions and empirical findings suggest that teenage motherhood may affect externalizing behavior differently for girls versus boys. Gender socialization hypotheses (Chodorow 1978) argue that when exposed to a risk factor, girls’ maladjustment profile is less likely to result in externalizing behavior because such behavior does not fit gendered behavioral norms (Broidy and Agnew 1997). Consistently, a narrative review concluded that prevalence rates of conduct disorder are elevated among boys (Berkout et al. 2011). Similarly, an early review study suggested that being born to teen mothers might affect boys’ externalizing behavior more than girls (Brooksgunn and Furstenberg 1986). Yet gendered behavioral norms have changed, and early onset of externalizing behavior among girls is no longer uncommon (Fontaine et al. 2009)—this notion suggests smaller or possibly no gender differences. Because the relevant empirical evidence is limited regarding for which gender the impact of young maternal age on children’s externalizing behavior is worse, these feasible hypotheses remain conceptual.
Further, holding a social status related to less power and fewer resources in a given society may also condition the association between teenage motherhood and children’s externalizing behavior. Race, a potent social status marker, fundamentally shapes the probability of risk exposure of any type (Williams et al. 2010), including teen pregnancy (Manlove et al. 2013). Further, once exposed, a given risk will be fully potentiated for those who hold a less privileged racial status, often leading to worse consequences, because access to personal and social resources is often structured unfavorably for those who hold a less privileged position in this potent social status marker (Adler and Rehkopf 2008). Supporting such conceptual speculation, teen pregnancy rates in United States, for example, are much higher among Black (27.5%) and Hispanic teens (28.9%) than among White teens (13.25%; Romero et al. 2016). The role of race as a potential moderator has not received much empirical attention in relevant studies and thus remains to be clarified.
Children’s developmental stage may also moderate the impact of teenage motherhood on children’s externalizing behavior. First, externalizing behavior is inherently developmental. On average, a moderate level of externalizing behavior is developmentally appropriate and typically emerges in infancy and toddlerhood (Tremblay et al. 2004), decreases during childhood (Miner and Clarke-Stewart 2008), then increases and peaks during adolescence (Moffitt 1993). The developmental nature of externalizing behavior emphasizes the importance of applying a developmental lens when examining the association between teenage motherhood and children’s externalizing behavior. By definition, negative influences of teenage motherhood on children’s externalizing behavior imply that children born to teen mothers may deviate from normative trends in an undesirable direction and experience higher levels of externalizing behavior problems. Such deviation among children born to teen mothers may not emerge clearly during developmental periods when externalizing behavior is normatively expected to be high (i.e., infancy, toddlerhood, and adolescence). In contrast, increased externalizing behavior in children born to teen mothers may become more evident during developmental periods when externalizing behavior is normatively expected to be low (i.e., childhood). Although existing studies have examined the possible influences of young maternal age on children’s externalizing behaviors during varying developmental periods, these studies typically focused on one developmental period rather than multiple developmental epochs. As such, the extent to which the influences of young maternal age on children’s externalizing behaviors vary across developmental epochs is unknown.
Finally, teen pregnancy rates at a societal level may influence the effects of young maternal age at birth on externalizing behavior. Teen pregnancy rates have declined since 1990 in many developed countries (World Health Organization 2015) including the United States (Child Trends Databank 2018). On one hand, when teen pregnancy rates are low at a societal level, allocation of resources and services for a given child born to teen mothers can be more generous. These social resources and services may mitigate the impacts of teenage motherhood on child developmental outcomes. On the other hand, when teen pregnancy rates are low, stigma associated with teen pregnancy at a societal level (SmithBattle 2013) might become intensified. Such stigma associated with teen pregnancy can further exacerbate challenges in the transition to young motherhood for teen mothers (SmithBattle 2013), possibly leading to further compromised child developmental outcomes. Teen pregnancy rates at a societal level vary across years and locations. As such, exploration of substantial variation based on publication year or location is warranted, yet hard to achieve in an empirical study typically focusing on a data source from a single location in a single year.
Prior Review Studies
Studies examining the impacts of being born to a teenage mother on children’s developmental outcomes have increased, and the current study is not the first attempt to generate a systematic synthesis on this topic. Prior review studies (Brooksgunn and Furstenberg 1986; Coley and Chase-Lansdale 1998; Corcoran 1998; Coyne and D’Onofrio 2012; Gibbs et al. 2012; Hofferth 1987; Paranjothy et al. 2009; Ruedinger and Cox 2012) have unearthed common ground in the relevant literature and revealed gaps that future studies should pursue. However, existing reviews tended to broadly assess offspring’s developmental outcomes, and no prior known review studies have focused on externalizing behavior problems in children born to teen mothers. In studies with such a broad focus, it is challenging to incorporate the unique characteristics and developmental nature of externalizing behavior. A developmentally informed and targeted synthesis of available literature is essential to revealing a consensus in existing studies and addressing whether, on what, and when to intervene to prevent the emergence of externalizing behavior in children born to teen mothers.
Current Study
Young maternal age at birth has been consistently recognized as a risk factor contributing to child behavioral problems, including externalizing behavior. However, estimates of the magnitude of this association across existing studies are inconsistent. Such inconsistencies make it difficult to interpret the literature in a coherent way. Further, existing studies typically focused on a single developmental period, in a single location, and from a specific year. Thus, the extent to which the influences of young maternal age on children’s externalizing behaviors vary across different developmental epochs and across varying contexts is unknown. Similarly, limited empirical attention has been given to possible moderating effects by gender and race, two potent social status markers. Moderation analyses will enhance the field’s capacity to evaluate needs and locate a subgroup of children born to teen mothers with particularly heightened vulnerabilities.
To address these research gaps, the current study addressed two central research questions. First, it quantified the magnitude of the association between being born to young mothers and children’s externalizing behavior using a meta-analysis to reveal where the current empirical evidence stands. Second, moderation meta-analysis models were conducted to examine whether the influences of teenage motherhood on children’s externalizing behavior are stronger for a specific gender, during specific developmental periods, for people of color, or across varying teen pregnancy rates.
Methods
Literature Search
The current study followed the PRISMA guidelines (Liberati et al. 2009). The search utilized multiple electronic databases including Web of Science, ProQuest, PubMed, and Ovid MEDLINE. It also involved reviews of reference lists of identified studies to ensure a thorough, comprehensive, and systematic search. Search terms with respect to maternal age were “teen childbearing,” “teen parenthood,” “maternal age,” “children of teen mother,” “children of young mothers,” “children born to teen mothers,” “adolescent parents,” “teenage birth,” “teenage mothers,” “adolescent mother,” “early child bearer,” and “age at first birth.” Regarding child behavioral problems, search terms were “externalizing,” “ADHD,” “attention problem,” “hyperactivity,” “conduct problem,” “delinquency,” “aggression,” “offending,” “Child Behavior Check List,” “child behavior,” “behavioral outcome,” “behavioral well-being,” “behavioral problem,” and “behavioral development.” Broader terms were used including “young adult outcome,” “adolescent outcome,” “adult outcome,” and “psychosocial behavior” to ensure a thorough search. Only English language publications were included. Considering that no prior review study focused on young maternal age and children’s externalizing behavior problems, no publication date restriction was imposed. The initial search was completed in February 2015 and updated in July 2019 with a targeted search for publications between 2015 and 2019.
Study Selection and Data Extraction
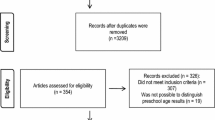
The study selection and screening process was completed via four steps. First, two researchers (JOL and CHJ) reviewed the titles and abstracts of using the pre-established screening criteria: (a) children’s externalizing behavior was a main outcome measure and (b) maternal age was the key predictor and was clearly defined or could be derived from available information. When titles and abstracts were insufficient to determine eligibility of a given study, full articles were reviewed. Second, for studies that met the initial screening criteria, four researchers (JOL, CHJ, CY, and JAC) conducted a full-text review to decide whether a given paper had all needed information and was in line with the focus of the present meta-analysis. Third, two researchers (JOL and JAC) evaluated the quality of studies that qualified for the full-text review using a quality assessment tool for quantitative studies (Effective Public Health Practice Project 1998). Disagreements in ratings between the reviewers were resolved by discussion. Studies that both reviewers rated to have weak quality in study design were excluded (n = 6), yielding 35 studies for further screening. Fourth, studies with insufficient available data to calculate effect sizes (n = 10), effect sizes incomparable with other studies (n = 5; modeling strategies incompatible with the included studies), or operationalization of externalizing behaviors incompatible with other studies (n = 2; delinquency, conviction, and involvement in crime) were excluded (Borenstein 2009), resulting in 18 studies being included in the meta-analysis (see Fig. 1).
Two standard data extraction forms for the meta-analysis were developed and refined during data extraction. Three researchers (CHJ, CY, and MN) extracted key information, including specific operationalization of maternal age, children’s externalizing behavior problems, and effect sizes and variances, from the included studies. Disagreements between reviewers were resolved by discussion and through consultation with the study team, particularly the first author (JOL). Applying these selection and screening criteria resulted in 21 effect sizes from 18 studies (n = 133,585) for the meta-analysis. The PRISMA flow diagram illustrates the process of study selection (Fig. 1).
Statistical Strategy for Meta-Analysis
Standardized mean difference, also known as Cohen’s d, was used as a summary estimate of effect size. Cohen’s d was calculated as d = (M1−M2)/swithin, wherein M1 and M2 are the sample means of teenage mothers and nonteenage mothers and derived from the fully adjusted model in a given study, and swithin is the pooled standard deviation across the groups. Transformation formulas for different types of effect sizes were adopted from Borenstein (2009) and Lipsey and Wilson (2001; see online supplementary Appendix A). When a study reported separate effect sizes by subgroups (e.g., effect sizes reported separately for boys and girls), combined effect sizes were calculated using weights by each group size and pooled standard deviation (Headrick 2009). If multiple outcome measures were reported or two independent samples were used, multiple effect sizes were extracted.
A random-effects model was conducted due to expected heterogeneity in samples and methodologies across studies (Borenstein 2009). To minimize possible bias in estimation, the Hartung-Knapp-Sidik-Jonkman adjustment was implemented (IntHout et al. 2014; Knapp and Hartung 2003). Next, to evaluate whether the influence of being born to teen mothers on children’s externalizing behavior was stronger for a specific gender, specific race, specific developmental period, or across teen pregnancy rates, moderation analyses were conducted following the guidelines established in the literature on meta-analysis (Borenstein 2009; Schwarzer et al. 2015). Each potential moderator was entered in a separate regression model for the effect sizes of being born to teen mothers on children’s externalizing behavior and then evaluated for whether it explained the variance of the observed effect sizes. Regarding possible moderating effects by teen pregnancy rates, publication years were also examined, because teen pregnancy rates have declined in many developed countries (World Health Organization 2015) including the United States (Child Trends Databank 2018) over time.
Sensitivity analyses were conducted to evaluate the model choice (i.e., random-effects model) and probe possible biases and uncertainty in the estimation for the meta-analysis. First, heterogeneity across the included studies was assessed using Higgins’ I2, which describes the percentage of total variation in estimated effects across studies due to heterogeneity rather than chance (Higgins and Thompson 2002). An I2 value less than 30% indicates mild heterogeneity; a value higher than 50% suggests notable heterogeneity (Higgins and Thompson 2002). For subgroup analyses, Q-value, the weighted sum of squared deviations of each study’s effect size from the combined effect size, was used to test heterogeneity in effect sizes among subgroups. A significant Q-value indicates variance in effect sizes across groups (Borenstein 2009). Second, the influence analysis method (Viechtbauer and Cheung 2010) was used to detect studies with extreme effect sizes that might distort a general trend in results across all studies. To address this concern, sensitivity analyses were conducted only with studies without extreme effect sizes. Third, funnel plots (Lewis and Clarke 2001) and Egger’s test (Egger et al. 1997) were employed to evaluate possible publication bias by testing whether funnel plots were not symmetrical (Sedgwick 2013). Fourth, to address potential bias due to treating multiple effect sizes from a single study as independent, multilevel meta-analysis was conducted. Fifth, the fail-safe N for effect sizes—the number of studies with null results needed to cancel the effect size—was calculated to evaluate the robustness of the effect size in the current study, using the Rosenberg method (Rosenberg 2005).
R statistical software version 3.6.0 with the ‘meta’ and ‘dmetar’ packages was used for main meta-analyses. Moderation analyses relied on the ‘metareg' function in R package, which was developed specifically for evaluating moderating effects in a meta-analysis framework (Schwarzer et al. 2015).
Results
Meta-Analysis: Effects of Maternal Age at Birth on Externalizing Behaviors
Table 1 summarizes characteristics of the studies included in the meta-analysis, including the percentage of children born to teen mothers (2.06–62.38%). A forest plot (Fig. 2) was used to assess the weighted overall effect size of maternal age of birth on externalizing behavior problems. As shown in the forest plot (Fig. 2), with an exception of one study (Hao and Matsueda 2006), the majority of standardized mean differences—effect sizes from each study—were positive, indicating that teenage motherhood was associated with increases in externalizing problem among youth in each study. The random-effects meta-analysis model produced a combined effect size of d = 0.21 (95% CI = 0.14, 0.28; k = 21) across studies, suggesting that having a teen mother was associated with increased externalizing behaviors across studies. Tests of heterogeneity revealed significant variability between studies (Higgins’ I2 = 83.7%), motivating moderator analyses.
Moderation Meta-Analysis: Gender, Age, Race, and Teen Pregnancy Rates Moderation
To examine whether the influences of being born to teen mothers on children’s externalizing behavior are stronger for a specific gender, the influences of percentage of female were evaluated. The effect was not statistically significant (b = 0.11, SE = 0.40, p = 0.78; k = 11), suggesting that the effect of being born to teen mothers on children’s externalizing behavior is not sensitive to the child’s gender.
To examine whether the influence of teenage motherhood on children’s externalizing behavior varies across racial and ethnic groups, a variable representing the proportions of racial and ethnic minorities was created and evaluated using meta-regression with studies that reported these percentages. The effect was not statistically significant (b = −0.01, SE = 0.09, p = 0.89; k = 9), suggesting the association of teenage motherhood with children’s externalizing behavior is similar across racial and ethnic groups.
For possible moderation by child age, three groups were created: early childhood (age 0–5, k = 7), school age (age 6–12, k = 6), and adolescence (age 13–18, k = 3). When study samples had a wide age range without information about the distribution of each age group and thus could not be assigned to any specific age group, they were excluded (k = 5). The relevant moderation analysis detected no statistically significant effect (b = −0.045, SE = 0.050, p = 0.39; k = 16), suggesting that the association between young maternal age and children’s externalizing behavior does not vary across developmental stages.
To test the potential moderating effects of teen pregnancy rates in a given location, teen pregnancy rates for that location in the publication year for each study were pulled from World Bank’s (2017) epidemiology data source for countries. The effect was not statistically significant (b = −0.003, SE = 0.003, p = 0.29, k = 21), suggesting that the influences of teenage motherhood on externalizing behaviors among youth do not differ by teen pregnancy rates at a societal level.
Finally, publication years were also examined, because teen pregnancy rates have declined in many developed countries (World Health Organization 2015) including the United States (Child Trends Databank 2018) over time. The relevant moderation analysis detected no statistically significant moderating effects of publication years (b = −0.001, SE = 0.007, p = 0.93; k = 21), suggesting no variation in the linkage between young maternal age at birth and children’s externalizing behavior across years.
Sensitivity Analyses for Meta-Analysis
To examine possible biases in the current meta-analysis results stemming from heterogeneity (Higgins’ I2 = 83.7%, as previously reported), analyses explored whether the association between maternal age and children’s externalizing behavior problems was sensitive to five dimensions of study characteristics: (a) having varying operational definitions of children’s externalizing behavior; (b) having extreme effect sizes (i.e., outlier); (c) examining mothers’ age at first birth (MAFB) vs. mothers’ age at the birth of the study child (MASC); (d) having more than one effect size; and (e) having publication bias. First, regarding heterogeneity in operational definitions of externalizing behavior, a Q-value (Borenstein and Higgins 2013) was calculated to test differences in effect sizes across subtypes of externalizing behavior. The test yielded a nonsignificant result (Q = 0.28, df = 2, p = 0.87), suggesting no differences in effect sizes across subtypes of externalizing behavior (online supplementary Appendix B). Second, to probe and address possible bias in the current meta-analysis results associated with studies with extreme effect sizes, an influence analysis was conducted (Viechtbauer and Cheung 2010; online supplementary Appendix C) and three outlier studies were detected (Hao and Matsueda 2006; Moffitt and the E-Risk Study Team 2002; Pohlabeln et al. 2017). The 95% confidence intervals of these three studies fall outside the 95% confidence interval of the pooled effect. This observation is consistent with other diagnostic measures. The absolute value of studentized residuals for these studies (Appendix C, D.1), for example, were greater than 2 and covariance ratios of these three studies (Appendix C, D.4) were particularly low. Taken together, these diagnostic measures suggest that the precision of parameter estimates may improve without these three studies (Shadish et al. 2014). A sensitivity analysis was conducted without these studies, resulting in a slightly decreased overall effect size (d = 0.19; 95% CI = 0.15, 0.23; k = 18). Third, to evaluate possible influences stemming from investigating MAFB in some studies and MASC in others, two additional meta-analyses were conducted—one with studies focused on MAFB (k = 9) and the other with studies focused on MASC (k = 12). MAFB (d = 0.18) showed a slightly lower effect size than MASC (d = 0.23), but the difference was not statistically significant (Q = 0.51, p = 0.48). Fourth, to address potential bias associated with studies with more than one outcome measure (k = 3), a multilevel meta-analysis was conducted. There was no variance between the multiple outcomes within studies (σ2 = 0), supporting the single-level model used in the current study. Fifth, to evaluate publication bias, a funnel plot was generated and Egger’s test was conducted to evaluate whether it was symmetrical. The result was not significant (t = 1.21, p = 0.24), suggesting that the funnel plot was symmetrical (online supplementary Appendix D) and thus providing no evidence of publication bias (Sedgwick 2013). Finally, the fail-safe N for young maternal age was robust, indicating 52 studies with null results would be needed to cancel out the effect sizes.
Discussion
Having teen mothers has been associated with increased developmental problems for children, including externalizing behavior. Despite a steady increase in number, existing studies have provided mixed conclusions regarding the existence and extent of this association. Such inconsistencies cloud the interpretation of the literature and highlight the need for a systematic synthesis of existing empirical evidence. Further, whether the association varies across genders, racial and ethnic groups, different developmental epochs, and varying contexts remains unknown. Relatedly, despite many efforts to generate a systematic synthesis, no prior review studies have explicitly focused on externalizing behavior problems in children born to teen mothers. To address these gaps, the present study quantified the magnitude of the association between being born to teen mothers and children’s externalizing behavior across existing studies using meta-analysis. Subsequent moderation meta-analyses examined whether the influence of being born to young mothers on children’s externalizing behavior differed across genders, racial and ethnic groups, developmental periods, and contexts with varying teen pregnancy rates.
The meta-analysis results suggest a small yet significant association between young maternal age and children’s externalizing behavior problems. Having teen mothers is equally associated with an increased risk of externalizing behavior problems for girls and boys with different racial and ethnic backgrounds. The risk does not vary as a function of child developmental period or varying teen pregnancy rates at a societal level.
Using 18 independent samples in the meta-analysis (n = 133,585), the current study demonstrated that being born to teen mothers was associated with increased vulnerability to externalizing behavior problems among children. This finding echoes previous review works (Brooksgunn and Furstenberg 1986; Coley and Chase-Lansdale 1998; Corcoran 1998; Coyne and D’Onofrio 2012; Gibbs et al. 2012; Hofferth 1987; Paranjothy et al. 2009; Ruedinger and Cox 2012) in documenting that being born to teen mothers is associated with compromised child developmental outcomes in a broad sense. The current study findings suggest that such developmental repercussions associated with having a teen mother exist in children’s externalizing behavior.
However, the effect size (d = 0.21) across studies is small to medium (Cohen 1988). This suggests that the link between being born to teen mothers and externalizing behavior may be less deterministic than previously presumed regarding intergenerational continuity in vulnerability among teen mothers and their children (Rutter 2004). Although being born to a teen mother may exacerbate children’s externalizing behavior, children born to teen mothers experience developmental fluidity, often referred to as multifinality (Cicchetti and Rogosch 1996), and thus are more heterogeneous than homogenous (Coyne and D’Onofrio 2012). Such consideration calls for more inquiries into factors contributing to within-group variability in children born to teen mothers along with between-group variability (i.e., comparing children born to teen mothers to those born to older mothers). A balanced investigation of within- and between-group variability will enhance the field’s ability to locate specific mechanisms that facilitate healthy development among children born to teen mothers, despite the odds of presumed susceptibility to poorer developmental outcomes.
No evidence was found for possible gender differences in the linkage between young maternal age and children’s externalizing behavior. Traditional gender norms for externalizing behavior have changed, as suggested by narrowing gender differences in early onset of externalizing behavior (Fontaine et al. 2009). The current findings support this notion and suggest that challenges of being born to teen mothers can manifest as elevated externalizing behavior problems for girls and boys. This finding echoes prior studies (Habersaat et al. 2018) advocating for the need to more clearly study and create clinical practice strategies to attend to externalizing behavior in girls, who have been overlooked due to relatively lower prevalence rates compared to boys.
No evidence was found that race and ethnicity, particularly belonging to a racial and ethnic minority, shapes the association between teenage motherhood and children’s externalizing behavior. This finding suggests that although there is differential exposure in risk by race (i.e., teen pregnancy rates are disproportionately concentrated among racial and ethnic minority groups; Romero et al. 2016), teenage motherhood doesn’t necessarily lead to differential vulnerability across generations. Instead, teenage motherhood exerts similar influences on children’s externalizing problems.
Similarly, no evidence was found for a stronger association between maternal age and children’s externalizing behaviors by developmental period, refuting the hypothesis of the present study that the negative influence of being born to teen mothers may be more evident during developmental periods when externalizing behavior is expected to be low in general (i.e., childhood). The absence of age moderation in the current study suggests that the developmental repercussions of being born to teen mothers may be independent of a child’s developmental stage and instead remain consistent across stages regarding the child’s externalizing behavior. In addition to this straightforward interpretation, at least two other possibilities might explain these null findings. First, the operationalization of children’s developmental age in the present study might not have been sensitive enough to capture developmental fluctuation in children’s externalizing behavior over time. In the current study, developmental periods were trichotomized: early childhood, school age, and adolescence. Although the operational definition of child age in the present study represents distinct developmental epochs, it did not capture possible fluctuations in externalizing behavior in each developmental period. Examining the influence of being born to teen mothers with more fine-grained, age-specific data may further clarify the possibility of age moderation. Similarly, applying special modeling strategies for detecting such a time-dependent influence, such as time-varying effects modeling (Tan et al. 2012), might be a promising analytic approach in future studies. Further, null findings might be a function of not having enough power to detect such moderation in this meta-analysis. There were few effect sizes for each developmental period—early childhood (k = 7), school age (k = 6), and adolescence (k = 3). This possibility once again indicates the need to explicitly consider the developmental nature of externalizing behavior in the association between young maternal age and children’s externalizing behavior.
Finally, no evidence was found for the influences of teen pregnancy rates at a societal level on the impacts of teenage motherhood on children’s externalizing behavior. As with the other moderation analyses, the practice implications for teen pregnancy rates analysis include locating a subgroup of children born to teen mothers with particularly heightened vulnerabilities. The current findings suggest that no specific gender, race, sensitive period, or pregnancy rates place children born to teen mothers at elevated risk of externalizing behavior problems. This supports implementing a universal prevention strategy. However, considering the current study findings along with existing studies on the effectiveness of a widely used universal prevention strategy, prevention strategies for externalizing behaviors in this specific group may benefit from a hybrid approach that combines universal, selective, and indicated prevention strategies. The most widely used prevention strategies in the United States for teenage mothers and their children, for example, are universal prevention programs, particularly home visitation and case management (Lachance et al. 2012). These universal prevention strategies have generated positive effects on a wide range of developmental outcomes for young mothers and their children (Duffee et al. 2017). However, a randomized controlled trial reported that the Nurse-Family Partnership program, the most widely known program in the United States that has been replicated in many other countries (Duffee et al. 2017), did not result in positive effects on children’s externalizing behaviors (Kitzman et al. 2010). As such, it might be worth integrating effective prevention strategies focused on externalizing behaviors with a universal prevention strategy for youth born to teen mothers, regardless of their gender, race, age, and teen pregnancy rates at a societal level. Further, findings indicate no moderating effects by child’s age along with widely documented stability (Pihlakoski et al. 2006) over time and a cascade process (Bornstein et al. 2013) in externalizing behavior starting at the onset of early childhood. Thus, integrating a universal prevention strategy with an indicated prevention strategy during earlier developmental periods, such as the Prevention Programme for Externalizing Problem Behavior (Hanisch et al. 2010), might be a promising way to enhance the field’s capacity to curb the emergence of externalizing behavior among youth born to young mothers.
The current study findings should be contextualized in light of a few methodological limitations. First, heterogeneity across studies presented challenges in establishing comparability (Young et al. 2011). However, the sensitivity analyses in the present study did not find empirical evidence suggesting that such heterogeneity might have introduced bias in the current meta-analysis results, rendering confidence in the study findings. Second, the current meta-analysis focused on whether the association between teenage motherhood and children’s externalizing behaviors exists. The study did not explicitly examine the question of why teenage motherhood is associated with increased risk of externalizing behavior. The nature of the relation between young maternal age and children’s externalizing behavior is subject to continued debate (Coyne et al. 2013). The social selection hypothesis suggests that the association between teenage motherhood and children’s externalizing behavior is spurious and may be a byproduct of pre-existing differences in teen mothers and older mothers, such as low academic achievement, socioeconomic disadvantage, mothers’ earlier externalizing behavior, or genetically shared vulnerability to externalizing behavior. Consistently, the impacts of maternal age on children’s externalizing behavior were substantially attenuated and became statistically nonsignificant with factors reflecting social selection in some studies (Terry-Humen et al. 2005). In contrast, such drastic changes were not observed in other studies (Harden et al. 2007), limiting the field’s capacity to reach a more generalizable conclusion about the role of social selection factors in shaping the influences of young maternal age on children’s externalizing behavior. A review study with a keen focus on this question of why young motherhood influences children’s externalizing behavior will be a fruitful future direction to reveal the current consensus and which possibly critical domains of risk and protective factors have been overlooked. Finally, following a guideline widely used for meta-analysis to ensure a certain degree of quality (Aldao et al. 2010), only studies published in peer-reviewed journals were included. As such, the possibility of omitting important studies can’t be completely ruled out, particularly unpublished reports or those with null findings.
Some study limitations are related to critical gaps in the existing literature. First, as shown in Table 1, study participants in prior works were predominately embedded in a Western culture, which reflects a lack of diversity in locations across published studies. As such, the current study could not fully consider policy and cultural contexts with varying behavioral norms, gender expectations, and policy protection that may influence externalizing behavior problems (Lansford et al. 2018) in this population. The current findings regarding gender differences, for example, may be different in regional areas where traditional gender norms about behavior are relatively strong. Similarly, the degree of social protection, such as universal access to different social services, likely affects the impacts of teenage motherhood on child developmental outcomes, because barriers to needed services are relatively lower in countries with universal access to social services compared to countries with means-based eligibility tests. Typologies of welfare states, for example, classify countries based on various elements of social policies, such as universal access to different services (Bergqvist et al. 2013). According to Esping-Anderson’s (1990) widely used typology of welfare states, 15 of the 18 studies in the current meta-analysis were published in countries characterized as a liberal welfare state. Studies in regional areas representing different cultural and policy contexts would help advance the field’s understanding of the impacts of young maternal age on children’s externalizing behavior and potential variability by child gender and other social factors. Second, as shown in Table 1, study participants in the review study represented mostly White and Black racial and ethnic groups. This limitation also highlights a critical gap in the existing literature. Study findings regarding racial and ethnic differences may be different among Latinx youth born to teen mothers, a subgroup with particularly heightened risk of teen pregnancy (U.S. Department of Health and Human Services 2018) in the United States. Latinx represents the largest (Passel et al. 2011) and youngest (U.S. Census Bureau 2014) racial and ethnic minority group, and Latinx youth and their families experience distinct risk and protective factors, cultural contexts, and social climate (Coleman-Minahan 2017). Thus, it is imperative to advance the current understanding of possible sources of risk and protection for Latinx children born to young mothers.
Despite its limitations, the present study made four important contributions to the relevant literature, which previously had produced mixed results. First, the current meta-analysis results revealed a consensus across existing studies. Second, the current study evaluated possible moderation effects of gender, race, age, and context (specifically, teen pregnancy rates) in a meta-analytic framework. Such moderation analysis determined the need to support subgroups of children born to teen mothers with heightened vulnerability, which did not receive much empirical attention in existing studies. Finally, the current study focused on externalizing behavior rather than a wide range of child developmental outcomes, enabling incorporation of developmental characteristics unique to externalizing behavior problems. By focusing this meta-analysis on externalizing behavior, the present findings generated more direct implications for research and practice.
Conclusion
Coupled with the absence of a targeted systematic synthesis, mixed findings in existing studies on the association between teenage motherhood and children’s externalizing behavior have made it challenging to draw a coherent conclusion on the association. To address these gaps, the present study aimed to reveal a common thread across existing studies and roles of moderators using a meta-analysis strategy. The current study findings provide quantified evidence that the impact of young maternal age on children’s externalizing behavior is small, yet independent. Further, such impacts of young maternal age were similar for girls and boys and across varying racial and ethnic backgrounds. The impacts of teenage motherhood were not sensitive to developmental periods or different contexts either. Prevention efforts seeking to curb the emergence of youth’s externalizing behavior should focus on parenting teens, regardless of their child’s gender, race, age, or contexts, and take a hybrid approach that combines universal, selective, and indicated prevention strategies.
References
Achenbach, T. M., & Rescorla, L. A. (2001). Manual for the ASEBA school-age forms & profiles. Burlington, VT: University of Vermont, Research Center for Children, Youth, & Families.
Adler, N. E., & Rehkopf, D. H. (2008). U.S. disparities in health: descriptions, causes, and mechanisms. Annual Review of Public Health, 29, 235–252. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.publhealth.29.020907.090852.
Agnafors, S., Bladh, M., Svedin, C. G., & Sydsjo, G. (2019). Mental health in young mothers, single mothers and their children. BMC Psychiatry, 19, 112.
Aldao, A., Nolen-Hoeksema, S., & Schweizer, S. (2010). Emotion-regulation strategies across psychopathology: a meta-analytic review. Clinical Psychology Review, 30, 217–237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cpr.2009.11.004.
American Psychiatric Association (2013). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. 5th ed. Arlington, VA: Author.
Bergqvist, K., Yngwe, M. A., & Lundberg, O. (2013). Understanding the role of welfare state characteristics for health and inequalities: an analytical review. BMC Public Health, 13, 1234 https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2458-13-1234.
Berkout, O. V., Young, J. N., & Gross, A. M. (2011). Mean girls and bad boys: recent research on gender differences in conduct disorder. Aggression and Violent Behavior, 16, 503–511. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.avb.2011.06.001.
Borenstein, M. (2009). Introduction to meta-analysis. Chichester, England: John Wiley & Sons.
Borenstein, M., & Higgins, J. P. T. (2013). Meta-analysis and subgroups. Prevention Science, 14, 134–143. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11121-013-0377-7.
Bornstein, M. H., Hahn, C. S., & Suwalsky, J. T. D. (2013). Developmental pathways among adaptive functioning and externalizing and internalizing behavioral problems: cascades from childhood into adolescence. Applied Developmental Science, 17, 76–87. https://doi.org/10.1080/10888691.2013.774875.
Broidy, L., & Agnew, R. (1997). Gender and crime: a general strain theory perspective. Journal of Research in Crime and Delinquency, 34, 275–306.
Brooksgunn, J., & Furstenberg, F. F. (1986). The children of adolescent mothers: physical, academic, and psychological outcomes. Developmental Review, 6, 224–251. https://doi.org/10.1016/0273-2297(86)90013-4.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (2013). Mental health surveillance among children—United States, 2005—2011. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, 62, 1–35.
Chang, Z., Lichtenstein, P., D’Onofrio, B. M., Almqvist, C., Kuja-Halkola, R., & Sjolander, A., et al. (2014). Maternal age at childbirth and risk for ADHD in offspring: a population-based cohort study. International Journal of Epidemiology, 43, 1815–1824. https://doi.org/10.1093/ije/dyu204.
Child Trends Databank (2018). Teen pregnancy. Retrieved from https://www.childtrends.org/indicators/teen-pregnancy.
Chodorow, N. (1978). Mothering, object-relations, and the female oedipal configuration. Feminist Studies, 4, 137–158. https://doi.org/10.2307/3177630.
Chudal, R., Joelsson, P., Gyllenberg, D., Lehti, V., Leivonen, S., & Hinkka-Yli-Salomäki, S., et al. (2015). Parental age and the risk of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: a nationwide, population-based cohort study. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 54, 487–494.e481.
Cicchetti, D., & Rogosch, F. A. (1996). Equifinality and multifinality in developmental psychopathology. Development and Psychopathology, 8, 597–600.
Coghill, D., & Sonuga-Barke, E. J. S. (2012). Annual research review: categories versus dimensions in the classification and conceptualisation of child and adolescent mental disorders—implications of recent empirical study. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 53, 469–489. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-7610.2011.02511.x.
Cohen, J. (1988). Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences. 2nd ed. Hillsdale, NJ: Routledge.
Coleman-Minahan, K. (2017). The socio-political context of migration and reproductive health disparities: the case of early sexual initiation among Mexican-origin immigrant young women. Social Science & Medicine, 180, 85–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.socscimed.2017.03.011.
Coley, R. L., & Chase-Lansdale, P. L. (1998). Adolescent pregnancy and parenthood. American Psychologist, 53, 152–166.
Corcoran, J. (1998). Consequences of adolescent pregnancy/parenting: a review of the literature. Social Work in Health Care, 27, 49–67. https://doi.org/10.1300/J010v27n02_03.
Coyne, C. A., & D’Onofrio, B. M. In: J. B. Benson (Ed.) (2012). Some (but not much) progress toward understanding teenage childbearing: a review of research from the past decade. Advances in child development and behavior. (Vol. 42. 113–152). Waltham, MA: Academic Academic Press.
Coyne, C. A., Långström, N., Rickert, M. E., Lichtenstein, P., & D’Onofrio, B. M. (2013). Maternal age at first birth and offspring criminality: using the children of twins design to test causal hypotheses. Development and Psychopathology, 25, 17–35. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0954579412000879.
Danielson, M. L., Bitsko, R. H., Ghandour, R. M., Holbrook, J. R., Kogan, M. D., & Blumberg, S. J. (2018). Prevalence of parent-reported ADHD diagnosis and associated treatment among U.S. children and adolescents, 2016. Journal of Clinical Child & Adolescent Psychology, 47, 199–212. https://doi.org/10.1080/15374416.2017.1417860.
Duffee, J. H., Mendelsohn, A. L., Kuo, A. A., Legano, L. A., & Earls, M. F. (2017). Early childhood home visiting. Pediatrics, 140, e20172150 https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2017-2150.
Effective Public Health Practice Project (1998). Quality Assessment Tool for Quantitative Studies. Retrieved from https://merst.ca/ephpp/.
Egger, M., Davey Smith, G., Schneider, M., & Minder, C. (1997). Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ, 315, 629–634. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.315.7109.629.
Esping-Anderson, G. (1990). The three worlds of welfare capitalism. London, England: Polity.
Fontaine, N., Carbonneau, R., Vitaro, F., Barker, E. D., & Tremblay, R. E. (2009). Research review: a critical review of studies on the developmental trajectories of antisocial behavior in females. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 50, 363–385. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-7610.2008.01949.x.
Galera, C., Cote, S. M., Bouvard, M. P., Pingault, J. B., Melchior, M., & Michel, G., et al. (2011). Early risk factors for hyperactivity-impulsivity and inattention trajectories from age 17 months to 8 years. Archives of General Psychiatry, 68, 1267–1275.
Gibbs, C. M., Wendt, A., Peters, S., & Hogue, C. J. (2012). The impact of early age at first childbirth on maternal and infant health. Paediatric and Perinatal Epidemiology, 26, 259–284. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3016.2012.01290.x.
Guevremont, A., & Kohen, D. (2012). The physical and mental health of Inuit children of teenage mothers. Health Reports, 23, 15–22.
Guèvremont, A., & Kohen, D. (2013a). The physical and mental health of off-reserve first nations children of teen mothers. International Indigenous Policy Journal, 4, 1–25.
Guèvremont, A., & Kohen, D. (2013b). Do factors other than SES explain differences in child outcomes between children of teenage and older mothers for off-reserve first nations children? International Indigenous Policy Journal, 4, 6.
Habersaat, S., Boonmann, C., Schmeck, K., Stephan, P., Francescotti, E., & Fegert, J. M., et al. (2018). Differences and similarities in predictors of externalizing behavior problems between boys and girls: a 1-year follow-up study. Criminal Justice and Behavior, 45, 1852–1870. https://doi.org/10.1177/0093854818800364.
Hanisch, C., Freund-Braier, I., Hautmann, C., Janen, N., Pluck, J., & Brix, G., et al. (2010). Detecting effects of the Indicated Prevention Programme for Externalizing Problem Behaviour (PEP) on child symptoms, parenting, and parental quality of life in a randomized controlled trial. Behavioural and Cognitive Psychotherapy, 38, 95–112. https://doi.org/10.1017/s1352465809990440.
Hao, L., & Matsueda, R. L. (2006). Family dynamics through childhood: a sibling model of behavior problems. Social Science Research, 35, 500–524. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssresearch.2004.10.003.
Harachi, T. W., Fleming, C. B., White, H. R., Ensminger, M. E., Abbott, R. D., & Catalano, R. F., et al. (2006). Aggressive behavior among girls and boys during middle childhood: predictors and sequelae of trajectory group membership. Aggressive Behavior, 32, 279–293.
Harden, K. P., Lynch, S. K., Turkheimer, E., Emery, R. E., D’Onofrio, B. M., & Slutske, W. S., et al. (2007). A behavior genetic investigation of adolescent motherhood and offspring mental health problems. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 116, 667–683. https://doi.org/10.1037/0021-843x.116.4.667.
Headrick, T. C. (2009). Statistical simulation: power method polynomials and other transformations. Boca Raton, FL: Chapman and Hall/CRC.
Higgins, J. P., & Thompson, S. G. (2002). Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Statistics in Medicine, 21, 1539–1558. https://doi.org/10.1002/sim.1186.
Hinshaw, S. P. (1987). On the distinction between attentional deficits hyperactivity and conduct problems aggression in child psychopathology. Psychological Bulletin, 101, 443–463. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-2909.101.3.443.
Hofferth, S. (1987). The children of teen childbearers. In S. L. Hofferth & C. D. Hayes (Eds.), Risking the future: adolescent sexuality, pregnancy, and childbearing, volume II: Working papers and statistical appendices. Washington, DC: National Research Council, Panel on Adolescent Pregnancy and Childbearing.
Hofferth, S. L., & Reid, L. (2002). Early childbearing and children’s achievement and behavior over time. Perspectives on Sexual and Reproductive Health, 34, 41–49.
IntHout, J., Ioannidis, J. P., & Borm, G. F. (2014). The Hartung-Knapp-Sidik-Jonkman method for random effects meta-analysis is straightforward and considerably outperforms the standard DerSimonian-Laird method. BMC Medical Research Methodology, 14, 25 https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2288-14-25.
Kitzman, H. J., Olds, D. L., Cole, R. E., Hanks, C. A., Anson, E. A., & Arcoleo, K. J., et al. (2010). Enduring effects of prenatal and infancy home visiting by nurses on children follow-up of a randomized trial among children at age 12 years. Archives of Pediatrics & Adolescent Medicine, 164, 412–418. https://doi.org/10.1001/archpediatrics.2010.76.
Knapp, G., & Hartung, J. (2003). Improved tests for a random effects meta-regression with a single covariate. Statistics in Medicine, 22, 2693–2710. https://doi.org/10.1002/sim.1482.
Lachance, C. R., Burrus, B. B., & Scott, A. R. (2012). Building an evidence base to inform interventions for pregnant and parenting adolescents: a call for rigorous evaluation. American Journal of Public Health, 102, 1826–1832. https://doi.org/10.2105/ajph.2012.300871.
Lansford, J. E., Godwin, J., Bornstein, M. H., Chang, L., Deater-Deckard, K., & Di Giunta, L., et al. (2018). Parenting, culture, and the development of externalizing behaviors from age 7 to 14 in nine countries. Development and Psychopathology, 30, 1937–1958. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0954579418000925.
Lewis, S., & Clarke, M. (2001). Forest plots: trying to see the wood and the trees. BMJ, 322, 1479–1480. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.322.7300.1479.
Liberati, A., Altman, D. G., Tetzlaff, J., Mulrow, C., Gotzsche, P. C., & Ioannidis, J. P. A., et al. (2009). The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: explanation and elaboration. PLOS Medicine, 6, e1000100 https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1000100.
Lipsey, M. W., & Wilson, D. B. (2001). Practical meta-analysis. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Liu, J. (2004). Childhood externalizing behavior: theory and implications. Journal of Child and Adolescent Psychiatric Nursing, 17, 93–103. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1744-6171.2004.tb00003.x.
Loth, A., Drabick, D., Leibenluft, E., & Hulvershorn, L. (2014). Do childhood externalizing disorders predict adult depression? A meta-analysis. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 42, 1103–1113. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10802-014-9867-8.
Manlove, J., Steward-Streng, N., Peterson, K., Scott, M., & Wildsmith, E. (2013). Racial and ethnic differences in the transition to a teenage birth in the United States. Perspectives on Sexual and Reproductive Health, 45, 89–100. https://doi.org/10.1363/4508913.
Martin, J. A., Hamilton, B. E., Osterman, M. J. K., Driscoll, A. K., & Drake, P. (2018). Births: final data for 2017. National Vital Statistics Reports, 67, 1–50.
McGrath, J. J., Petersen, L., Agerbo, E., Mors, O., Mortensen, P. B., & Pedersen, C. B. (2014). A comprehensive assessment of parental age and psychiatric disorders. JAMA Psychiatry, 71, 301–309. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2013.4081.
Miner, J. L., & Clarke-Stewart, K. A. (2008). Trajectories of externalizing behavior from age 2 to age 9: relations with gender, temperament, ethnicity, parenting, and rater. Developmental Psychology, 44, 771–786. https://doi.org/10.1037/0012-1649.44.3.771.
Mingebach, T., Kamp-Becker, I., Christiansen, H., & Weber, L. (2018). Meta-meta-analysis on the effectiveness of parent-based interventions for the treatment of child externalizing behavior problems. PLoS ONE, 13(9), e0202855 https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0202855.
Moffitt, T. E. (1993). Adolescence-limited and life-course-persistent antisocial behavior: a developmental taxonomy. Psychological Review, 100, 674–701. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-295x.100.4.674.
Moffitt, T. E., the E-Risk Study Team. (2002). Teen-aged mothers in contemporary Britain. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry and Allied Disciplines, 43, 727–742. https://doi.org/10.1111/1469-7610.00082.
Moore, K., Morrison, D., & Green, A. (1997). The effects on the children born to adolescent mothers. In R. Maynard (Ed.), Kids having kids (pp. 145–180). Washington, DC: Urban Institute Press.
Mosher, W. D., Jones, J., & Abma, J. C. (2012). Intended and unintended births in the United States: 1982–2010. National Health Statistics Reports, 55, 1–28.
Mullin, B. C., & Hinshaw, S. P.(2007). Emotion regulation and externalizing disorders in children and adolescents. In J. J. Gross (Ed.), Handbook of emotion regulation ( pp. 523–541). New York, NY: Guilford Press.
Nagin, D. S., & Tremblay, R. E. (2001). Parental and early childhood predictors of persistent physical aggression in boys from kindergarten to high school. Archives of General Psychiatry, 58, 389–394.
Paranjothy, S., Broughton, H., Adappa, R., & Fone, D. (2009). Teenage pregnancy: who suffers? Archives of Disease in Childhood, 94, 239–245. https://doi.org/10.1136/adc.2007.115915.
Passel, J. S., Cohn, D., & Lopez, M. H. (2011). Census 2010: 50 million Latinos Hispanics account for more than half of the nation’s growth in past decade. Washington, DC: Pew Research Center.
Pihlakoski, L., Sourander, A., Aromaa, M., Rautava, P., Helenius, H., & Sillanpaa, M. (2006). The continuity of psychopathology from early childhood to preadolescence: a prospective cohort study of 3-12-year-old children. European Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 15, 409–417. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00787-006-0548-1.
Pohlabeln, H., Rach, S., De Henauw, S., Eiben, G., Gwozdz, W., & Hadjigeorgiou, C., et al. (2017). Further evidence for the role of pregnancy-induced hypertension and other early life influences in the development of ADHD: results from the IDEFICS study. European Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 26, 957–967. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00787-017-0966-2.
Reef, J., Diamantopoulou, S., van Meurs, I., Verhulst, F. C., & van der Ende, J. (2011). Developmental trajectories of child to adolescent externalizing behavior and adult DSM-IV disorder: results of a 24-year longitudinal study. Social Psychiatry and Psychiatric Epidemiology, 46, 1233–1241. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00127-010-0297-9.
Romero, L., Pazol, K., Warner, L., Cox, S., Kroelinger, C., & Besera, G., et al. (2016). Reduced disparities in birth rates among teens aged 15–19 years—United States, 2006–2007 and 2013–2014. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, 65, 409–414.
Rosenberg, M. S. (2005). The file-drawer problem revisited: a general weighted method for calculating fail-safe numbers in meta-analysis. Evolution, 59, 464–468.
Ruedinger, E., & Cox, J. E. (2012). Adolescent childbearing: consequences and interventions. Current Opinion in Pediatrics, 24, 446–452. https://doi.org/10.1097/MOP.0b013e3283557b89.
Rutter, M. (2004). Intergenerational continuities and discontinuities in psychological problems. In P. L. Chase-Lansdale., K. Kiernan. & R. J. Friedman (Eds), Human development across lives and generations: the potential for change ( pp. 239–277). New York, NY: Cambridge University Press.
Sagiv, S. K., Epstein, J. N., Bellinger, D. C., & Korrick, S. A. (2013). Pre- and postnatal risk factors for ADHD in a nonclinical pediatric population. Journal of Attention Disorders, 17, 47–57.
Schneider, H., & Eisenberg, D. (2006). Who receives a diagnosis of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in the United States elementary school population? Pediatrics, 117, E601–E609. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2005-1308.
Schwarzer, G., Carpenter, J. R., Rücker, G., Gentleman, R., Hornik, K., & Parmigiani, G. (2015). Meta-analysis with R. Cham, Switzerland: Springer.
Sedgwick, P. (2013). Meta-analyses: How to read a funnel plot. BMJ, 346, f1342 https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.f1342.
Shadish, W. R., Hedges, L. V., & Pustejovsky, J. E. (2014). Analysis and meta-analysis of single-case designs with a standardized mean difference statistic: a primer and applications. Journal of School Psychology, 52, 123–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsp.2013.11.005.
Shaw, M., Lawlor, D. A., & Najman, J. M. (2006). Teenage children of teenage mothers: psychological, behavioural and health outcomes from an Australian prospective longitudinal study. Social Science & Medicine, 62, 2526–2539. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.socscimed.2005.10.007.
Silva, D., Colvin, L., Hagemann, E., & Bower, C. (2014). Environmental risk factors by gender associated with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Pediatrics, 133, e14–e22.
SmithBattle, L. I. (2013). Reducing the stigmatization of teen mothers. MCN: American Journal of Maternal/Child Nursing, 38, 235–241. https://doi.org/10.1097/NMC.0b013e3182836bd4.
Tan, X. M., Shiyko, M. P., Li, R. Z., Li, Y. L., & Dierker, L. (2012). A time-varying effect model for intensive longitudinal data. Psychological Methods, 17, 61–77. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0025814.
Tearne, J. E. (2015). Older maternal age and child behavioral and cognitive outcomes: a review of the literature. Fertility and Sterility, 103, 1381–1391. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fertnstert.2015.04.027.
Terry-Humen, E., Manlove, J., & Moore, K. (2005). Playing catch-up: how children born to teen mothers fare. Washington, DC: National Campaign to Prevent Teen Pregnancy.
Thomas, R., Sanders, S., Doust, J., Beller, E., & Glasziou, P. (2015). Prevalence of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Pediatrics, 135, e994–e1001. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2014-3482.
Tremblay, R. E., Nagin, D. S., Seguin, J. R., Zoccolillo, M., Zelazo, P. D., & Boivin, M., et al. (2004). Physical aggression during early childhood: trajectories and predictors. Pediatrics, 114, E43–E50. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.114.1.e43.
U.S. Census Bureau. (2014). Hispanic Heritage Month 2014: Sept. 15–Oct. 15. Retrieved from https://www.census.gov/newsroom/facts-for-features/2014/cb14-ff22.html.
U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. (2018). Trends in teen pregnancy and childbearing. Retrieved from https://www.hhs.gov/ash/oah/adolescent-development/reproductive-health-and-teen-pregnancy/teen-pregnancy-and-childbearing/trends/index.html.
Viechtbauer, W., & Cheung, M. W. (2010). Outlier and influence diagnostics for meta-analysis. Research Synthesis Methods, 1, 112–125. https://doi.org/10.1002/jrsm.11.
Wakschlag, L. S., Estabrook, R., Petitclerc, A., Henry, D., Burns, J. L., & Perlman, S. B., et al. (2015). Clinical implications of a dimensional approach: the normal:abnormal spectrum of early irritability. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 54, 626–634. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaac.2015.05.016.
Williams, D. R., Mohammed, S. A., Leavell, J., & Collins, C. (2010). Race, socioeconomic status, and health: Complexities, ongoing challenges, and research opportunities. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1186, 69–101.
World Bank. (2017). Adolescent fertility rate (births per 1,000 women ages 15-19). Retrieved from https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/SP.ADO.TFRT?end=2017&name_desc=false&start=1999.
World Health Organization. (2015). Maternal, newborn, child and adolescent health: adolescent pregnancy. Retrieved from https://www.who.int/maternal_child_adolescent/topics/maternal/adolescent_pregnancy/en/.
Young, M. E. D., Deardorff, J., Ozer, E., & Lahiff, M. (2011). Sexual abuse in childhood and adolescence and the risk of early pregnancy among women ages 18-22. Journal of Adolescent Health, 49, 287–293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jadohealth.2010.12.019.
Zimmerman, M. A., Tuttle, L., Kieffer, E., Parker, E., Caldwell, C. H., & Maton, K. I. (2001). Psychosocial outcomes of urban African American adolescents born to teenage mothers. American Journal of Community Psychology, 29, 779–805.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JOL originated the study and guided data analyses, the evaluation of the quality of studies, and the writing of the article; CHJ extracted key information from each study while updating the literature search and conducted the main and sensitivity analyses; CY conducted the initial literature search and information extraction from each study and conducted the preliminary analyses; JMB contributed to the analysis framework, troubleshooting of analysis, and interpretation of the study findings; AJU contributed to the interpretation of the study findings and contextualized findings in different racial and ethnic groups, particularly young Latina mothers and their children; MN organized the database and ensured the accuracy of information from each study in the database used in the present study; JAC contributed to the conceptualization of the study and the interpretation of findings and evaluated the quality of studies. In addition, all authors have been involved in drafting and critically revising the manuscript for important intellectual content. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by grant R03HD097379 from National Institute of Child Health and Human Development. The content of this paper is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the funding agency. The funding agency played no role in the study design; in the collection, analysis, and interpretation of data; in the writing of the report; or in the decision to submit this article for publication.
Data Sharing Declaration
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article (and its supplementary information files).
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
The current manuscript used published studies as the sole data source and did not involve any other data collection or direct interactions with human participants. As such, seeking approval from a human subjects review committee is irrelevant.
Informed Consent
As with ethical approval, securing informed consent forms is irrelevant. The study didn’t involve any data collection or direct interactions with participants.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, J.O., Jeong, C.H., Yuan, C. et al. Externalizing Behavior Problems in Offspring of Teen Mothers: A Meta-Analysis. J Youth Adolescence 49, 1146–1161 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10964-020-01232-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10964-020-01232-y