Abstract
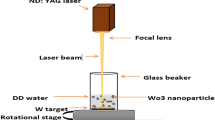
Tungsten oxide nanoparticles (WO3) were successfully produced using the Pulsed Laser Ablation method in organic solvent (2-methoxyethanol) for the first time. The ablation process was carried out using a Q-switched Nd:YAG laser of 1064 nm wavelength with different numbers of pulses 100, 200, 300, and 400 to irradiate the target. The resulting tungsten oxide nanoparticles were characterized using various techniques such as infrared spectroscopy to determine the effective groups and bonding pattern, as well as studying the morphology of those nanoparticles through an atomic force microscope. The study included also to study the optical properties, calculate the optical constants, and finally study the electrical properties of nanoparticles suspended in organic solution. The study showed that the effect of the number of pulses resulted in a difference in the size of the nanoparticles, which in turn showed a clear effect on the optical and electrical properties of tungsten oxide. A new model to understand the electrical conductivity results at different grain sizes was applied in this study.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
W.H. Eisa, M.F. Zayed, B. Anis, L.M. Abbas, S.S. Ali, A.M. Mostafa, Clean production of powdery silver nanoparticles using Zingiber officinale: the structural and catalytic properties. J. Clean. Prod. 241, 118398 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.118398
M.S. Hasanin, A.M. Mostafa, E.A. Mwafy, O.M. Darwesh, Eco-friendly cellulose nano fibers via first reported Egyptian Humicola fuscoatra Egyptia X4: isolation and characterization, environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manage. 10, 409–418 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enmm.2018.10.004
M.H. Mahdieh, B. Fattahi, Effects of water depth and laser pulse numbers on size properties of colloidal nanoparticles prepared by nanosecond pulsed laser ablation in liquid. Opt. Laser Technol. 75, 188–196 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlastec.2015.07.006
M.R. Parra, F.Z. Haque, Aqueous chemical route synthesis and the effect of calcination temperature on the structural and optical properties of ZnO nanoparticles. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 3, 363–369 (2014)
K.L. McGilvray, M.R. Decan, D. Wang, J.C. Scaiano, Facile photochemical synthesis of unprotected aqueous gold nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 128, 15980–15981 (2006)
M. Sakamoto, M. Fujistuka, T. Majima, Light as a construction tool of metal nanoparticles: Synthesis and mechanism. J. Photochem. Photobiol. C 10, 33–56 (2009)
D.-H. Chen, X.-R. He, Synthesis of nickel ferrite nanoparticles by sol–gel method. Mater. Res. Bull. 36, 1369–1377 (2001)
J. Xu, H. Yang, W. Fu, K. Du, Y. Sui, J. Chen, Y. Zeng, M. Li, G. Zou, Preparation and magnetic properties of magnetite nanoparticles by sol–gel method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 309, 307–311 (2007)
M. Aziz, S.S. Abbas, W.R.W. Baharom, Size-controlled synthesis of SnO2 nanoparticles by sol–gel method. Mater. Lett. 91, 31–34 (2013)
H. Zeng, X. Du, S.C. Singh, S.A. Kulinich, S. Yang, J. He, W. Cai, Nanomaterials via laser ablation/irradiation in liquid: a review. Adv. Funct. Mater. 22, 1333–1353 (2012)
S. Petersen, J. Jakobi, A. Hörtinger, S. Barcikowski, In-situ conjugation–tailored nanoparticle-conjugates by laser ablation in liquids. J. Laser Micro/Nanoeng. 4, 71–74 (2009)
F. Stokker-Cheregi, T. Acsente, I. Enculescu, C. Grisolia, G. Dinescu, Tungsten and aluminum nanoparticles synthesized by laser ablation in liquids. Dig. J. Nanomater. Biostruct. 7, 1569–1576 (2012)
D. Riabinina, M. Chaker, J. Margot, Dependence of gold nanoparticle production on pulse duration by laser ablation in liquid media. Nanotechnology 23, 135603–135607 (2012)
J.S. Jeon, C.S. Yeh, Studies of silver nanoparticles by laser ablation method. J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 45, 721–726 (1998)
M.S. Majeed, S.M. Hassan, S.A. Fadhil, AgO nanoparticles synthesis by different Nd:YAG laser pulse energies. Lasers Manuf. Mater. Process. 9, 228–240 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40516-022-00174-6
A.M. Mostafa, Preparation and study of nonlinear response of embedding ZnO nanoparticles in PVA thin film by pulsed laser ablation. J. Mol. Struct. 1223, 129007 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2020.129007
K.S. Khashan, G.M. Sulaiman, A.H. Hamad, F.A. Abdulameer, A. Hadi, Generation of NiO nanoparticles via pulsed laser ablation in deionised water and their antibacterial activity. Appl. Phys. A 123, 190 (2017)
B.J. Alwan, L.G. Subhi, A.N. Abd, Preparation of colloidal silver oxide nanoparticles by pulsed laser ablation in methanol. IOP Conf. Ser.: Mater. Sci. Eng. 454, 012101 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/454/1/012101
K.S. Khashan, G.M. Sulaiman, F.A. Abdulameer, Synthesis and antibacterial activity of CuO nanoparticles suspension induced by laser ablation in liquid. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 41, 301–310 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-015-1733-7
F. Barreca, N. Acacia, S. Spadaro, G. Currò, F. Neri, Tungsten trioxide (WO3−x) nanoparticles prepared by pulsed laser ablation in water. Mater. Chem. Phys. 127, 197–202 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2011.01.059
Y. Wang, X. Wang, Y. Xu, T. Chen, M. Liu, F. Niu, S. Wei, J. Liu, Simultaneous synthesis of WO3−x quantum dots and bundle-like nanowires using a one-pot template-free solvothermal strategy and their versatile applications. Small 13, 1603689 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201603689
G. Mansoureh, V. Parisa, Synthesis of Metal Nanoparticles Using Laser Ablation Technique, Emerging Applications of Nanoparticles and Architecture Nanostructures (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2018), pp.575–596
S. Yamazaki, D. Shimizu, S. Tani, K. Honda, M. Sumimoto, K. Komaguchi, Effect of dispersants on photochromic behavior of tungsten oxide nanoparticles in methylcellulose. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 10, 19889–19896 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.8b04875
A. Ragunathan, R. Krishnan, B.A. Kamaludeen, Stability of tungsten oxide nanoparticles in different media. J. Chem. Res. 39, 622–626 (2015). https://doi.org/10.3184/174751915X14446446579178
N. Lavanya, A. Anithaa, C. Sekar, K. Asokan, A. Bonavita, N. Donato, S. Leonardi, G. Neri, Effect of gamma irradiation on structural, electrical and gas sensing properties of tungsten oxide nanoparticles. J. Alloys Compd. 693, 366–372 (2017)
M. Kim, B.Y. Lee, H.C. Ham, J. Han, S.W. Nam, H.S. Lee, J.H. Park, S. Choi, Y. Shin, Facile one-pot synthesis of tungsten oxide (WO3−x) nanoparticles using sub and supercritical fluids. J. Supercrit. Fluids 111, 8–13 (2016)
A. Ragunathan, R. Krishnan, B.A. Kamaludeen, Stability of tungsten oxide nanoparticles in different media. J. Chem. Res. 39, 622–626 (2015)
B.A. Wasmi, A.A. Al-Amiery, A.A.H. Kadhum, A.B. Mohamad, Novel approach: tungsten oxide nanoparticle as a catalyst for malonic acid ester synthesis via ozonolysis. J. Nanomater. 2014, 1–7 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/715457
D. Fukushi, A. Sasaki, H. Hirabayashi, M. Kitano, Effect of oxygen vacancy in tungsten oxide on the photocatalytic activity for decomposition of organic materials in the gas phase. Microelectron. Reliab. 79, 1–4 (2017)
Y. Zhan, Y. Liu, Q. Liu, Z. Liu, H. Yang, B. Lei, J. Zhuang, C. Hu, Size-controlled synthesis of fluorescent tungsten oxide quantum dots via one-pot ethanol-thermal strategy for ferric ions detection and bioimaging. Sens. Actuators B 255, 290–298 (2018)
Z. Zhao, Y. Bai, W. Ning, J. Fan, J. Gu, H. Chang, S. Yin, Effect of surfactants on the performance of 3D morphology W18O49 by solvothermal synthesis. Appl. Surf. Sci. 471, 537–544 (2019)
Z. Famili, D. Dorranian, A.H. Sari, Laser ablation-assisted synthesis of tungsten sub-oxide (W17O47) nanoparticles in water: effect of laser fluence. Opt. Quant. Electron. 52, 305 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-020-02425-2
E.A. Mwafy, A.M. Mostafa, N.S. Awwad, H.A. Ibrahium, Catalytic activity of multi-walled carbon nanotubes decorated with tungsten trioxides nanoparticles against 4-nitrophenol. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 158, 110252 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2021.110252
V.A. Svetlichnyi, A.V. Shabalina, I.N. Lapin, D.A. Goncharova, Metal Oxide Nanoparticle Preparation by Pulsed Laser Ablation of Metallic Targets in Liquid (IntechOpen, Rijeka, 2016). https://www.intechopen.com/chapters/52559
J. Theerthagiri, K. Karuppasamy, S.J. Lee et al., Fundamentals and comprehensive insights on pulsed laser synthesis of advanced materials for diverse photo- and electrocatalytic applications. Light Sci Appl 11, 250 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41377-022-00904-7
M.J. Rivera-Chaverra, E. Restrepo-Parra, C.D. Acosta-Medina, A. Mello, R. Ospina, Synthesis of oxide iron nanoparticles using laser ablation for possible hyperthermia applications. Nanomaterials (Basel, Switzerland) 10, 2099 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10112099
A.H. Badran, A. Al-Maliki, R.K.F. Alfahed, B.A. Saeed, A.Y. Al-hmad, F.A. Al-Saymari, R.S. Elias, Synthesis, surface profile, nonlinear reflective index and photophysical properties of curcumin compound. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 29, 10890–10903 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-9167-0
R.K. Fakher Alfahed, A.S. Al-Asadi, M.F. Al-Mudhaffer, H.A. Badran, Synthesis, morphological and optical characterizations of the poly (O-toluidine)-LiCl networks thin film. Opt. Laser Technol. 133, 106524 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlastec.2020.106524
G. Guohua, Z. Zenghai, W. Guangming, J. Xiaobo, Engineering of coloration responses of porous WO3 gasochromic films by ultraviolet irradiation. RSC Adv. 4, 30300–30307 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1039/C4RA03181D
Y. Suzuko, S. Dai, T. Seiji, H. Kensuke, S. Michinori, K. Kenji, Effect of dispersants on photochromic behavior of tungsten oxide nanoparticles in methylcellulose. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 10, 19889–19896 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.8b04875
Z. Zhao, Y. Bai, W. Ning, J. Fan, Z. Gu, H. Chang, S. Yin, Effect of surfactants on the performance of 3D morphology W18O49 by solvothermal synthesis. Appl. Surf. Sci. 471, 537–544 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.12.041
F.A. Mohamed, E.T. Salim, A.I. Hassan, Monoclinic tungsten trioxide (WO3) thin films using spraying pyrolysis: electrical, structural and stoichiometric ratio at different molarity. Dig. J. Nanomater. Biostruct. 17, 1029–1043 (2022)
Z. Fang, S. Jiao, B. Wang, W. Yin, S. Liu, R. Gao, Z. Liu, G. Pang, S. Feng, Synthesis of reduced cubic phase WO3−x nanosheet by direct reduction of H2WO4·H2O. Mater. Today Energy 6, 146–153 (2017)
M.B. Johansson, G.A. Niklasson, L. Österlund, Structural and optical properties of visible active photocatalytic WO3 thin films prepared by reactive dc magnetron sputtering. J. Mater. Res. 27, 3130–3140 (2012)
S.S. Kalanur, H. Yoo, I.S. Cho, H. Seo, Effect of oxygen vacancies on the band edge properties of WO3 producing enhanced photocurrents. Electrochim. Acta 296, 517–527 (2019)
A.M. Mostafa, S.A. Yousef, W.H. Eisa, M.A. Ewaida, E.A. Al-Ashkar, WO3 quantum dot: synthesis, characterization and catalytic activity. J. Mol. Struct. 1185, 351–356 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2019.03.007
R. Mahfouz, F.J. Cadete Santos Aires, A. Brenier, B. Jacquier, J.C. Bertolini, Synthesis and physic-chemical characteristics of nanosized particles produced by laser ablation of a nickel target in water. Appl. Surf. Sci. 254, 5181–5190 (2008)
F. Mafune, J. Kohno, Y. Takeda, T. Kondow, Formation and size control of silver nanoparticles by laser ablation in aqueous solution. J. Phys. Chem. B 104, 9111–9117 (2000)
H.S. Desarkar, P. Kumbhakar, A.K. Mitra, Effect of ablation time and laser fluence on the optical properties of copper nano colloids prepared by laser ablation technique. Appl. Nanosci. 2, 285–291 (2012)
A. Takami, H. Kurita, S. Koda, Laser-induced size reduction of noble metal particles. J. Phys. Chem. B 103, 1226–1232 (1999)
M. Fakhari, M.J. Torkamany, S.N. Mirnia, Linear and nonlinear optical properties of WO3 nanoparticles synthesized at different fluences of pulsed Nd: YAG laser. Eur. Phys. J. Appl. Phys. 84, 30401 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1051/epjap/2018180264
N. Mirghassemzadeh, M. Ghamkhari, D. Dorranian, Dependence of laser ablation produced gold nanoparticles characteristics on the fluence of laser pulse. Soft Nanosci. Lett. 3, 101–106 (2013)
T. He, J. Yao, Photochromic materials based on tungsten oxide. J. Mater. Chem. 17, 4547–4557 (2007)
M. Rashidian, D. Dorranian, Effect of concentration on the plasmonic absorption and optical nonlinearity of gold nanoparticles. Opt. Eng. 51, 089001 (2012)
S.Z. Karazhanov, Y. Zhang, A. Mascarenhas, S. Deb, L.W. Wang, Oxygen vacancy in cubic WO3 studied by first-principles pseudopotential calculation. Solid State Ion. 165, 43–49 (2003)
S. Mandal, Y. Hou, M. Wang, T.D. Anthopoulos, K.L. Choy, Surface modification of hetero-phase nanoparticles for low-cost solution-processable high-k dielectric polymer nanocomposites. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 15, 7371–7379 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.2c19559
D. Zhang, Z. Li, K. Sugioka, Laser ablation in liquids for nanomaterial synthesis: diversities of targets and liquids. J. Phys. Photonics 3, 042002 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1088/2515-7647/ac0bfd
M.S. Majeed, T.K. Hamad, E.T. Hashim, ZnO nanoparticle synthesis using ND:YAG laser for increasing hydrogen fuel cell performance. Int. J. Mech. Prod. Eng. Res. Dev. 8, 497–506 (2018)
E. Yuliza, R. Murniati, A. Rajak, M.A. Khairurrijal, Effect of particle size on the electrical conductivity of metallic particles, advances in social science, education and humanities research, in Proeedings of the 2014 International Conference on Advances in Education Technology. (2015), pp.151–154
D. Mi, Z. Zhao, H. Bai, Effects of orientation and dispersion on electrical conductivity and mechanical properties of carbon nanotube/polypropylene composite. Polymers 15, 2370 (2023)
S.A. Fadhil, J.H. Azeez, M.A. Hassan, Derivation of a new multiscale model: I. Derivation of the model for the atomic, molecular and nano material scalesIndian. J. Phys. 95, 209–217 (2021)
S.A. Fadhil, M.A. Hassan, J.H. Azeez, M.S. Majeed, Derivation of a new multiscale model: II. Deriving a modified Hall-Petch relation from the multiscale model and testing it for nano, micro, and macro materials. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 881, 012098 (2020)
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Ali Abed Bayoud participated in conducting most of the experiments and analyzing the data. R.K. Fakher Al-Fahd interpreted the results and wrote the research. Faten Sh. Zainulabdeen participated in developing the action plan to complete the study as well as reading and revising the writing. All authors reviewed the results and approved the final case study presented here.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bayyoodh, A.A., Alfahed, R.K.F. & Zainulabdeen, F.S. The effect of nanoparticle size on the structural, optical, and electrical properties of tungsten oxide prepared by laser ablation method. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 35, 1098 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-024-12821-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-024-12821-z