Abstract
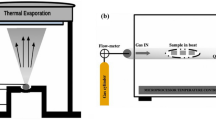
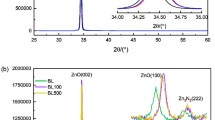
This investigation focuses on the elaboration of undoped zinc oxide (ZnO) thin films and ZnO thin films doped with 6% of nickel (Ni), cobalt (Co), and iron (Fe). The fabrication process employed the Successive Ionic Layer Adsorption and Reaction (SILAR) method, involving 30 SILAR cycles, and annealing at 400 °C in an oxygen-rich environment. Structural analysis via X-ray diffraction (XRD) revealed a hexagonal wurtzite structure characteristic of ZnO. No secondary phases associated with Ni, Fe, or Co were identified. The incorporation of dopants led to decreased crystallinity, indicated by a reduction in XRD peak intensities and a change in preferred orientation. Optical characterization unveiled a red shift in the transmittance spectra of doped ZnO thin films, signifying a reduction in the bandgap energy when compared to undoped ZnO. This reduction holds promise for augmenting photocatalytic performance and enhancing electrical conductivity in practical applications. Morphological investigations showed modifications in grain size and distribution within the doped samples, aligning with the structural observations. Energy-dispersive X-ray (EDX) analysis confirmed the successful integration of dopant atoms into the ZnO lattice. Electrical measurements confirmed that all doped ZnO samples exhibited n-type semiconductor behavior, characterized by lowered resistivity, increased mobility, and carrier concentration relative to undoped ZnO. These enhancements can be attributed to the introduction of additional electrons by the dopants. This comprehensive examination offers valuable insights into the structural, optical, and electrical characteristics of doped ZnO thin films, providing a promising route for their integration into optoelectronic and energy conversion devices.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets produced and examined during the present study can be obtained by reaching out to the corresponding author upon a reasonable request.
References
S. Arya, P. Mahajan, S. Mahajan, A. Khosla, R. Datt, V. Gupta, S.-J. Young, S.K. Oruganti, Influence of processing parameters to control morphology and optical properties of sol-gel synthesized ZnO nanoparticles. ECS J. Solid State Sci. Technol. 10, 023002 (2021)
S. Heinonen, J.-P. Nikkanen, E. Huttunen-Saarivirta, E. Levänen, Investigation of long-term chemical stability of structured ZnO films in aqueous solutions of varying conditions. Thin Solid Films 638, 410–419 (2017)
F. Pan, C. Song, X.J. Liu, Y.C. Yang, Zeng, Ferromagnetism and possible application in spintronics of transition-metal-doped ZnO films. Mater. Sci. Engineering: R: Rep. 62, 1–35 (2008)
X. Fang, Y. Bando, U.K. Gautam, T. Zhai, H. Zeng, X. Xu, M. Liao, D. Golberg, ZnO and ZnS nanostructures: ultraviolet-light emitters, lasers, and sensors. Crit. Rev. Solid State Mater. Sci. 34, 190–223 (2009)
P.K. Shrestha, X. Chang, M. Pryn, J. Li, G. Rughoobur, K. Li, K. Surowiecka, D. Chu, Large-size updatable optically addressed spatial light modulator (OASLM) based on ZnO nanoparticles for large-area holographic 3D displays. OSA Continuum OSAC 3, 1703–1710 (2020)
W. Han, S. Oh, C. Lee, J. Kim, H.-H. Park, ZnO nanocrystal thin films for quantum-dot light-emitting devices. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 3, 7535–7542 (2020)
O. Lahr, M.S. Bar, H. von Wenckstern, M. Grundmann, All-oxide transparent thin-film transistors based on amorphous zinc tin oxide fabricated at room temperature: approaching the thermodynamic limit of the subthreshold swing. Adv. Electron. Mater. 6, 2000423 (2020)
S. Maqsood, Z. Ali, K. Ali, M. Ishaq, M. Sajid, A. Farhan, A. Rahdar, S. Pandey, Assessment of different optimized anti-reflection coatings for ZnO/Si heterojunction solar cells Ceram. Int. 49, 37118–37126 (2003)
A.K.A. Darman, M.L. Ibrahim, H.A. Rafaie, M.S. Mastuli, M.F. Kasim, Photocatalytic activity of transition metals (Mn, Fe, Ag and Ni doped ZnO) nanomaterials synthesised via sol-gel method: active sites over band gap. IOP Conf. Ser. : Mater. Sci. Eng. 839, 012006 (2020)
J. Gupta, K.C. Barick, P.K. Sahoo, Magnetic and photoluminescence behavior of transitional metal ions-doped ZnO nanoparticles. Mater. Today: Proc. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2023.10.071
A. Paskaleva, K. Buchkov, A. Galluzzi, D. Spassov, B. Blagoev, T. Ivanov, V. Mehandzhiev, I.A. Avramova, P. Terzyiska, P. Tzvetkov, D. Kovacheva, M. Polichetti, Magneto-optical and muliferroic properties of transition-metal (Fe, Co, or Ni)-doped ZnO layers deposited by ALD. ACS Omega 7, 43306–43315 (2022)
K. Ueda, H. Tabata, T. Kawai, Magnetic and electric properties of transition-metal-doped ZnO films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 79, 988–990 (2001)
M.Y. Ali, M.K.R. Khan, A.M.M.T. Karim, M.M. Rahman, M. Kamruzzaman, Effect of Ni doping on structure, morphology and opto-transport properties of spray pyrolised ZnO nano-fibe. Heliyon 6, e03588 (2020)
I. Benaicha, J. Mhalla, A. Raidou, A. Qachaou, M. Fahoume, Effect of Ni doping on optical, structural, and morphological properties of ZnO thin films synthesized by MSILAR: experimental and DFT study. Materialia 15, 101015 (2021)
T.M. Bawazeer, M.S. Alsoufi, M. Shkir, B.M. Al-Shehri, M.S. Hamdy, Excellent improvement in photocatalytic nature of ZnO nanoparticles via Fe doping content. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 130, 108668 (2021)
N. Abirami, A.M.S. Arulanantham, K.S.J. Wilson, Structural and magnetic properties of cobalt doped ZnO thin films deposited by cost effective nebulizer spray pyrolysis technique. Mater. Res. Express. 7, 026405 (2020)
S. Kuriakose, B. Satpati, S. Mohapatra, Enhanced photocatalytic activity of Co doped ZnO nanodisks and nanorods prepared by a facile wet chemical method. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 16, 12741–12749 (2014)
M. Ayachi, F. Ayad, A. Djelloul, L. Benharrat, S. Anas, Synthesis and characterization of Ni-Doped ZnO Thin films prepared by Sol–Gel spin. Coat. Method Semicond. 55, 482–490 (2021)
A. Nebatti, C. Pflitsch, B. Atakan, Unusual application of aluminium-doped ZnO thin film developed by metalorganic chemical vapour deposition for surface temperature sensor. Thin Solid Films. 636, 532–536 (2017)
H. Koo, J.-A. Lee, Y.-W. Heo, J.-H. Lee, H.Y. Lee, J.-J. Kim, Effects of oxygen partial pressure on the structural and electrical properties of Al and Sb co-doped p-type ZnO thin films grown by pulsed laser deposition. Thin Solid Films. 708, 138130 (2020)
Z. Starowicz, A. Zięba, J. Ostapko, M. Wlazło, G. Kołodziej, M. Jakub Szczerba, G. Putynkowski, R. Piotr Socha, Synthesis and characterization of Al-doped ZnO and Al/F co-doped ZnO thin films prepared by atomic layer deposition. Mater. Sci. Eng.: B 292, 116405 (2023)
D. Spassov, A. Paskaleva, B. Blagoev, V. Mehandzhiev, Electric characterization of transition metal (Co, Ni, Fe) doped ZnO thin layers prepared by atomic layer deposition. J. Phys. : Conf. Ser. 2436, 012014 (2023)
R. Bairy, P. shankaragouda Patil, S.R. Maidur, H. Vijeth, M.S. Murari, U. Bhat, The role of cobalt doping in tuning the band gap, surface morphology and third-order optical nonlinearities of ZnO nanostructures for NLO device applications. RSC Adv. 9, 22302–22312 (2019)
E.R. Shaaban, M. El-Hagary, E.S. Moustafa, H.S. Hassan, Y.A.M. Ismail, M. Emam-Ismail, A.S. Ali, Structural, linear and nonlinear optical properties of co-doped ZnO thin films. Appl. Phys. A 122, 20 (2015)
S. Karamat, R.S. Rawat, P. Lee, T.L. Tan, R.V. Ramanujan, Structural, elemental, optical and magnetic study of Fe doped ZnO and impurity phase formation. Progress Nat. Science: Mater. Int. 24, 142–149 (2014)
O. Muktaridha, M. Adlim, S. Suhendrayatna, I. Ismail, Progress of 3d metal-doped zinc oxide nanoparticles and the photocatalytic properties. Arab. J. Chem. 14, 103175 (2021)
X. Cai, T. Hu, H. Hou, P. Zhu, R. Liu, J. Peng, W. Luo, H. Yu, A review for nickel oxide hole transport layer and its application in halide perovskite solar cells. Mater. Today Sustain. 23, 100438 (2023)
P.G. Ramos, J. Espinoza, L.A. Sánchez, J. Rodriguez, Enhanced photocatalytic degradation of rhodamine B employing transition metal (Fe, Cu, Co) doped ZnO/rGO nanostructures synthesized by electrospinning-hydrothermal technique. J. Alloys Compd. 966, 171559 (2023)
C. Abinaya, M. Marikkannan, M. Manikandan, J. Mayandi, P. Suresh, V. Shanmugaiah, C. Ekstrum, J.M. Pearce, Structural and optical characterization and efficacy of hydrothermal synthesized Cu and Ag doped zinc oxide nanoplate bactericides. Mater. Chem. Phys. 184, 172–182 (2016)
S. Das, S. Das, D. Das, S. Sutradhar, Tailoring of room temperature ferromagnetism and electrical properties in ZnO by Co (3d) and gd (4f) element co-doping. J. Alloys Compd. 691, 739–749 (2017)
I. Jellal, K. Nouneh, J. Jedryka, D. Chaumont, J. Naja, Non-linear optical study of hierarchical 3D Al doped ZnO nanosheet arrays deposited by successive ionic adsorption and reaction method. Opt. Laser Technol. 130, 106348 (2020)
M.Y. Zaki, K. Nouneh, M.E. Touhami, E. Matei, P. Badica, M. Burdusel, C.C. Negrila, M. Baibarac, L. Pintilie, A.C. Galca, Influence of boric acid concentration on the properties of electrodeposited CZTS absorber layers. Phys. Scr. 95, 054001 (2020)
M. Ayachi, F. Ayad, A. Djelloul, S. Sali, S. Anas, M. Guezzoul, L. Benharrat, L. Zougar, S. Kermadi, Investigation of structural, morphological, and optical properties of (Ni/Co, Fe/Co, and Fe/Ni) co-doped ZnO thin films prepared by sol-gel spin coating technique. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-024-06376-y
I. Benaicha, I. Jellal, J. Mhalla, A. Fahmi, M. Addou, A. Qachaou, M. Fahoume, Atmospheric growth of ZnO thin films doped and co-doped with Ni and Co via UMVD: experimental and theoretical study. J. Mater. Sci: Mater. Electron. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-07880-z
T.A. Abdel-Baset, M. Abdel-Hafiez, Effect of metal dopant on structural and magnetic properties of ZnO nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci: Mater. Electron. 32, 16153–16165 (2021)
S.H. Khan, B. Pathak, M.H. Fulekar, A study on the influence of metal (Fe, Bi, and Ag) doping on structural, optical, and antimicrobial activity of ZnO nanostructures. Adv. Compos. Hybrid. Mater. 3, 551–569 (2020)
B. Radha, R. Rathi, K.C. Lalithambika, A. Thayumanavan, K. Ravichandran, S. Sriram, Effect of Fe doping on the photocatalytic activity of ZnO nanoparticles: experimental and theoretical investigations. J. Mater. Sci: Mater. Electron. 29, 13474–13482 (2018)
A. Goktas, S. Modanlı, A. Tumbul, A. Kilic, Facile synthesis and characterization of ZnO, ZnO:Co, and ZnO/ZnO:Co nano rod-like homojunction thin films: role of crystallite/grain size and microstrain in photocatalytic performance. J. Alloys Compd. 893, 162334 (2022)
A.N. Orelusi, V.A. Owoeye, J.B. Dada, A.O. Salau, H.O. Boyo, S.A. Adewinbi, Investigation of microstructure and optical characteristics of Ti-doped ZnO thin films as an effective solar collector in photovoltaic solar cell applications using digitally controlled spray pyrolysis. J. Mater. Res. 38, 4192–4200 (2023)
B. Chander Joshi, A.K. Chaudhri, Sol–gel-derived Cu-doped ZnO thin films for optoelectronic applications. ACS Omega 7, 21877–21881 (2022)
Funding
The authors confirm that there was no external funding provided for the research presented in this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The authors of this scientific article contributed to the study as follows: Ismail Benaicha and Youness Ait-Alla: conceptualization, study design, and overall supervision. Jaouad Mhalla, Ridouane Bakkali, Othmane Daoudi, and Ilyass Jelall: Conducted a comprehensive literature review and provided critical insights during manuscript development. Khalid Nouneh: Contributed to the literature review and provided valuable feedback on the manuscript. Mounir Fahoume: Responsible for technical measurements and data analysis. Ahmed Qachaou: Provided supervision, guidance, and oversight throughout the entirety of the study.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Benaicha, I., Ait-Alla, Y., Mhalla, J. et al. SILAR-engineered ZnO thin films: exploring the impact of Ni, Co, and Fe dopants on structural, optical, and electronic properties. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 35, 919 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-024-12678-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-024-12678-2