Abstract
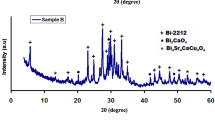
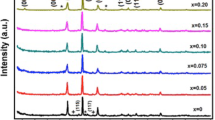
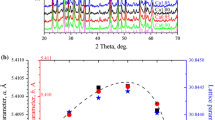
Bi-2212 is one of the most competitive high-temperature superconducting materials for the fabrication of high field magnet, but its superconducting transmission mechanism is not clear yet. To further investigate the effects of both weak connections and magnetic flux pinning on the current transition process, polycrystalline bulks of Bi2Sr2CaCuO8+δ (Bi-2212) with different chemical compositions and microstructures were prepared with the introduction of Pb doping and spark plasma sintering process. Both XRD and SEM indicated that nearly single phase Bi-2212 bulks with high (00l) texture could be achieved with spark plasma sintering. The texture degree of Bi-2212 bulks was positively correlated with Tcj and Tp, and negatively related to ΔT, indicating that the increase of texture degree could improve the intergranular connectivity. Besides, it was found that grain size had a stronger impact on the self-field Jc than texture degree by analyzing the relationship between full-width at half maximum of (008) and self-field Jc. In addition, by analyzing the flux pinning properties, it indicated that Pb doping could enhance the point pinning property, while the improving textural structure could enhance the surface pinning property.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
C. Yao, Y.W. Ma, iScience 24, 102541 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isci.2021.102541
D. Uglietti, Supercond. Sci. Technol. 32, 053001 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6668/ab06a2
A. Molodyk, D.C. Larbalestier, Science. 380, 1220–1222 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.abq4137
Y. Oz, J.Y. Jiang, M. Matras, T.A. Oloye, F. Kametani, E.E. Hellstrom, D.C. Larbalestier, Phys. Rev. Mater. 5, 074803 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevMaterials.5.074803
T.A. Oloye, M. Matras, J.Y. Jiang, S.I. Hossain, Y.F. Su, U.P. Trociewitz, E.E. Hellstrom, D.C. Larbalestier, F. Kametani, Supercond. Sci. Technol. 34, 035018 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6668/abd575
H.P. Miao, K.R. Marken, M. Meinesz, B. Czabaj, S. Hong, IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 15, 2554–2557 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1109/tasc.2005.847648
J.Y. Jiang, G. Bradford, S.I. Hossain, M.D. Brown, J. Cooper, E. Miller, Y.B. Huang, H.P. Miao, J.A. Parrell, M. White, A. Hunt, S. Sengupta, R. Revur, T.M. Shen, S. Member, F. Kametani, U.P. Trociewitz, E.E. Hellstrom, D.C. Larbalestier, IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 29, 1–5 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/TASC.2019.2895197
T.M. Shen, L.G. Fajardo, Instruments 4, 17 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/instruments4020017
P. Chen, U.P. Trociewitz, J. Lu, E.S. Bosque, J.Y. Jiang, E.E. Hellstrom, D.C. Larbalestier, IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 27, 1–5 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/TASC.2017.2652849
G.M. Wang, M.J. Raine, D.P. Hampshire, Supercond. Sci. Technol. 31, 024001 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6668/aaa1b8
R. Kang, D. Uglietti, Y. Song, IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 30, 1–9 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/tasc.2020.3000229
W. Labban, W. Malaeb, K. Habanjar, M.S. Hassan, R. Sakagami, Y. Kamihara, R. Awad, Phase Transit. 93, 1055–1066 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1080/01411594.2020.1837371
C.W. Chu, L.Z. Deng, B. Lv, Phys. C 514, 290–313 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physc.2015.02.047
G.M. Wang, M.J. Raine, D.P. Hampshire, Supercond. Sci. Technol. 30, 104001 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6668/aa7f24
S.N. Zhang, X.B. Ma, L.J. Cui, Y.J. Huang, X.Q. Liu, C.S. Li, J.Q. Feng, P.X. Zhang, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 30, 3418–3425 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-00616-y
B. Özkurt, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 32, 6028–6037 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-05322-w
S.N. Zhang, C.S. Li, Q.B. Hao, T.N. Lu, P.X. Zhang, Phys. C 511, 26–32 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physc.2015.02.004
S.N. Zhang, M. Liang, C.S. Li, Q.B. Hao, J.Q. Feng, P.X. Zhang, Mater. Lett. 157, 197–200 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2015.05.096
M. Gürsul, I. Ergin, C. Özçelik, T. Depci, B. Özçelik, M.A. Madre, A. Sotelo, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 32, 17686–17699 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-06305-7
U. Erdem, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 32, 28587–28604 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-07236-z
J. Kumar, P.K. Ahluwalia, H. Kishan, V.P.S. Awana, J. Supercond. Novel Magn. 23, 493–499 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-009-0622-2
A. Sotelo, S. Rasekh, G. Constantinescu, H. Amaveda, M.A. Torres, M.A. Madre, J.C. Diez, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 34, 2977–2982 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2014.04.010
S.N. Zhang, C.S. Li, Q.B. Hao, X.B. Ma, T.N. Lu, P.X. Zhang, Supercond. Sci. Technol. 28, 045014 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1088/0953-2048/28/4/045014
Z.B. Li, G.Q. Liu, K. Yao, G.F. Jiao, X.Y. Xu, Q.B. Hao, L.H. Jin, C.S. Li, J. Supercond. Novel Magn. 36, 843–861 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-023-06531-6
B. Özkurt, J. Supercond, Novel Magn. 34, 1059–1066 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-021-05819-9
A. Jeremie, K. Alami-Yadri, J. Grivel, R. Flükiger, Supercond. Sci. Technol. 6, 730 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1088/0953-2048/6/10/005
İ. Öz, C. Terzioglu, M. Öz, A.T. Ülgen, M.B. Türköz, Ü. Erdem, G. Yildirim, Ceram. Int. 49, 8417–8427 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2022.11.004
F.I.N. de Vera, B.G. Singidas, R.V. Sarmago, Cryogenics. 121, 103406 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cryogenics.2021.103406
Ö. Bilgili, M. Yurddaskal, J. Electron. Mater. 50, 4999–5006 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-021-09023-2
B. Özçelik, I. Ergin, M.A. Madre, A. Sotelo, J. Supercond Novel Magn. 33, 1285–1292 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-019-05360-w
Acknowledgements
This study was financially supported by National Key Research and Development Program 2021YFB3800200, the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 52277029), and the Shaanxi Natural Science Foundation Project (No.2020JM-650).
Funding
This study was financially supported by National Key Research and Development Program 2021YFB3800200, the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 52277029), and the Shaanxi Natural Science Foundation Project (No. 2020JM-650).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YZ: investigation, formal analysis, visualization, writing—original draft, writing—review and editing. SZ: conceptualization, methodology, supervision, validation, writing—review and editing. XL: validation, writing—original draft, writing—review and editing. YH: methodology, supervision, validation. JL: investigation, conceptualization. JF: investigation, conceptualization. CL: investigation, conceptualization. PZ: investigation, supervision.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This study does not involve experiments with human tissue or others requiring bioethical approval.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Zhang, S., Liu, X. et al. Synergism effect of Pb doping and microstructure optimization on the superconducting properties of Bi-2212 ceramics. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 35, 816 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-024-12608-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-024-12608-2