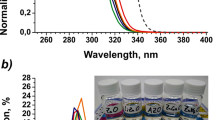
Abstract
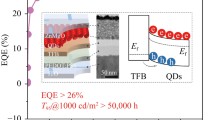
Colloidal quantum-dot light-emitting diodes (QLEDs) are rapidly gaining recognition as formidable contenders in the realm of next-generation lighting and display devices. Notwithstanding, the journey to commercialization of QLED devices encounters a roadblock in the form of inadequate flexibility exhibited by the electron transport layer, which is typically made of ZnO nanoparticles. The hindrance stems from the substantial specific surface area, existence of surface defect states, and the fixed ZnO bandgap. To surmount these obstacles, we delved into the potential of integrating Mg element as a dopant in ZnO, aiming to enhance the surface chemistry, electrical characteristics, and film morphology of colloidal ZnO nanoparticles. The results clearly indicated that Mg doping played a critical role in diminishing surface defects in ZnO, while simultaneously reducing the density of oxygen vacancies, thereby regulating its electron mobility. Through modulation of the Mg doping concentration, the bandgap width of ZnO can be fine-tuned, leading to the creation of a more suitable electron transport layer. The inverted QLED devices based on Zn1−xMgxO electron transport layers exhibited remarkable advancements, with a peak external quantum efficiency and current efficiency of 6.7% and 29 cd A−1, respectively. These values surpassed those of reference devices by 35 and 28%, underscoring the efficacy of Zn1−xMgxO as a viable approach for enhancing the efficiency of QLED devices.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Authors state that data supporting the results of our work are present within this research paper. The raw data collected during experiments are obtainable from the corresponding author, if required, on reasonable request.
References
Y.Z. Sun, Y.B. Jiang, X.W. Sun, S. Zhang, S. Chen, Beyond OLED: efficient quantum dot light-emitting diodes for display and lighting application. Chem. Rec 19, 1729–1752 (2019)
H. Zhang, Q. Su, S. Chen, Recent progress in the device architecture of white quantum-dot light-emitting diodes. J. Inf. Disp. 20, 169–180 (2019)
D. Zhang, T. Huang, L. Duan, Emerging self-emissive technologies for flexible displays. Adv. Mater. 32, 1902391 (2020)
X. Qu, J. Ma, P. Liu, K. Wang, X.W. Sun, On the voltage sweep behavior of quantum dot light-emitting diode. Nano Res. 16, 5511–5516 (2023)
V.L. Colvin, M.C. Schlamp, A.P. Alivisatos, Light-emitting diodes made from cadmium selenide nanocrystals and a semiconducting polymer. Nature. 370, 354–357 (1994)
J. Song, O. Wang, H. Shen, Q. Lin, Z. Li, L. Wang, X. Zhang, L.S. Li, Over 30% external quantum efficiency light-emitting diodes by engineering quantum dot-assisted energy level match for hole transport layer. Adv. Funct. Mater. 29, 1808377 (2019)
X. Li, Q. Lin, J. Song, H. Shen, H. Zhang, L.S. Li, X. Li, Z. Du, Quantum-dot light-emitting diodes for outdoor displays with high stability at high brightness. Adv. Opt. Mater. 8, 1901145 (2020)
H. Zhang, Q. Su, Y.Z. Sun, S. Chen, Efficient and color stable white quantum-dot light-emitting diodes with external quantum efficiency over 23%. Adv. Opt. Mater. 6, 1800354 (2018)
D. Chen, L. Ma, Y. Chen, X. Zhou, S. Xing, Y. Deng, Y. Hao, C. Pu, X. Kong, Y. Jin, Electrochemically stable ligands of ZnO electron-transporting layers for quantum-dot light-emitting diodes. Nano Lett. 23, 1061–1067 (2023)
A. Soultati, A. Fakharuddin, E. Polydorou, C. Drivas, A. Kaltzoglou, M.I. Haider, F. Kournoutas, M. Fakis, L.C. Palilis, S. Kennou, D. Davazoglou, P. Falaras, P. Argitis, S. Gardelis, A. Kordatos, A. Chroneos, L. Schmidt-Mende, M. Vasilopoulou, Lithium doping of ZnO for high efficiency and stability fullerene and non-fullerene organic solar cells. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2, 1663–1675 (2019)
H.S. Kim, D.H. Lee, B. Kim, B. Hwang, C.K. Kim, Improved performance of quantum dot light emitting diodes by introducing WO3 hole injection layers. Mol. Cryst. Liq Cryst. 735, 51–60 (2022)
J.W. Stouwdam, R.A.J. Janssen, Red, green, and blue quantum dot LEDs with solution processable ZnO nanocrystal electron injection layers. J. Mater. Chem. 18, 1889–1894 (2008)
S. Wang, Y. Guo, D. Feng, L. Chen, Y. Fang, H. Shen, Z. Du, Bandgap tunable Zn1-xMgxO thin films as electron transport layers for high performance quantum dot light-emitting diodes. J. Mater. Chem. C 5, 4724–4730 (2017)
X. Dai, Z. Zhang, Y. Jin, Y. Niu, H. Cao, X. Liang, L. Chen, J. Wang, X. Peng, Solution-processed, high-performance light-emitting diodes based on quantum dots. Nature 515, 96–99 (2014)
J. Zeng, Y. Li, X. Fan, Significant breakthroughs in interface engineering for high-performance colloidal QLEDs: a mini review. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 56, 343001 (2023)
Y.J. Lee, H.H. Kim, Y.J. Lee, J.H. Kim, H.J. Choi, W.K. Choi, Electron transport phenomena at the interface of Al electrode and heavily doped degenerate ZnO nanoparticles in quantum dot light emitting diode. Nanotechnology. 30, 035207 (2019)
K.H. Lee, J.H. Lee, H.D. Kang, B. Park, Y. Kwon, H. Ko, C. Lee, J. Lee, H. Yang, Over 40 cd/A efficient green quantum dot electro luminescent device comprising uniquely large-sized quantum dots. ACS Nano. 8, 4893–4901 (2014)
W. Cao, C. Xiang, Y. Yang, Q. Chen, L. Chen, X. Yan, L. Qian, Highly stable QLEDs with improved hole injection via quantum dot structure tailoring. Nat. Commun. 9, 2608 (2018)
A. Alexandrov, M. Zvaigzne, D. Lypenko, L. Nabiev, P. Samokhvalov, Al-, Ga-, Mg-, or Li-doped zinc oxide nanoparticles as electron transport layers for quantum dot light-emitting diodes. Sci. Rep. 10, 7496 (2020)
W.H. Shan, A. Alan, H. Javed, K. Rashid, A. Ali, L. Ali, A. Safeen, M.R. Ali, M. Sohail, G. Chambashi, Tuning of the band gap and dielectric loss factor by Mn doping of Zn1-xMnxO nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 13, 8646 (2023)
K. Noh, M. Kim, S.H. Lee, H.S. Yun, T.H. Lim, Y. Choi, K.J. Kim, Y. Jiang, K. Beom, M. Kim, Y.G. Kim, P. Lee, N. Oh, B.H. Kim, C. Shin, H.H. Lee, T.S. Yoon, M. Shim, J. Lim, K.B. Kim, S.Y. Cho, Effect of ethanolamine passivation of ZnO nanoparticles in quantum dot light emitting diode structure. Curr. Appl. Phys. 19, 998–1005 (2019)
O.S. Kim, B.H. Kang, J.S. Lee, S.W. Lee, S.H. Cha, J.W. Lee, S.W. Kim, S.H. Kim, S.W. Kang, Efficient quantum dots light-emitting devices using polyvinyl pyrrolidone-capped ZnO nanoparticles with enhanced charge transport. IEEE Electr. Device L 37, 1022–1024 (2016)
H.M. Kim, J. Kim, J. Lee, J. Jang, Inverted quantum-dot light emitting diode using solution processed p-type WOx doped PEDOT: PSS and Li doped ZnO charge generation layer. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 7, 24592–24600 (2015)
S. Cao, J. Zheng, J. Zhao, Z. Yang, C. Li, X. Guan, W. Yang, M. Shang, T. Wu, Enhancing the performance of quantum dot light-emitting diodes using room-temperature-processed Ga-doped ZnO nanoparticles as the electron transport layer. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 9, 15605–15614 (2017)
Y. Sun, W. Wang, H. Zhang, Q. Su, J. Wei, P. Liu, S. Chen, S. Zhang, High-performance quantum dot light-emitting diodes based on Al-doped ZnO nanoparticles electron transport layer. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 10, 18902–18909 (2018)
D.M. Bagnall, Y.F. Chen, M.Y. Shen, Z. Zhu, T. Goto, T. Yao, Room temperature excitonic stimulated emission from znic oxide epilayer grown by plasma-assisted MBE. J. Cryst. Growth. 184, 605–609 (1988)
L. Qian, Y. Zheng, J. Xue, P.H. Holloway, Stable and efficient quantum-dot light-emitting diodes based on solution-processed multilayer structures. Nat. Photonics. 5, 543–548 (2011)
Z. Yang, Q. Wu, G. Lin, X. Zhou, W. Wu, X. Yang, J. Zhang, W. Li, All-solution processed inverted green quantum dot light-emitting diodes with concurrent high efficiency and long lifetime. Mater. Horiz. 10, 2009–2015 (2019)
S. Bai, Y. Jin, X. Liang, Z. Ye, Z. Wu, B. Sun, Z. Ma, Z. Tang, J. Wang, U. Würfel, F. Gao, F. Zhang, Ethanedithiol treatment of solution-processed ZnO thin films: controlling the intragap states of electron transporting interlayers for efficient and stable inverted organic photovoltaics. Adv. Energy Mater. 5, 1401606 (2015)
D. Costenaro, F. Carniato, G. Gatti, L. Marchese, C. Bisio, Preparation of luminescent ZnO nanoparticles modified with aminopropyltriethoxy silane for optoelectronic applications. New. J. Chem. 37, 2103–2109 (2013)
X. Tang, S. He, Y. Deng, X. Lu, X. Zhu, W. Jin, Y. Jin, Mg-diffusion of ZnO-based electron-transport layers for highly conductive quantum-dot light-emitting diodes. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 14, 5812–5817 (2023)
K. Nomura, H. Ohta, A. Takagi, M. Hirano, H. Hosono, Room-temperature fabrication of transparent flexible thin-film transistors using amorphous oxide semiconductors. Nature 432, 488–492 (2004)
H.M. Kim, S. Cho, J. Kim, H. Shin, J. Jang, Li and mg co-doped zinc oxide electron transporting layer for highly efficient quantum dot light-emitting diodes. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 10, 24028–24036 (2018)
C.J. Ku, W.C. Hong, T. Mohsin, R. Li, Z. Duan, Y. Lu, Improvement of negative bias stress stability in Mg0.03Zn0.97O thin-film transistors. IEEE Electr. Device L. 36, 914–916 (2015)
Y.L. Shi, F. Liang, Y. Hu, M.P. Zhuo, X.D. Wang, L.S. Liao, High performance blue quantum dot light emitting diodes employing polyethylenimine ethoxylated as the interfacial modifier. Nanoscale 9, 14792–14797 (2017)
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, Grant No. 52202168, the Excellent Youth Fund of Henan Natural Science Foundation, China, Grant No. 212300410031, Key Technologies R&D Program of Henan, Grant No. 232102210168 and 242102211083, the Scientific Research Foundation of the Higher Education Institutions of Henan Province, China, Grant No. 23A140019 and 22B430009, and the Henan University of Engineering Foundation, China, Grant No. DKJ2019012.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Ethical approval
This article does not involve animal studies. Finally, all authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, L., Zhang, Y., Kun, Y. et al. The Zn1−xMgxO electron transport layer for charge balance in high-brightness inverted quantum-dot light-emitting diodes. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 35, 754 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-024-12556-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-024-12556-x