Abstract
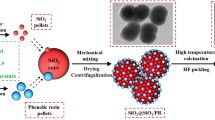
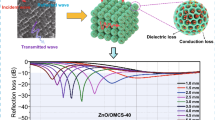
The increasing problem of electromagnetic pollution has significant drawbacks on both the accurate functioning of electronic facilities and the welfare of humans. To combat and eliminate the impact of electromagnetic radiation, it is crucial to design microwave-absorbing materials that possess both strong absorption strength and a broad frequency range. This study employed a straightforward sol–gel technique to regulate the hydrolysis reaction of tetraethyl orthosilicate (TEOS) and the synthesis reaction of phenolic resin. The objective was to fabricate a core–shell precursor consisting of silica coated with phenolic resin/silica spheres. Hollow carbon spheres with a porous structure were created using a process including high-temperature calcination with argon gas atmosphere and pickling etching. The manipulation of calcination temperature allows for the convenient adjustment of both the degree of graphitization and dielectric characteristics of hollow porous carbon spheres. The micromorphology, phase composition, graphitization degree, specific surface area, pore size, dielectric properties, and absorption properties were investigated through scanning electron microscopy (SEM), X-ray diffractometry (XRD), Raman spectroscopy, specific surface and porosity analyzer, and vector network analysis, respectively. The result indicates a positive correlation between the graphitization degree and the calcination temperature. With an ultralow filling ratio of 3.6 wt%, hollow porous carbon spheres calcinated at 1000 °C have a minimum reflection loss (RL) value of − 60.92 dB at a thickness of 2.3 mm, and the absorption bandwidth for RL ≤ − 10 dB is as large as 7.64 GHz at a thickness of 2.6 mm. The aforementioned observation provides evidence that the manipulation of graphitization degrees in hollow porous carbon spheres holds promise for improving their absorption bandwidth. The results obtained from this research can provide a foundational framework for the progress and use of absorbent materials based on carbon.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be made available on request.
References
L. Zhou, X.B. Liu, F. Luo, J.J. Yu, D.P. Zhang, Z.J. Wang, H.Y. Jia, H.B. Wang, Dielectric and microwave absorption properties of FexCoyP-loaded porous Al2O3 composites. Ceram. Int. 49, 30417 (2023)
L. Zhou, Y.J. Cao, J.Y. Qiu, F. Luo, Y. Zhai, Z.J. Wang, H.Y. Jia, Mechanical, dielectric, and microwave absorption properties of rGO nanosheets and ZnO filled ZnAl2O4 composites with broad bandwidth and strong absorption. J. Alloy. Compd. 966, 171587 (2023)
Y. Liu, J.N. Qin, L.L. Lu, J. Xu, X.L. Su, Enhanced microwave absorption property of silver decorated biomass ordered porous carbon composite materials with frequency selective surface incorporation. Int. J. Min. Met. Mater. 30, 525 (2023)
M.T. Qiao, J.X. Li, S.N. Li, D. Wei, X.F. Lei, W.Y. Lei, J. Wei, Q.Y. Zhang, M.L. Ma, Hierarchical CoNi alloys toward microwave absorption application: chain-like versus particle-like. J. Alloy. Compd. 926, 166854 (2022)
Y.Y. Zhou, W.C. Zhou, Y.C. Qing, Fa. Luo, D.M. Zhu, Temperature dependence of the electromagnetic properties and microwave absorption of carbonyl iron particles/silicone resin composites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 374, 345 (2015)
H.Y. Wei, Z.P. Zhang, G. Hussain, L.S. Zhou, Q. Li, K.K. Ostrikov, Techniques to enhance magnetic permeability in microwave absorbing materials. Appl. Mate. Today 19, 100596 (2020)
L. Quan, F.X. Qin, D. Estevez, H. Wang, H.X. Peng, Magnetic graphene for microwave absorbing application: towards the lightest graphene-based absorber. Carbon 125, 630 (2017)
Y.Y. Wang, Z.H. Zhou, J.L. Zhu, W.J. Sun, D.X. Yan, K. Dai, Z.M. Li, Low-temperature carbonized carbon nanotube/cellulose aerogel for efficient microwave absorption. Compos. Part B Eng. 220, 108985 (2021)
Y.Y. Wang, Z.H. Zhou, C.G. Zhou, W.J. Sun, J.F. Gao, K. Dai, D.X. Yan, Z.M. Li, Lightweight and robust carbon nanotube/polyimide foam for efficient and heat-resistant electromagnetic interference shielding and microwave absorption. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 12, 8704 (2020)
Z.Y. Jiang, H.X. Si, Y. Li, D. Li, H.H. Chen, C.H. Gong, J.W. Zhang, Reduced graphene oxide@carbon sphere based metacomposites for temperature-insensitive and efficient microwave absorption. Nano Res. 15, 8546 (2022)
W.Q. Dong, X.A. Li, K.X. Jin, Y.N. Shi, C.S. Wang, W.C. Guo, K.S. Tian, H.Y. Wang, Controllable synthesis of N-doped carbon nanoparticles with proper electrical conductivity for excellent microwave absorption performance. Compos. Part A-Appl. S. 165, 107363 (2023)
D.D. Wang, J. Jin, Y. Guo, H. Liu, Z.H. Guo, C.T. Liu, C.Y. Shen, Lightweight waterproof magnetic carbon foam for multifunctional electromagnetic wave absorbing material. Carbon 202, 464 (2023)
X. Yan, X. Huang, Y. Chen, Y. Liu, L. Xia, T. Zhang, H. Lin, D. Jia, B. Zhong, G. Wen, Y. Zhou, A theoretical strategy of pure carbon materials for lightweight and excellent absorption performance. Carbon 174, 662 (2021)
F. Wu, P. Hu, F. Hu, Z. Tian, J. Tang, P. Zhang, L. Pan, M.W. Barsoum, L. Cai, Z. Sun, Multifunctional MXene/C aerogels for enhanced microwave absorption and thermal insulation. Nano-Micro Lett. 15, 194 (2023)
H.L. Xu, X.W. Yin, M. Zhu, M.K. Han, Z.X. Hou, X.L. Li, L.T. Zhang, L.F. Cheng, Carbon hollow microspheres with a designable mesoporous shell for high-performance electromagnetic wave absorption. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 9, 6332 (2017)
H.L. Xu, X.W. Yin, M.H. Li, F. Ye, M.K. Han, Z.X. Hou, X.L. Li, L.T. Zhang, L.F. Cheng, Mesoporous carbon hollow microspheres with red blood cell like morphology for efficient microwave absorption at elevated temperature. Carbon 132, 343 (2018)
Y.X. Qin, M.Q. Wang, W. Gao, S.F. Liang, Rationally designed structure of mesoporous carbon hollow microspheres to acquire excellent microwave absorption performance. RSC Adv. 11, 14787 (2021)
Y. Cheng, Z.Y. Li, Y. Li, S.S. Dai, G.B. Ji, H.Q. Zhao, J.M. Cao, Y.W. Du, Rationally regulating complex dielectric parameters of mesoporous carbon hollow spheres to carry out efficient microwave absorption. Carbon 127, 643 (2018)
H.X. Zhang, B.B. Wang, A.L. Feng, N. Zhang, Z.R. Jia, Z.Y. Huang, X.H. Liu, G.L. Wu, Mesoporous carbon hollow microspheres with tunable pore size and shell thickness as efficient electromagnetic wave absorbers. Compos. Part B-Eng. 167, 690 (2019)
J.B. Chen, X.H. Liang, W. Liu, W.H. Gu, B.S. Zhang, G.B. Ji, Mesoporous carbon hollow spheres as a light weight microwave absorbing material showing modulating dielectric loss. Dalton Trans. 48, 10145 (2019)
H.X. Zhang, Z.R. Jia, A.L. Feng, Z.H. Zhou, C.H. Zhang, K.K. Wang, N. Liu, G.L. Wu, Enhanced microwave absorption performance of sulfur-doped hollow carbon microspheres with mesoporous shell as a broadband absorber. Compos. Commun. 19, 42 (2020)
J.Q. Tao, J.T. Zhou, Z.J. Yao, Z.B. Jiao, B. Wei, R.Y. Tan, Z. Li, Multi-shell hollow porous carbon nanoparticles with excellent microwave absorption properties. Carbon 172, 542 (2021)
H.Y. Nan, F. Luo, H.Y. Jia, H.J. Pan, Z.B. Huang, H.W. Deng, Y.C. Qing, C.H. Wang, Q. Chen, The effect of temperature on structure and permittivity of carbon microspheres as efficient absorbent prepared by facile and large-scale method. Carbon 185, 650 (2021)
D.G. Fan, B. Wei, R.X. Wu, J.T. Zhou, C.Y. Zhou, Dielectric control of ultralight hollow porous carbon spheres and excellent microwave absorbing properties. J. Mater. Sci. 56, 6830 (2021)
W. Xie, H.F. Cheng, Z.Y. Chu, Z.H. Chen, C.G. Long, Effect of carbonization temperature on the structure and microwave absorbing properties of hollow carbon fibres. Ceram. Int. 37, 1947 (2011)
J. Liu, X.Y. Wang, J. Gao, Y.W. Zhang, Q. Lu, M. Liu, Hollow porous carbon spheres with hierarchical nanoarchitecture for application of the high performance supercapacitors. Electrochim. Acta 211, 183 (2016)
M. Baca, K. Cendrowski, P. Banach, B. Michalkiewicz, E. Mijowska, R.J. Kalenczuk, B. Zielinska, Effect of Pd loading on hydrogen storage properties of disordered mesoporous hollow carbon spheres. Int. J. Hydrogen Energ. 42, 30461 (2017)
C.G. Pope, X-Ray Diffraction and the Bragg Equation. J. Chem. Educ. 74, 129 (1997)
J. Maire, J. Mering, Graphitization of soft carbons. Chem. Phys. Carbon 6, 125 (1970)
S. Pérez-Rodríguez, N. Rilloa, M.J. Lázaro, E. Pastor, Pd catalysts supported onto nanostructured carbon materials for CO2 valorization by electrochemical reduction. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 163, 83 (2015)
R.W. Shu, W.J. Li, Y. Wu, J.B. Zhang, G.Y. Zhang, Nitrogen-doped Co-C/MWCNTs nanocomposites derived from bimetallic metal-organic frameworks for electromagnetic wave absorption in the X-band. Chem. Eng. J. 362, 513 (2019)
W. Yang, R. Li, B. Jiang, T.H. Wang, L.Q. Hou, Z.X. Li, Z.C. Liu, F. Yang, Y.F. Li, Production of hierarchical porous carbon nanosheets from cheap petroleum asphalt toward lightweight and high-performance electromagnetic wave absorbents. Carbon 166, 218 (2020)
J. Ouyang, Z.L. He, Y. Zhang, H.M. Yang, Q.H. Zhao, Trimetallic FeCoNi@C nanocomposite hollow spheres derived from metal-organic frameworks with superior electromagnetic wave absorption ability. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 11, 39304 (2019)
A.C. Ferrari, J. Robertson, Interpretation of Raman spectra of disordered and amorphous carbon. Phys. Rev. B 61, 14095 (2000)
S. Gao, G.S. Wang, L. Guo, S.H. Yu, Tunable and ultraefficient microwave absorption properties of trace N-doped two-dimensional carbon-based nanocomposites loaded with multi-rare earth oxides. Small 16, 1906668 (2020)
H. Zhang, O. Noonan, X. Huang, Y. Yang, C. Xu, L. Zhou, C. Yu, Surfactant-free assembly of mesoporous carbon hollow spheres with large tunable pore sizes. ACS Nano 10, 4 (2016)
X. Liang, X. Zhang, W. Liu, D. Tang, B. Zhang, G. Ji, A simple hydrothermal process to grow MoS2 nanosheets with excellent dielectric loss and microwave absorption performance. J. Mater. Chem. C 4, 28 (2016)
P.J. Liu, Z.J. Yao, J.T. Zhou, Z.H. Yang, L. Bing Kong, Small magnetic Co-doped NiZn ferrite/graphene nanocomposites and their dual-region microwave absorption performance. J. Mater. Chem. C 4, 9738 (2016)
C.H. Tian, Y.C. Du, P. Xu, R. Qiang, Y. Wang, D. Ding, J.L. Xue, J. Ma, H.T. Zhao, X.J. Han, Constructing uniform core-shell PPy@PANI composites with tunable shell thickness toward enhancement in microwave absorption. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 7, 20090 (2015)
H.X. Zhang, Z.R. Jia, B.B. Wang, X.M. Wu, T. Sun, X.H. Liu, L. Bi, G.L. Wu, Construction of remarkable electromagnetic wave absorber from heterogeneous structure of Co-CoFe2O4@mesoporous hollow carbon spheres. Chem. Eng. J. 421, 129960 (2021)
H.L. Lv, G.B. Ji, X.H. Liang, H.Q. Zhang, Y.W. Du, A novel rod-like MnO2@Fe loading on graphene giving excellent electromagnetic absorption properties. J. Mater. Chem. C 3, 5056 (2015)
W. Liu, S.J. Tan, Z.H. Yang, G.B. Ji, Hollow graphite spheres embedded in porous amorphous carbon matrices as lightweight and low-frequency microwave absorbing material through modulating dielectric loss. Carbon 138, 143 (2018)
L. Lei, Z.J. Yao, J.T. Zhou, W.J. Zheng, B. Wei, J.Q. Zu, K.Y. Yan, Hydrangea-like Ni/NiO/C composites derived from metal-organic frameworks with superior microwave absorption. Carbon 173, 69 (2021)
Z. Lou, R. Li, P. Wang, Y. Zhang, B. Chen, C. Huang, C. Wang, H. Han, Y. Li, Phenolic foam-derived magnetic carbon foams (MCFs) with tunable electromagnetic wave absorption behavior. Chem. Eng. J. 391, 123571 (2019)
Y. Song, F.X. Yin, C.W. Zhang, W.B. Guo, L.Y. Han, Y. Yuan, Three-dimensional ordered mesoporous carbon spheres modified with ultrafine zinc oxide nanoparticles for enhanced microwave absorption properties. Nano-Micro Lett. 13, 76 (2021)
H. Lv, X. Liang, Y. Cheng, H. Zhang, D. Tang, B. Zhang, Y. Du, Coin-like αFe2O3@CoFe2O4 core-shell composites with excellent electromagnetic absorption performance. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 7, 8 (2015)
L. Zhou, J.X. Yan, J.L. Huang, H.B. Wang, X.G. Wang, Z.J. Wang, Dielectric and microwave absorption properties of FeSiAl/Al2O3 composites containing FeSiAl particles of different sizes. Ceram. Int. 47, 7831 (2021)
L. Zhou, H. Xu, G.X. Su, L.B. Zhao, H.B. Wang, Z.J. Wang, Z. Li, Tunable electromagnetic and broadband microwave absorption of SiO2-coated FeSiAl absorbents. J. Alloy. Compd. 861, 157966 (2021)
Z.H. Yang, H.L. Lv, R.B. Wu, Rational construction of graphene oxide with MOF-derived porous NiFe@C nanocubes for high-performance microwave attenuation. Nano Res. 9, 3671 (2016)
H.L. Lv, Y.H. Guo, Y. Zhao, H.Q. Zhang, B.S. Zhang, G.B. Ji, Z.C.J. Xu, Achieving tunable electromagnetic absorber via graphene/carbon sphere composites. Carbon 110, 130 (2016)
G.L. Wu, Y.H. Cheng, Z.H. Yang, Z.R. Jia, H.J. Wu, L.J. Yang, H.L. Li, P.Z. Guo, H.L. Lv, Design of carbon sphere/magnetic quantum dots with tunable phase compositions and boost dielectric loss behavior. Chem. Eng. J. 333, 519 (2018)
X.F. Zhou, Z.R. Jia, A.L. Feng, K.K. Wang, X.H. Liu, L. Chen, H.J. Cao, G.L. Wu, Dependency of tunable electromagnetic wave absorption performance on morphology controlled 3D porous carbon fabricated by biomass. Compos. Commun. 21, 100404 (2020)
L.F. Lyu, F.L. Wang, X. Zhang, J. Qiao, C. Liu, J.R. Liu, CuNi alloy/carbon foam nanohybrids as high-performance electromagnetic wave absorbers. Carbon 172, 488 (2021)
H.Y. Nan, Y.C. Qing, H. Gao, H.Y. Jia, F. Luo, W.C. Zhou, Synchronously oriented Fe microfiber & flake carbonyl iron/epoxy composites with improved microwave absorption and lightweight feature. Compos. Sci. Technol. 184, 107882 (2019)
C. Zhou, S. Geng, X.W. Xu, T.H. Wang, L.Q. Zhang, X.J. Tian, F. Yang, H.T. Yang, Y.F. Li, Lightweight hollow carbon nanospheres with tunable sizes towards enhancement in microwave absorption. Carbon 108, 234 (2016)
J.Y. Fang, Y.S. Shang, Z. Chen, W. Wei, Y. Hu, X.G. Yue, Z.H. Jiang, Rice husk-based hierarchically porous carbon and magnetic particles composites for highly efficient electromagnetic wave attenuation. J. Mater. Chem. C 5, 4695 (2017)
H.Q. Zhao, Y. Cheng, Z. Zhang, J.W. Yu, J. Zheng, M. Zhou, L. Zhou, B.S. Zhang, G.B. Ji, Rational design of core-shell Co@C nanotubes towards lightweight and high-efficiency microwave absorption. Compos. Part B-Eng. 196, 108119 (2020)
S. Qiu, H.L. Lyu, J.R. Liu, Y.Z. Liu, N.N. Wu, W. Liu, Facile synthesis of porous nickel/carbon composite microspheres with enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption by magnetic and dielectric losses. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 8, 20258 (2016)
H.G. Wang, F.B. Meng, J.Y. Li, T. Li, Z.J. Chen, H.B. Luo, Z.W. Zhou, Carbonized design of hierarchical porous carbon/Fe3O4@Fe derived from loofah sponge to achieve tunable high-performance microwave absorption. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 6, 11801 (2018)
Funding
This study was funded by the Shaanxi Provincial Innovative Talent Promotion Plan—Youth Science and Technology New Star Project (Talent) (No. 2023KJXX-075), the Youth Innnovation Team of Shaanxi Universities Project (No. 23JP072), the Natural Science Basic Research Plan in Shaanxi Province of China (Grant No. 2022JM-188), and Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program for University Students (No. 202311736004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YYZ: conceptualization, experiment, data measurement and analysis, writing. YXZ: experiment, writing. SYZ: experiment, analysis. YYC: formal analysis. CYZ: data analysis. HND: methodology. CQY: formal curation. DC: review editing. HX: supervision and project administration.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, Y., Zhang, Y., Zhang, S. et al. The impact of carbonization temperature on the microwave-absorbing properties of hollow porous carbon spheres. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 35, 789 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-024-12549-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-024-12549-w