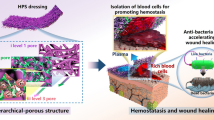
Abstract
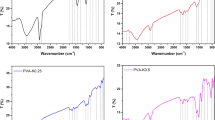
Hemorrhage control is crucial in both military and civilian contexts. Despite unprecedented improvements in hemostatic products, efficient treatment solutions to control hemorrhage upon wound healing are still necessary. Chitosan (CS) and dextran (Dex) are natural, biocompatible and biodegradable hydrogel-forming polysaccharides with enhanced hemostatic and wound healing properties. Bioglass nanoparticles (BG-nps) in turn possess documented hemostatic properties. In this context, in the present work, a series of BGnps-doped chitosan (CS)/oxidized-dextran (ODEX) adhesive sponges were developed through a Schiff base reaction. The successful synthesis of the materials was confirmed by FTIR spectroscopy, their crystallinity was analyzed by XRD, the sponge morphology was investigated by SEM analysis, water swelling, and viscosity of the hydrogels were also investigated. All materials were developed in powder and sponge form with the aim to allow their application to wound lesions of any shape and depth and enable suppression of external bleeding for which other methods of bleeding control are not applicable. All prepared hemostatic products showed hemocompatibility, and it was observed that the CS-ODEX-BGnps sponges decreased the blood clotting time compared to CS neat and mainly those with the highest percentages of BGnps (1% and 2% w/w).
Graphical abstract













Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Huang Z, Wang D, Sønderskov SM, Xia D, Wu X, Liang C et al (2023) Tannic acid-functionalized 3D porous nanofiber sponge for antibiotic-free wound healing with enhanced hemostasis, antibacterial, and antioxidant properties. J Nanobiotechnol 21(1):1–15
Zhang H, Lv X, Zhang X, Wang H, Deng H, Li Y et al (2015) Antibacterial and hemostatic performance of chitosan-organic rectorite/alginate composite sponge. RSC Adv 5(62):50523–50531
Khoshmohabat H, Paydar S, Makarem A, Karami MY, Dastgheib N, Zahraei SAH et al (2019) A review of the application of cellulose hemostatic agent on trauma injuries. Open Access Emerg Med 11:171–177
Bagher Z, Ehterami A, Hossein M, Khastar H (2019) Wound healing with alginate/chitosan hydrogel containing hesperidin in rat model. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol 2020(55):101379
Bai Q, Gao Q, Hu F, Zheng C, Chen W, Sun N et al (2022) Chitosan and hyaluronic-based hydrogels could promote the infected wound healing. Int J Biol Macromol 232:123271
Elieh Ali Komi D, Sharma L, Dela Cruz CS (2018) Chitin and its effects on inflammatory and immune responses. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol 54(2):213–223
Lazaridou M, Bikiaris DN, Lamprou DA (2022) 3D bioprinted chitosan-based hydrogel scaffolds in tissue engineering and localised drug delivery. Pharmaceutics 14(9):1978
Ding A, Teng L, Zhou Y, Chen P, Nie W (2018) Synthesis and characterization of bovine serum albumin-loaded microspheres based on star-shaped PLLA with a xylitol core and their drug release behaviors. Polym Bull 75(7):2917–2931
Applications A. Chemical Engineering Journal Ultrafast in situ-forming hydrogels with enhanced hemostatic and antibacterial activities for effective wound management in trauma emergency.
Liu J, Zhou X, Zhang Y, Zhu W, Wang A, Xu M et al (2022) Rapid hemostasis and excellent antibacterial cerium-containing mesoporous bioactive glass/chitosan composite sponge for hemostatic material. Mater Today Chem 23:100735
Mehrabi T, Mesgar AS, Mohammadi Z (2020) Bioactive glasses: a promising therapeutic ion release strategy for enhancing wound healing. ACS Biomater Sci Eng 6(10):5399–5430
Roy P, Saha R, Dattaray D, Saha S, Mandal TK, Srivastava P et al (2024) Bioactive glass incorporated dressing matrix for rapid hemostatic action with antibacterial activity. Mater Chem Phys 315:128942
Li Z, Li B, Li X, Lin Z, Chen L, Chen H et al (2021) Ultrafast in-situ forming halloysite nanotube-doped chitosan/oxidized dextran hydrogels for hemostasis and wound repair. Carbohydr Polym 267(April):118155
Peng T, De YK, Yuan C, Goosen MFA (1994) Structural changes of pH-sensitive chitosan/polyether hydrogels in different pH solution. J Polym Sci A Polym Chem 32(3):591–596
Marzocco S, Saebø IP, Bjørås M, Franzyk H, Helgesen E, Booth JA (2023) Optimization of the hemolysis assay for the assessment of cytotoxicity. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24032914
Koumentakou I, Terzopoulou Z, Michopoulou A, Kalafatakis I, Theodorakis K, Tzetzis D et al (2020) Chitosan dressings containing inorganic additives and levofloxacin as potential wound care products with enhanced hemostatic properties. Int J Biol Macromol 162:693–703
Esmaeilzadeh J, Borhan S, Haghbin M, Khorsand ZA (2024) Assessments of EISA-synthesized mesoporous bioactive glass incorporated in chitosan-gelatin matrix as potential nanocomposite scaffolds for bone regeneration. Int J Polym Mater Polym Biomater 73(8):646–660
Lazaridou M, Nanaki S, Zamboulis A, Papoulia C, Chrissafis K, Klonos PA et al (2021) Super absorbent chitosan-based hydrogel sponges as carriers for caspofungin antifungal drug. Int J Pharm 606:120925
Guinesi LS, Cavalheiro ÉTG (2006) Influence of some reactional parameters on the substitution degree of biopolymeric Schiff bases prepared from chitosan and salicylaldehyde. Carbohydr Polym 65(4):557–561
Khalil KD, Ahmed HA, Bashal AH, Bräse S, Nayl AA, Gomha SM (2022) Thiazoles with a chitosan-capped calcium oxide nanocomposite. Polymers (Basel) 14:3347
Khalil KD, Riyadh SM, Alkayal NS, Bashal AH, Alharbi KH, Alharbi W (2022) Chitosan-strontium oxide nanocomposite: preparation, characterization, and catalytic potency in thiadiazoles synthesis. Polymers (Basel) 14(14):2827
Tang ESK, Huang M, Lim LY (2003) Ultrasonication of chitosan and chitosan nanoparticles. Int J Pharm 265(1–2):103–114
Wang T, Nie J, Yang D (2012) Dextran and gelatin based photocrosslinkable tissue adhesive. Carbohydr Polym 90(4):1428–1436
Lee KY, Mooney DJ (2001) Hydrogels for tissue engineering. Chem Rev 101(7):1869–1879
Hunt JA, Chen R, Van Veen T, Bryan N (2014) Hydrogels for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. J Mater Chem B 2(33):5319–5338
Tavares L, Esparza Flores EE, Rodrigues RC, Hertz PF, Noreña CPZ (2020) Effect of deacetylation degree of chitosan on rheological properties and physical chemical characteristics of genipin-crosslinked chitosan beads. Food Hydrocoll 106:105876
Weng L, Chen X, Chen W (2007) Rheological characterization of in situ crosslinkable hydrogels formulated from oxidized dextran and N-carboxyethyl chitosan. Biomacromol 8(4):1109–1115
Duan J, Liang X, Cao Y, Wang S, Zhang L (2015) High strength chitosan hydrogels with biocompatibility via new avenue based on constructing nanofibrous architecture. Macromolecules 48(8):2706–2714
Wia̧cek AE, Gozdecka A, Jurak M (2018) Physicochemical characteristics of chitosan-TiO2 biomaterial. 1. Stability and swelling properties. Ind Eng Chem Res 57(6):1859–1870
Ikram M, Muhammad Khan A, Haider A, Haider J, Naz S, Ul-Hamid A et al (2022) Facile synthesis of La- and chitosan-doped CaO nanoparticles and their evaluation for catalytic and antimicrobial potential with molecular docking studies. ACS Omega 7(32):28459–28470
Pavoni JMF, Luchese CL, Tessaro IC (2019) Impact of acid type for chitosan dissolution on the characteristics and biodegradability of cornstarch/chitosan based films. Int J Biol Macromol 138:693–703
Gupta N, Kozlovskaya V, Dolmat M, Yancey B, Oh J, Lungu CT et al (2020) Photocatalytic nanocomposite microsponges of polylactide-titania for chemical remediation in water. ACS Appl Polym Mater 2(11):5188–5197
Gheorghiță D, Moldovan H, Robu A, Bița AI, Grosu E, Antoniac A et al (2023) Chitosan-based biomaterials for hemostatic applications: a review of recent advances. Int J Mol Sci 24(13):10540
Patil G, Torris A, Suresha PR, Jadhav S, Badiger MV, Ghormade V (2021) Design and synthesis of a new topical agent for halting blood loss rapidly: a multimodal chitosan-gelatin xerogel composite loaded with silica nanoparticles and calcium. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 198:111454
Ali SW, Mangrio FA, Li F, Dwivedi P, Rajput MU, Ali R et al (2021) Co-delivery of artemether and piperine via core-shell microparticles for enhanced sustained release. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol 63(March):102505
Luanda A, Badalamoole V (2023) Past, present and future of biomedical applications of dextran-based hydrogels: a review. Int J Biol Macromol 15(228):794–807
Fernandes G, Vanyo ST, Alsharif SBA, Andreana S, Visser MB, Dziak R (2019) Strontium effects on human gingival fibroblasts. J Oral Implantol 45(4):274–280
Arkin VHR, Narendrakumar U, Madhyastha H, Manjubala I (2021) Characterization and in vitro evaluations of injectable calcium phosphate cement doped with magnesium and strontium. ACS Omega 6(4):2477–2486
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling Editor: Annela M. Seddon.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bikiaris, R.E., Tsamesidis, I., Kontonasaki, E. et al. Chitosan/oxidized-dextran dressings containing mesoporous bioglass nanoparticles for hemostatic applications. J Mater Sci (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-024-10241-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-024-10241-2