Abstract
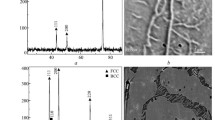
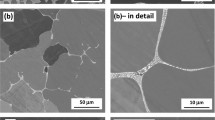
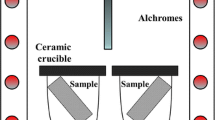
This study is concerned with the mechanism and kinetics of isothermal oxidation of a newly developed oxide dispersion strengthened Fe3Al with Cr and Ti additions (Fe–12.7Al–5.8Cr–0.25Ti–0.35Y2O3) at 900 and 1050 °C for a duration of 2000 h under ambient atmosphere. The oxidation rate is similar at both the temperatures up to 1200 h, beyond which, the rate is higher for the samples oxidized at 1050 °C. The spallation of oxidation products is higher at 900 °C. The rate constants for the reaction and instantaneous rate constants confirm the formation of various types of oxides and other associated processes as a function of time and temperature. The alloy under study has been proven to exhibit superior resistance to oxidation at high temperatures, when compared to other commercially available ODS–Fe3Al alloys and superalloys developed for similar applications. The superior oxidation of this material is due to the formation of stable α-Al2O3 layer along with layers of Fe2O3, Cr2O3 and assimilation of metastable TiO.














Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Liu CT, Cahn RW, Sauthoff G eds (2012) Ordered intermetallics: physical metallurgy and mechanical behaviour. Springer Science and Business Media
Liu CT, Sikka VK (1986) Nickel aluminides for structural use. JOM 38(5):19–21
Zamanzade M, Barnoush A (2014) An overview of the hydrogen embrittlement of iron aluminides. Proced mater sci 3:2016–2023
Hagel WC (1965) The oxidation off iron, nickel and cobalt-base alloys containing aluminum. Corrosion 21(10):316–326
Boggs WE (1971) The Oxidation of Iron-Aluminum Alloys from 450 to 900 C. J Electrochem Soc 118(6):906
Tortorelli PF, Brady MP (2000) Alloy design approaches for high-temperature oxidation resistance. JOM 52(1):15
Tomaszewicz P, Wallwork GR (1978) Iron–Aluminum alloys: a review of their oxidation behavior. Rev High-Temp Mater 4(1):75–105
DeVan JH, Tortorelli PF (1993) Oxidation/sulfidation of iron-aluminium alloys. Mater High Temp 11(1–4):30–35
Heinonen MH et al (2011) Initial oxidation of Fe–Al and Fe–Cr–Al alloys: Cr as an alumina booster. Oxid Met 76:331–346
Guan SW, Smeltzer WW (1994) Oxygen solubility and a criterion for the transition from internal to external oxidation of ternary alloys. Oxid Met 42:375–391
Lipkin DA, Clarke DR (1996) Measurement of the stress in oxide scales formed by oxidation of alumina-forming alloys. Oxid Met 45:267–280
Wright IG, Pint BA, Tortorelli PF (2001) High-temperature oxidation behavior of ODS–Fe3Al. Oxid Met 55:333–357
Cueff R, Buscail H, Caudron E, Issartel C, Riffard F (2003) Oxidation of alumina formers at 1173 K: effect of yttrium ion implantation and yttrium alloying addition. Corros Sci 45(8):1815–1831
Kofstad P (1988) High Temperature Corrosion, Elsevier Applied Science. London, 211p
Wang X, Shen X (2023) Research Progress of ODS FeCrAl Alloys–a review of composition design. Materials 16(18):6280
Liu T, Wang C, Shen H, Chou W, Iwata NY, Kimura A (2013) The effects of Cr and Al concentrations on the oxidation behavior of oxide dispersion strengthened ferritic alloys. Corros Sci 76:310–316
Qiao Y, Wang P, Qi W, Du S, Liu Z, Meng F, Zhang X, Wang K, Li Q, Yao Z, Bai C (2020) Mechanism of Al on FeCrAl steam oxidation behavior and molecular dynamics simulations. J Alloys Compd 828:154310
Hsiung LL, Fluss MJ, Tumey SJ, Choi BW, Serruys Y, Willaime F, Kimura A (2010) Formation mechanism and the role of nanoparticles in Fe-Cr ODS steels developed for radiation tolerance. Phys Rev B Condens Matter Mater Phy 82(18):184103
Ul-Hamid A (2003) Effect of Y2O3 content on the oxidation behavior of Fe–Cr–Al-based ODS alloys. J Mater Eng Perform 12:87–94
Chinnappan R (2014) Thermodynamic stability of oxide phases of Fe–Cr based ODS steels via quantum mechanical calculations. Calphad 45:188–193
Durga PV et al (2022) Effect of fine grain structure and nano oxide dispersoids on improved strength and ductility of iron aluminide based intermetallics. Metall Mater Trans A 53(5):1597–1603
Durga PV et al (2020) Microstructural and mechanical properties of oxide dispersion strengthened iron aluminides produced by mechanical milling and hot extrusion. J Alloy Compd 834:155218
Durga PV, Nagini M, Jyothirmayi A, Reddy AV, Bakshi SR, Vijay R (2022) Electrochemical corrosion behaviour of oxide dispersion strengthened iron aluminides in 3.5 wt% NaCl solution. Mater Chem Phy 290:126586
Weisenburger A, Jianu A, Doyle S, Bruns M, Fetzer R, Heinzel A, DelGiacco M, An W, Müller G (2013) Oxide scales formed on Fe–Cr–Al-based model alloys exposed to oxygen containing molten lead. J Nucl Mater 437(1–3):282–292
Turker M, Hughes TA (1995) Oxidation behavior of three commercial ODS alloys at 1200 °C. Oxid Met 44:505–525
Türker M (1999) The long-term oxidation behaviour of ferritic ODS alloys at 1100–1200 °C in air and nitrogen–2% oxygen. Corros Sci 41(10):1921–1935
ISO 21608: International Standard, Corrosion of metals and alloys - Test method for isothermal-exposure oxidation testing under high-temperature corrosion conditions for metallic materials. ISO 21608:2012, ISO TC156 WG 13 (High Temperature Corrosion). 19–12–2006, 2012 Ref Type: Report
HJT Ellingham 1944 J Soc Chem Ind (London) 63 125
Young CT, Tenney DR, Herring HW (1975) Dynamic oxidation behavior of TD-NiCr alloy with different surface pretreatments. Metall and Mater Trans A 6:2253–2265
Tedmon CS (1966) The effect of oxide volatilization on the oxidation kinetics of Cr and Fe–Cr alloys. J Electrochem Soc 113(8):766
Seki I, Yamaura S-I (2017) Reduction of titanium dioxide to metallic titanium by nitridization and thermal decomposition. Mater Trans 58(3):361–366
Vedmid’ LB, Krasikov SA, Zhilina EM, Nikitina EV, Evdokimova IV, Merkushev AG (2018) Evolution of phase formation during the aluminothermic reduction of titanium and zirconium from oxides. Russian Metall 2018:733–736
Whittle DP (1972) Spalling of protective oxide scales. Oxid Met 4(3):171–179
Chevalier S et al (2010) High-temperature oxidation of Fe3Al and Fe 3 Al–Zr intermetallics. Oxid Met 73:43–64
Wood GC (1970) High-temperature oxidation of alloys. Oxid Met 2(1):11–57
Smialek JL (1978) Oxide morphology and spalling model for NiAl. Metall transac A. 9:309–320
Kuenzly JD, Douglass DL (1974) The oxidation mechanism of Ni3Al containing yttrium. Oxid Met 8(3):139–178
Pilling NB, Bedworth RE (1925) Oxidation of copper–nickel alloys at high temperatures. Ind Eng Chem 17(4):372–376
Vedmid’ LB, Krasikov SA, Zhilina EM, Nikitina EV, Evdokimova IV, Merkushev AG (2018) Evolution of phase formation during the aluminothermic reduction of titanium and zirconium from oxides. Russ Metall 2018:733–736
Mrowec St (1967) On the mechanism of high temperature oxidation of metals and alloys. Corros Sci 7(9):563–578
Evans HE (1995) Stress effects in high temperature oxidation of metals. Int Mater Rev 40(1):1–40
Stott FH, Wood GC, Hobby MG (1971) A comparison of the oxidation behavior of Fe–Cr–Al, Ni–Cr–Al, and Co–Cr–Al alloys. Oxid Met 3(2):103–113
Babu N, Balasubramaniam R, Ghosh A (2001) High-temperature oxidation of Fe3Al-based iron aluminides in oxygen. Corros Sci 43(12):2239–2254
Archana M et al (2021) High-temperature air and steam oxidation and oxide layer characteristics of Alloy 617. J Mater Eng Perform 30:931–943
Mathiazhagan, Palanivel, and Anand Sawroop Khanna (2011) High temperature oxidation behavior of P91, P92 and E911 alloy steels in dry andwet atmospheres. 43–50
Sanviemvongsak T, Monceau D, Macquaire B (2018) High temperature oxidation of IN 718 manufactured by laser beam melting and electron beam melting: effect of surface topography. Corros Sci 141:127–145
Birks, Neil, Gerald H. Meier, and Frederick S. Pettit. Introduction to the high temperature oxidation of metals. Cambridge university press, 2006
Durga P.V.(2023), Effect of Ti Zr and nano oxide dispersion on microstructure mechanical properties and corrosion behaviour of Fe3Al intermetallics (Doctoral Dissertation, Indian Institute of Technology, Madras), http://hdl.handle.net/10603/547276
Hampl M, Schmid-Fetzer R (2015) Thermodynamic description of the Ti–O system. Int J Mater Res 106(5):439–453
Tsai SC, Huntz AM, Dolin C (1996) Growth mechanism of Cr2O3 scales: oxygen and chromium diffusion, oxidation kinetics and effect of yttrium. Mater Sci Eng, A 212(1):6–13
Evans AG and Cannon RM (1989) Stresses in oxide films and relationships with cracking and spalling. In:Materials science forum, vol 43, pp 243–268. Trans Tech Publications Ltd
Doychak JLSJ, Smialek JL, Mitchell TE (1989) Transient oxidation of single-crystal β-NiAl. Metall Trans A 20:499–518
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Dr. Joydip Joardar for carrying out XRD and Dr. Nagini Macha for FESEM studies. The authors acknowledge the financial support from Department of Science and Technology (DST), Government of India, for the project National Centre for Development of Advanced Materials and Manufacturing processes for Clean Coal Technologies for Power Applications [No TMD/CERI/Clean Coal/2017/036 (ARCI) (G)]. Sincere gratitude is extended to Dr. A. Venugopal Reddy (Former Director RCMA) and Dr. T. Jayakumar (Former Director MMG, IGCAR) for their valuable insights and expertise. We also are grateful to Dr. Rangadhara Chary for his guidance in exploring the underlying mechanism of oxidation
Funding
ARCI,No TMD/CERI/Clean Coal/2017/036 (ARCI) (G),Narasaiah N
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Nima Haghdadi.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kiranchand, G.R., Durga, P.V., Vijay, R. et al. Evolution of surface oxide layers during isothermal oxidation of a multi-component oxide dispersion strengthened Fe3Al alloy. J Mater Sci 59, 15580–15598 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-024-10057-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-024-10057-0