Abstract
A series of new perovskite oxides Sr1.6K0.4Fe1+x Mo1−x O6−δ (x = 0.2, 0.4, 0.6) were synthesised by solid state reaction method. Synthesis of Sr1.6K0.4Fe1+x Mo1−x O6−δ (x = 0.2, 0.4, 0.6) was achieved above 700 °C in 5 % H2/Ar, albeit with the formation of impurity phases. Phase stability upon redox cycling was only observed for sample Sr1.6K0.4Fe1.4Mo0.6O6−δ. Redox cycling of Sr1.6K0.4Fe1+x Mo1−x O6−δ (x = 0.2, 0.4, 0.6) demonstrates a strong dependence on high temperature reduction to achieve high conductivities. After the initial reduction at 1200 °C in 5 %H2/Ar, then re-oxidation in air at 700 °C and further reduction at 700 °C in 5 %H2/Ar, the attained conductivities were between 0.1 and 58.4 % of the initial conductivity after reduction 1200 °C in 5 %H2/Ar depending on the composition. In the investigated new oxides, sample Sr1.6K0.4Fe1.4Mo0.6O6−δ is most redox stable also retains reasonably high electrical conductivity, ~70 S/cm after reduction at 1200 °C and 2–3 S/cm after redox cycling at 700 °C, indicating it is a potential anode for SOFCs.
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Solid oxide fuel cells (SOFCs) are electrochemical devices to efficiently convert chemical energy into electricity. The conventional Ni-based cermet anode for SOFCs exhibits excellent catalytic activity and high conductivity which is good but suffers sintering/coarsening at high temperature. The significant volume change between NiO and Ni on reduction may lead to delamination between the anode and electrolyte interface. Carbon deposition on the Ni-based anode when hydrocarbon fuels are used in the SOFCs is a challenge [1, 2]. Therefore, it is desired to develop new anode, particularly redox stable anode for SOFCs [3–10]. Double perovskite Sr2(TM)MoO6−δ (TM = Mn, Mg, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, Zn) as potential anode materials for SOFCs has been the subject of a substantial body of research [3, 5, 8, 9, 11], and good fuel cell performance has been achieved for Sr2MgMoO6−δ [5], Sr2MnMoO6−δ [5], Sr2CoMoO6−δ [12] and Sr2FeMoO6−δ [13] anodes; of these compounds, only Sr2MgMoO6−δ (SMMO) has been proven to be redox stable [14]. Despite achieving redox stability, the chemical reactivity of SMMO with common electrolytes, such as LSGM and YSZ, limits its utility [6].
Xiao et al. improved both the formability and stability of Sr2FeMoO6−δ through an increase in the iron content of the sample, with Sr2Fe1.33Mo0.66O6−δ formed at 800 °C in H2, 300 °C below the synthesis temperature of Sr2FeMoO6−δ in 5 % H2/Ar [13, 15]. The conductivity of Sr2Fe1.33Mo0.66O6−δ in 5 % H2/Ar ranges between 15 and 30 S cm−1 from 700 °C to 300 °C, sufficient for an IT-SOFC anode material. Further development of this series by Liu et al. formed Sr2Fe1.5Mo0.5O6−δ in air at 1000 °C and demonstrated high conductivity in both oxidising and reducing atmospheres [11]. Good performance of Sr2Fe1.5Mo0.5O6−δ as a symmetrical electrode was achieved, attaining ~500 mWcm−2 at 800 °C in humidified H2 with good stability over successive redox cycles.
It has been reported that potassium doping of Sr2FeMoO6−δ could improve the ionic conductivity of the parent material with minimal disruption to the compound structure, and good fuel cell performance has been achieved when Sr1.6K0.4FeMoO6−δ was used as the anode for a SOFC [16]. Synthesis of the potassium-doped strontium molybdenum ferrite was noted to improve the formability of these compounds, with the formation of single-phase Sr1.6K0.4FeMoO6−δ observed after reduction at 850 °C in H2, 250 °C lower than is required for the pure strontium analogue in 5 % H2/Ar [13]. The conductivity of these compounds was comparable to that of the pure strontium iron molybdate, despite the lower synthesis temperature. Acceptable fuel cell performance, 766 mWcm−2 at 800 °C in H2, was also observed for a Sr1.6K0.4FeMoO6−δ/LSGM/Sr0.9K0.1FeO3−δ cell [16], although the anodic composition was later determined to exhibit a mixture of SrMoO3 and SrFe0.6Mo0.4O2.7 phases. As the introduction of potassium had exhibited an improvement in the compound formability, it was posited that a further increase could be elicited through an increase in the iron content, as for the pure strontium analogue [11, 17]. To this end, the formability and redox stability of a series of new materials of the composition Sr1.6K0.4Fe1+x Mo1−x O6−δ (x = 0.2, 0.4, 0.6) was determined, and conclusions as to the suitability of these compounds for use as SOFC anode materials were drawn.
Experimental information
Materials synthesis
Sr1.6K0.4Fe1+x Mo1−x O6−δ (x = 0.2, 0.4, 0.6) were produced by solid state synthesis technique. Stoichiometric amounts of SrCO3 (>99.9 %, Sigma Aldrich), KHCO3 (99 %, Alfa Aesar), Fe2O3 (99.5 %, Alfa Aesar) and MoO3 (99.5 %, Alfa Aesar) were weighed and mixed in a planetary ball mill (Fritsch P6) for 2 h prior to firing at 900 °C for 5 h. A second firing at 1100 °C for 2 h was then performed. Pellets of all the samples (ø ≈ 13 mm × 2 mm) were uniaxially pressed at 221 MPa and sintered in air at 1200 °C for 2 h. To study the redox stability, some of the as-prepared pellets were further fired in 5 % H2/Ar for 10 h at 700 and 1200 °C, respectively.
Materials characterisation
Phase purity and crystal parameters of the samples were examined by X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis using a PANalytical X’Pert PRO MPD Multipurpose diffractometer (Cu Kα1 radiation, λ = 1.5405 Å). GSAS [18] software was used to perform a least squares refinement of the lattice parameters of all suitable samples.
The densities of the pellets were determined from the measured mass and volume. Theoretical densities were calculated using experimental lattice parameters and the chemical formula of the sample. The relative densities were calculated from the actual and theoretical density values. The density of the pellets was around 90 % for Sr1.6K0.4Fe1+x Mo1−x O6−δ (x = 0.2, 0.4, 0.6).
Thermal analysis was conducted using a Stanton Redcroft STA 1500 Thermal Analyser on heating from room temperature to 800 °C and on cooling from 800 °C to room temperature in air, with a heating/cooling rate of 10 °C min−1 in 5 % H2/Ar with a flow rate of 5 % H2/Ar of 50 ml min−1.
Conductivity measurements
Pellets for Sr1.6K0.4Fe1+x Mo1−x O6−δ (x = 0.2, 0.4, 0.6) were coated on opposing sides using silver paste after firing at 1200 °C for 8 h in 5 % H2/Ar. The conductivity of the samples was measured primarily in 5 % H2/Ar between 300 and 700 °C. Secondary measurements over the same temperature range were conducted in air following an equilibration step of 12 h at 700 °C in air. Final measurements over the same temperature range were conducted after an equilibration step of 12 h at 700 °C in 5 % H2/Ar. Measurements were conducted using a pseudo four terminal DC method using a Solartron 1470E potentiostat/galvanostat controlled by CellTest software with an applied current of 1.0–0.1 A [19].
Results and discussion
Synthesis of Sr1.6K0.4Fe1+x Mo1−x O6−δ (x = 0.2, 0.4, 0.6) in air
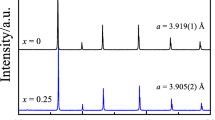
XRD of Sr1.6K0.4Fe1+x Mo1−x O6−δ (x = 0.2, 0.4, 0.6) after synthesis in air exhibited a single-phase double perovskite structure for composition Sr1.6K0.4Fe1.6Mo0.4O6−δ with space group Fm-3m as shown in Fig. 1. However, an additional SrMoO4−δ second phase (PDF: 01-085-0809) was observed for both Sr1.6K0.4Fe1.4Mo0.6O6−δ and Sr1.6K0.4Fe1.2Mo0.8O6−δ. The formation of a single-phase double perovskite structure for Sr1.6K0.4Fe1.6Mo0.4O6−δ correlates with previous research into iron-rich strontium iron ferrites, which suggests that the formability limit in air for Sr1.6K0.4Fe1+x Mo1−x O6−δ lies between x = 0.4 and x = 0.5 [15, 17, 20]. The Fe-rich composition will have better charge balance with the presence of Mo6+ ions in the perovskite oxide, facilitating the formation of single phase. At x = 0.2, if the charge for elements Fe and Mo in Sr1.6K0.4Fe1+x Mo1−x O6−δ is +3 and +6 respectively, the total positive charge is 12 then the oxygen sub-lattice should be stoichiometric, i.e. δ = 0. However, the oxygen sub-lattice in perovskite oxides tends to be non-stoichiometric with the formation of oxygen vacancies, i.e. δ > 0, after firing in air at high temperature [21, 22]. Under the circumstance, the positive charge will be greater than the negative charge, thus not balanced and difficult to form single-phase perovskite oxide. Therefore single-phase double perovskite oxide was not formed, while stable second-phase SrMoO4 was formed (Fig. 1). With the increase of x to 0.4, the total positive charge is fewer than 12, which allows the formation of oxygen vacancies, and thus the second-phase SrMoO4 was significantly reduced. Single-phase double perovskite oxide was formed with the Fe-rich sample Sr1.6K0.4Fe1.6Mo0.4O6−δ (Fig. 1).
STA of Sr1.6K0.4Fe1+x Mo1−x O6−δ (x = 0.2, 0.4, 0.6) in 5 %H2/Ar
Thermogravimetric analysis in 5 % H2/Ar of the Sr1.6K0.4Fe1+x Mo1−x O6−δ (x = 0.2, 0.4, 0.6) samples synthesised in air, is shown in Fig. 2a. The initial weight loss at a temperature below 150 °C for samples Sr1.6K0.4Fe1.4Mo0.6O6−δ and Sr1.6K0.4Fe1.2Mo0.8O6−δ is probably due to the desorption of adsorbed water and gases. The further weight loss for all samples at a temperature of ~500 °C is due to the reduction of both iron and molybdenum ions accompanying with the loss of lattice oxygen [23]. In general, it is believed that reduction of iron ions is easier than that of molybdenum ions. From this point of view, sample Sr1.6K0.4Fe1.6Mo0.4O6−δ is expected to have the lowest reduction temperature. However, in the Sr1.6K0.4Fe1+x Mo1−x O6−δ series, the lower reduction temperature was observed for sample Sr1.6K0.4Fe1.4Mo0.6O6−δ. This indicates that, in this study, the reduction of Sr1.6K0.4Fe1+x Mo1−x O6−δ oxides is more complicated than expected and it is hard to decide which ions, iron, or molybdenum, will be reduced first.
In perovskite oxides obtained in air, the charges of ion and molybdenum ions are normally in the Fe3+/Fe4+ and Mo6+ respectively. In a reducing atmosphere, the state of ion is changed to Fe3+/Fe2+ while for molybdenum it is normally reduced to Mo5+.
The reduction of Fe4+ to Fe3+ can be described as
The reduction of Fe3+ to Fe2+ can be described as
The reduction of Mo6+ to Mo5+ can be described as
In the defect equations above, Kröger–Vink notations are used.
It can be noticed that the reduction of both iron and molybdenum ions accompanies with the loss of lattice oxygen and formation of oxygen vacancies.
Differential scanning calorimetry, as shown in Fig. 2b, of all samples exhibits an exothermic peak at a temperature around 500 °C upon heating is probably due to the reduction of perovskite oxides because endothermic peaks were not observed on cooling therefore it is irreversible indicating not related to phase changes. For samples with second-phase SrMoO4, the reduction of SrMoO4 starts at 750 °C in 4 %H2/Ar which happens at a much higher temperature [24]. There were some exothermic effects around 700 °C on heating which could be related to the phase transformation associated to the reduction of perovskite oxides (Fig. 2b). Samples with x = 0.2 and 0.4 exhibit exothermic effects at ~700 °C on cooling (Fig. 2b) which might be associated to the second-phase SrMoO4 which was presented in both samples. The sudden dip at DSC curve on cooling from 800 °C was caused by the STA system itself [25].
Structure of reduced Sr1.6K0.4Fe1+x Mo1−x O6−δ (x = 0.2, 0.4, 0.6)
Reduction of Sr1.6K0.4Fe1.2Mo0.8O6−δ in 5 % H2/Ar at 700 °C leads to a significant reduction in the proportion of the secondary SrMoO4 phase (PDF: 01-085-0809) in the XRD pattern, shown in Fig. 3. SrMoO4 is a stable oxide. It has been reported that reduction of SrMoO4 in 4 %H2/Ar began at 750 °C and completed after holding at 800 °C for about 3 h [24]. The reducing temperature, 700 °C in this study was not enough to convert SrMoO4 into SrMoO3. Therefore SrMoO3 was not observed. During the firing process, some SrMoO4 may react with the double oxide forming a new oxide with more Mo accommodated in the lattice. This indicates that a reducing atmosphere is in favour of the formation of single-phase double perovskite which was also observed in previous reports [5, 17]. The pattern of sample Sr1.6K0.4Fe1.4Mo0.6O6−δ was unchanged whilst an extra peak at ~45° was observed for sample Sr1.6K0.4Fe1.6Mo0.4O6−δ which belongs to the strongest (110) peak of α-Fe (PDF: 6-696) after the reduction at 700 °C [23, 26]. The splitting of some peaks at low d-spacing for sample Sr1.6K0.4Fe1.4Mo0.6O6−δ after reduction in 5 %H2/Ar at 700 °C (Fig. 3) is probably due to the reduced symmetry of the perovskite phase [27].
XRD patterns of Sr1.6K0.4Fe1+x Mo1−x O6−δ (x = 0.2, 0.4, 0.6) samples after reduction in 5 %H2/Ar at 1200 °C for 10 h are shown in Fig. 4. All samples exhibited a double perovskite structure (SG: Fm-3m), albeit with presence of a small proportion of a secondary Fe phase (PDF: 6-696). The structure of these materials differs from that observed by Hou et al. [16] for Sr1.6K0.4FeMoO6−δ, which was refined as a mixture of two perovskite structures (SG: Pm-3m) with similar lattice parameters. GSAS analysis, shown in Table 1, demonstrates a linear reduction in the lattice parameter with reducing molybdenum content. The GSAS plots of samples after reduction in 5 %H2/Ar at 1200 °C are shown in Fig. 5. The size of the molybdenum cation (Mo6+ = 0.59 Å, Mo5+ = 0.61 Å) at CN = 6 is generally smaller than that of iron in the Fm-3m structure (Fe 2+LS = 0.61 Å, Fe 2+HS = 0.78 Å, Fe 3+LS = 0.55 Å, Fe 3+HS = 0.645 Å) [28] which would intimate that a reduction in the lattice should occur with increasing molybdenum content. However, the presence of oxygen vacancies in the oxides may lead to enlarged lattice parameters. As the valency of these cations is known to alter with compositional modifications [29], it may be possible that the reduction in the molybdenum and iron ions could result in a modification of the valency of the B-site cations in Sr1.6K0.4Fe1+x Mo1−x O6−δ (x = 0.2, 0.4, 0.6) with formation of oxygen vacancies, resulting in the observed increase in the lattice parameter. Further investigation using Mössbauer spectroscopy could determine the feasibility of this supposition. The proportion of the secondary iron phase increased with increasing iron content. The exsolved Fe on the surface may improve the catalytic activity of the anode which was observed in previous reports [30–32].
Conductivity of Sr1.6K0.4Fe1+x Mo1−x O6−δ (x = 0.2, 0.4, 0.6)
Figure 6 shows the d.c. conductivity of all three samples in different atmospheres and redox history. The conductivity of samples in air measured from samples obtained from firing in air at 1200 °C for 2 h (red) is in the range of 10−2–10−1 S/cm indicating that the conductivity in an oxidising atmosphere is very low thus the materials are not suitable to be used as cathode materials for SOFCs.
Conductivity of Sr1.6K0.4Fe1+x Mo1−x O6−δ, x = 0.2 (a), x = 0.4 (b) and x = 0.6 (c) in air (red), in 5 % H2/Ar after reduction in 5 % H2/Ar at 1200 °C (black), in 5 % H2/Ar after further re-oxidation of the 1200 °C pre-reduced sample in air at 700 °C for 10 h then equilibrium in 5 %H2/Ar at 700 °C for 10 h (blue) (Color figure online)
To measure the conductivity of the sample after reduction at a high temperature, the samples were reduced in 5 %H2/Ar at 1200 °C for 10 h first, then the conductivity was measured in the same atmosphere. Samples Sr1.6K0.4Fe1.2Mo0.8O6−δ and Sr1.6K0.4Fe1.4Mo0.6O6−δ exhibited high electronic conductivity in 5 %H2/Ar, >40 Scm−1, over the entire temperature range (black). The conductivity of sample Sr1.6K0.4Fe1.6Mo0.4O6−δ was significantly lower after the same treatment, <1 S cm−1 over the same temperature range. In this Fe-rich sample, at a very strong reducing atmosphere, majority of iron ions is reduced to Fe2+ (3d6) or Fe3+ (3d5) ions while the high electronic conductivity of iron ions relies on the Fe4+ which has a 3d4 outer orbital. Moving of electrons in the low spin of Fe2+ ions or high spin of Fe3+ ion is quite difficult resulting in reduced conductivity [8]. The reduction of Mo6+ (4 d0) to Mo5+(4 d1) will introduce an electron in the 4d orbital which can be an electron charge carrier thus makeing the oxide conductive [8, 9, 23].
In order to exam the effects of redox process on the dc conductivity, the pellets pre-reduced at 1200 °C in 5 %H2/Ar for 10 h were re-oxidised in air at 700 °C for 12 h. The as-oxidised pellet was then held at 700 °C in 5 %H2/Ar for 10 h to reach an equilibrium before conducting the conductivity measurement in 5 %H2/Ar. As shown in Fig. 6, the conductivities of samples Sr1.6K0.4Fe1.2Mo0.8O6−δ and Sr1.6K0.4Fe1.6Mo0.4O6−δ after the re-oxidation and reduction processes are in the range of 10−2–10−1 S/cm which is insufficient for these materials to be used as anode for SOFCs. Only sample Sr1.6K0.4Fe1.4Mo0.6O6−δ exhibits a conductivity of 2–3 S/cm which is just enough for planar design [6]. The compounds did not attain similar conductivities as those observed after reduction at 1200 °C in 5 % H2/Ar, with the percentage retained increasing with iron content, 0.1 % for Sr1.6K0.4Fe1.2Mo0.8O6−δ, 7.5 % for Sr1.6K0.4Fe1.4Mo0.6O6−δ and 58.4 % for Sr1.6K0.4Fe1.6Mo0.4O6−δ after the re-oxidation and reduction processes. As the ratio of both Fe3+/Fe2+ and Mo6+/Mo5+ is known to be highly dependent on the reducing atmosphere and temperature [33, 34], it is expected that the reduction in the conductivity is a result of a lower degree of mixed valency due to the lower reduction temperature. In terms of total conductivity, sample Sr1.6K0.4Fe1.4Mo0.6O6−δ is the best among the investigated three samples. The possible reason is that, for Fe-rich sample with x = 0.6, in a reducing atmosphere, mainly it is iron that is reduced to Fe3+/Fe2+ ions with low conductivity as described above. In the Mo-rich sample with x = 0.2, the lattice is very strong and thus either iron or molybdenum can be reduced at mild condition (700 °C), leading to low conductivity as well. This could be the reason the conductivity of sample Sr1.6K0.4Fe1.2Mo0.8O6−δ exhibits similar conductivity in both air and mild reducing atmosphere (Fig. 6a). In sample with x = 0.4, the perovskite lattice is less strong than sample with x = 0.2, thus Mo6+ is partially reduced to Mo5+, resulting in high conductivity. SrMoO4 can be reduced to SrMoO3 (from Mo6+ to Mo4+) at 750 °C in 4 %H2/Ar [24]. In this study, we used 5 %H2/Ar as the reducing reagent, and thus it is possible to partially reduce Mo6+ to Mo5+ at slightly lower temperature, say, 700 °C with the presence of a large amount of weak Fe–O bonds in the lattice.
STA on re-oxidation of Sr1.6K0.4Fe1+x Mo1−x O6−δ (x = 0.2, 0.4, 0.6) in air
Re-oxidation of Sr1.6K0.4Fe1+x Mo1−x O6−δ (x = 0.2, 0.4, 0.6) after reduction in 5 % H2/Ar at 1200 °C caused an increase in weight proportional to the molybdenum content, as exhibited in Fig. 7a. The Mo-rich sample with x = 0.2 gained the greatest weight whilst the Fe-rich sample with x = 0.6 gained the fewest. This indicates iron, instead of molybdenum, has to be reduced to low valances in order to balance the positive and negative charge to form the single-phase perovskite oxide for sample Sr1.6K0.4Fe1.2Mo0.8O6−δ. Re-oxidation was observed to begin between 400 and 600 °C, lower than the current operating temperature of SOFCs. Re-oxidation of the pre-reduced oxides is negligible at a temperature below 350 °C, which indicates the materials can be used as electrode materials for fuel cells or other electrochemical devices at low temperatures [35]. Re-oxidation of these materials occurs at a similar temperature to that of Sr2FeMoO6−δ [14], suggesting a minimal modification of the material redox stability after partial replacement of strontium by potassium at the A-site of double perovskite Sr2FeMoO6−δ. A significant deviation was observed between 600 and 800 °C by differential scanning calorimetry, shown in Fig. 7b, for sample Sr1.6K0.4Fe1.2Mo0.8O6−δ, which can be attributed to the formation of the secondary SrMoO4 phase observed in the XRD pattern after redox cycling, Fig. 8.
XRD of Sr1.6K0.4Fe1+x Mo1−x O6−δ (x = 0.2, 0.4, 0.6) after redox cycling
After the samples were reduced in 5 %H2/Ar at 1200 °C for 10 h, they were further oxidised in air at 700 °C for 10 h and then cooled down to room temperature in air. XRD patterns of re-oxidised Sr1.6K0.4Fe1+x Mo1−x O6−δ (x = 0.2, 0.4, 0.6) are shown in Fig. 8. Trace amount of Fe (PDF: 6-696) phase was observed for sample Sr1.6K0.4Fe1.6Mo0.4O6−δ after redox cycling, with an increase from 2.1 % (Table 1) to 3.2 % (Table 2) in the phase fraction, whilst a SrMoO4 phase (PDF: 01-085-0809) was observed for sample Sr1.6K0.4Fe1.2Mo0.8O6−δ. Sample Sr1.6K0.4Fe1.4Mo0.6O6−δ was dominated by double perovskite structure (SG: Fm-3m) although a weak peak at ~35° cannot be indexed by known compounds (Fig. 8) indicating it is most redox stable. GSAS analysis, shown in Table 2, demonstrated a reduction in the lattice parameters after redox cycling due to the oxidation of Fe and Mo ions, although the lattice parameters of Sr1.6K0.4Fe1+x Mo1−x O6−δ (x = 0.2, 0.4, 0.6) samples exhibit no observable trend, reflecting the complexity of two multi-valent elements at the B-sites.
Introduction of potassium into Sr2Fe1+x Mo1−x O6−δ (x = 0.2, 0.4, 0.6) appears to have a negligible effect on the formability of these compounds, with the variation of the iron content exhibiting greater influence on material formability. Sample Sr1.6K0.4Fe1.4Mo0.6O6−δ that is most redox stable also retains reasonably high electrical conductivity which is a potential anode for SOFCs.
Conclusion
Potassium substitution into Sr2Fe1+x Mo1−x O6−δ (x = 0.2, 0.4, 0.6) with the intention of increasing the formability and ionic conductivity was successful only for Sr1.6K0.4Fe1.4Mo0.6O6−δ composition. Synthesis of Sr1.6K0.4Fe1+x Mo1−x O6−δ (x = 0.2, 0.4, 0.6) was achieved above 700 °C in 5 % H2/Ar, albeit with the formation of some impurity phases. Phase stability upon redox cycling was observed for sample Sr1.6K0.4Fe1.4Mo0.6O6−δ.
Redox cycling of Sr1.6K0.4Fe1+x Mo1−x O6−δ (x = 0.2, 0.4, 0.6) demonstrates a strong dependence on high temperature reduction to achieve high conductivities, with re-reduction at lower temperatures attaining between 0.1 and 58.4 % of the initial conductivity observed after high-temperature reduction. The reliance of these compounds on high-temperature reduction is expected to limit their utility as SOFC anode materials, as the vulnerability to oxidation can have disastrous consequence for fuel cell durability. However, the re-oxidation process is negligible at a temperature below 350 °C indicates they can be used as electrode materials for low temperature electrochemical devices including low temperature fuel cells. In the investigated new oxides, sample Sr1.6K0.4Fe1.4Mo0.6O6−δ that is most redox stable also retains reasonably high electrical conductivity, ~70 S/cm after reduction at 1200 °C and 2–3 S/cm after redox cycling at 700 °C, indicating it is a potential anode for SOFCs.
References
Atkinson A, Barnett S, Gorte RJ, Irvine JTS, McEvoy AM, Mogensen M et al (2004) Advanced anodes for high-temperature fuel cells. Nat Mater 3:17–27
Tao S, Irvine JTS (2004) Discovery and characterization of novel oxide anodes for solid oxide fuel cells. The Chemical Record. 4:83–95
Tao SW, Irvine JTS (2003) A redox-stable efficient anode for solid-oxide fuel cells. Nat Mater 2:320–323
Ruiz-Morales JC, Canales-Vazquez J, Savaniu C, Marrero-Lopez D, Zhou WZ, Irvine JTS (2006) Disruption of extended defects in solid oxide fuel cell anodes for methane oxidation. Nature 439:568–571
Huang Y-H, Dass RI, Xing Z-L, Goodenough JB (2006) Double perovskites as anode materials for solid-oxide fuel cells. Science 312:254–257
Cowin PI, Petit CT, Lan R, Irvine JT, Tao SW (2011) Recent progress in the development of anode materials for solid oxide fuel cells. Advanced Energy Materials. 1:314–332
Ge X-M, Chan S-H, Liu Q-L, Sun Q (2012) Solid oxide fuel cell anode materials for direct hydrocarbon utilization. Advanced Energy Materials. 2:1156–1181
Tao SW, Canales-Vazquez J, Irvine JTS (2004) Structural and electrical properties of the perovskite oxide Sr2FeNbO6. Chem Mater 16:2309–2316
Tao SW, Irvine JTS (2002) Study on the structural and electrical properties of the double perovskite oxide SrMn0.5Nb0.5O3-delta. J Mater Chem 12:2356–2360
Sengodan S, Choi S, Jun A, Shin TH, Ju Y-W, Jeong HY et al (2015) Layered oxygen-deficient double perovskite as an efficient and stable anode for direct hydrocarbon solid oxide fuel cells. Nature Materilas. 14:205–209
Liu Q, Dong XH, Xiao GL, Zhao F, Chen FL (2010) A novel electrode material for symmetrical SOFCs. Adv Mater 22:5478–5482
Zhang P, Huang Y-H, Cheng J-G, Mao Z-Q, Goodenough JB (2011) Sr2CoMoO6 anode for solid oxide fuel cell running on H2 and CH4 fuels. J Power Sources 196:1738–1743
Zhang L, Zhou Q, He Q, He T (2010) Double-perovskites A2FeMoO6 (A = Ca, Sr, Ba) as anodes for solid oxide fuel cells. J Power Sources 195:6356–6366
Vasala S, Lehtimaki M, Huang YH, Yamauchi H, Goodenough JB, Karppinen M (2010) Degree of order and redox balance in B-site ordered double-perovskite oxides, Sr2MMoO6 (M = Mg, Mn, Fe Co, Ni, Zn). J Solid State Chem 183:1007–1012
Xiao G, Liu Q, Dong X, Huang K, Chen FL (2010) Sr2Fe4/3Mo2/3O6 as anodes for solid oxide fuel cells. J Power Sources 195:8071–8074
S-eE Hou, Aguadero A, Alonso JA, Goodenough JB (2011) Fe-based perovskites as electrodes for intermediate-temperature solid oxide fuel cells. J Power Sources 196:5478–5484
Liu Q, Xiao GL, Howell T, Reitz TL, Chen FL (2011) A novel redox stable catalytically active electrode for solid oxide fuel cells. ECS Trans 35:1357–1366
Larson AC, Dreele RBV (1994) General structural analysis system. Los Alamos National Laboratory Report LAUR.86
Petit CTG, Lan R, Cowin PI, Irvine JTS, Tao SW (2011) Novel redox reversible oxide, Sr-doped cerium orthovanadate to metavanadate. J Mater Chem 21:525–531
Liu GY, Rao GH, Feng XM, Yang HF, Ouyang ZW, Liu WF et al (2003) Structural transition and atomic ordering in the non-stoichiometric double perovskite Sr2Fe x Mo2−x O6. J Alloy Compd 353:42–47
Kruth A, Tabuchi M, Guth U, West AR (1998) Synthesis, structure, electrical and magnetic properties of the new nonstoichiometric perovskite phase, Ca2MnNbOy. J Mater Chem 8:2515–2520
Rager J, Zipperle M, Sharma A, MacManus-Driscoll JL (2004) Oxygen stoichiometry in Sr2FeMoO6, the determination of Fe and Mo valence states, and the chemical phase diagram of SrO-Fe3O4-MoO3. J Am Ceram Soc 87:1330–1335
Cowin PI, Lan R, Petit CTG, Tao SW (2015) Conductivity and redox stability of double perovskite oxide SrCaFe1+x Mo1−x O6−δ (x = 0.2, 0.4, 0.6). Mater Chem Phys 168:50–57
Smith BH, Gross MD (2011) A highly conductive oxide anode for solid oxide fuel cells. Electrochem Solid State Lett. 14:B1–B5
Cowin PI, Lan R, Zhang L, Petit CTG, Kraft A, Tao SW (2011) Study on conductivity and redox stability of iron orthovanadate. Mater Chem Phys 126:614–618
Xiong Y, Xie Y, Li Z, Zhang R, Yang J, Wu C (2003) Complexing-reagent assisted synthesis of [small alpha]-Fe and [gamma]-Fe2O3 nanowires under mild conditions. New J Chem 27:588–590
Tao SW, Irvine JTS (2006) Phase transition in perovskite oxide La0.75Sr0.25Cr0.5Mn0.5O3-δ observed by in situ high-temperature neutron powder diffraction. Chem Mater 18:5453–5460
Shannon RD (1976) Acta Crystallographia Section A. A32:751–767
Yasukawa Y, Lindan J, Chan TS, Liu RS, Yamauchi H, Karppinen M (2004) Iron valence in double-perovskite (Ba, Sr, Ca)2FeMoO6: isovalent substitution effect. J Solid State Chem 177:2655–2662
Neagu D, Oh T-S, Miller DN, Menard H, Bukhari SM, Gamble SR et al (2015) Nano-socketed nickel particles with enhanced coking resistance grown in situ by redox exsolution. Nat Commun 6:8120
Neagu D, Tsekouras G, Miller DN, Menard H, Irvine JTS (2013) In situ growth of nanoparticles through control of non-stoichiometry. Nature Chemistry. 5:916–923
Xu SS, Dong DH, Wang Y, Doherty W, Xie K, Wu YC (2014) Perovskite chromates cathode with resolved and anchored nickel nano-particles for direct high-temperature steam electrolysis. J Power Sources 246:346–355
Alonso JA, Casais MT, MartAnez-Lope MJ, MartAnez JL, Velasco P, Munoz A et al (1999) Preparation, crystal structure, and magnetic and magnetotransport properties of the double perovskite Ca2FeMoO6. Chem Mater 12:161–168
Niebieskikwiat D, Sanchez RD, Caneiro A, Morales L, Vasquez-Mansilla M, Rivadulla F et al (2000) High-temperature properties of the Sr2FeMoO6 double perovskite: electrical resistivity, magnetic susceptibility, and ESR. Physical Review B. 62:3340–3345
Petit CT, Lan R, Cowin PI, Irvine JT, Tao SW (2011) Structure, conductivity and redox reversibility of Ca-doped cerium metavanadate. J Mater Chem 21:8854–8861
Acknowledgements
The authors thank EPSRC Flame SOFCs (EP/K021036/2), UK-India Biogas SOFCs (EP/I037016/1) and SuperGen Fuel Cells (EP/G030995/1) projects for funding. One of the authors (Cowin) thanks ScotChem SPIRIT scheme for support of his PhD study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
About this article
Cite this article
Cowin, P.I., Lan, R., Petit, C.T.G. et al. Conductivity and redox stability of new double perovskite oxide Sr1.6K0.4Fe1+x Mo1−x O6−δ (x = 0.2, 0.4, 0.6). J Mater Sci 51, 4115–4124 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-016-9734-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-016-9734-9