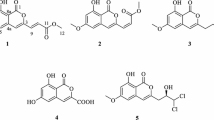
A new isocoumarin compound named setosphacohol A (1), together with six known ones, alternariol (2), isoaltenuene (3), phomasatin (4), alternariol 5-O-methyl ether (5), 1-deoxyrubralactone (6), and rubralactone (7), was isolated from the entomogenous fungus Setosphaeria sp. The structure of the new compound was elucidated by analysis of the 1D and 2D spectroscopic data as well as MS. Compounds 2, 5, 6 showed moderate cytotoxicity against six human tumor cell lines MCF-7, MGC-803, H1975, Huh-7, A549, and HeLa with IC50 values ranging from 23.04 to 96.91 μg·mL–1.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Isocoumarins comprise a six-membered oxygen heterocycle (α-pyranone) [1], along with one benzene ring, and exhibit a wide range of biological activities including anticancer, anti-HIV, antibacterial, antifungal, anti-inflamatory, antileukemic, antimalarial, antitubercular, and hepatoprotective activity [2]. Recently, an entomogenous fungus Setosphaeria sp. (strain LGWB-2) was isolated from Harmonia axyridis, obtained from Baoding (Hebei Province), People′s Republic of China. A new isocoumarin, setosphacohol A (1), together with six known ones (Fig. 1), was isolated from the methanol extract of the rice medium of Setosphaeria sp. Herein, we report the isolation, structural elucidation, and cytotoxicity of compounds 1–7 as shown in Fig. 1.
Compound 1 was obtained as a white solid. The molecular formula of 1 was determined as C16H22O7 by HR-ESI-MS at m/z 349.1241 [M + Na]+ (calcd 349.1263). The 1H NMR spectrum (Table 1) suggested the presence of one OH [δ 10.88 (1H, s, 8-OH)], one methyl [δ 0.97 (3H, t, J = 7.2 Hz, CH3-13)], three oxygenated methines [δ 4.46 (1H, m, H-3), 4.87 (1H, d, J = 10.2 Hz, H-4), and 4.15 (1H, m, H-10)], one aromatic proton [δ 6.77 (1H, s, H-5)], and two methoxy groups [δ 3.96 (3H, s, CH3O-6) and 3.89 (3H, s, CH3O-7)]. The 13C NMR spectrum (Table 1) of 1 showed 16 carbon resonances, including one methyl [δ 13.9 (q, C-13)], three methylenes, three oxygenated methine groups, two methoxy groups [56.3 (q, CH3O-6), and 60.8 (q, CH3O-7)], one olefinic carbon [δC 99.5 (d, C-5)], and six quaternary carbons (including one carbonyl δ 169.1). The NMR data of 1 showed close similarity to those in the literature [3], suggesting compound 1 possessed the same planar structure as that reported in the literature. This was further confirmed by interpretation of the HMBC long-range correlations from H-5 to C-4, C-6, C-7, C-8a and C-4a, H-4 to C-3, C-5, C-6, and C-4a, and H-9 to C-3 and C-4, and 1H–1H COSY H-3/H-4/H-9/H-10/H-11/H-12/H-13, as shown in Fig. 1.
The absolute configurations of compound 1 at C-3 and C-4 were determined from the NOESY and ECD spectra. The NOESY correlation of H-9/H-4 indicated the cis-configuration of H-3 and 4-OH. The simulated ECD spectrum for (3R,4R)-1 via Boltzmann statistics was compared with the experimental ECD spectrum (Fig. 2). According to Fig. 2, the calculated ECD spectral curve was a mirror-image of the experimental ECD spectrum. Therefore, the absolute configurations of C-3 and C-4 in compound 1 were determined as (3S,4S).
Compounds 2–7 were identified as alternariol (2) [4], isoaltenuene (3) [5], phomasatin (4) [6], alternariol 5-O-methyl ether (5, djalonensone) [7], 1-deoxyrubralactone (6) [8], and rubralactone (7) [9] by comparison of their NMR data with those reported in the literature. All compounds were evaluated for their cytotoxic activities against six human tumor cell lines MCF-7, MGC-803, H1975, Huh-7, A549, and HeLa by the MTT method, with cisplatin as positive control. Table 2 shows that compounds 2, 5, and 6 have moderate cytotoxicities with IC50 values ranging from 23.04 to 96.91 μg·mL–1, while compounds 1, 3, 4, and 7 were inactive against all the tested cancer cell lines with IC50 values over 100 μg·mL–1.
Experimental
General. Optical rotations were measured on a Perkin-Elmer 341 spectropolarimeter. Electronic circular dichroism spectra were measured using a JASCO J-715 circular dichroism spectrometer. IR spectra were acquired on a Perkin-Elmer 577 instrument. NMR spectra were recorded on a Bruker AM-600 spectrometer. HR-MS spectra were recorded on a Bruker apexultra 7.0T spectrometer. Column chromatography (CC) was conducted over silica gel (SiO2, 200–300 mesh; Yantai Zhi Fu Chemical Co., P. R. China), and Sephadex LH-20 gel (25–100 μm, GE Healthcare Co., Ltd., Sweden). TLC was conducted with silica gel GF254 plates (Yantai Zhi Fu Chemical Co., Ltd., P. R. China).
Fungus Material. The strain LGWB-2 was isolated from Harmonia axyridis collected in Baoding, Hebei Province of China. A voucher specimen of the fungus was deposited at the Key Laboratory of Medicinal Chemistry and Molecular Diagnosis of the Ministry of Education, College of Life Science of Hebei University. Setosphaeria sp. was inoculated into a 500 mL Erlenmeyer flask containing 200 mL of PD medium (20.0 g of glucose, 200.0 g of potato in 1 L of distilled H2O). Flask cultures were incubated at 25°C on a rotary shaker at 120 rpm/min for 4 days. Fermentation was carried out in 100 Erlenmeyer flasks (500 mL) each containing 80 g of rice, and 5 mL of culture liquid was transferred as seed into each flask and incubated at 27°C for 30 days.
Extraction and Isolation. The fermented material was extracted three times with methanol (25 L for each time), and the methanol extract was concentrated in vacuo to yield a yellow oily residue (132.0 g). This residue was subjected to SiO2 CC with gradient elution of petroleum ether (PE)–EtOAc (9:1, 6:1, 4:1, 2:1, and 1:1) to obtain six fractions (Frs. 1–6). Fraction 4 (4.3 g) was eluted with PE–EtOAc (30:1, 20:1, 15:1, 10:1, 5:1, and 1:1) to obtain six subfractions. Subfraction 4-3 was repeatedly purified by SiO2 CC and Sephadex LH-20 to afford compounds 1 (5.6 mg) and 2 (4.3 mg); the same method was used to obtain 3 (6.8 mg), and from Subfrs. 4-4 to obtain 4 (3.3 mg). Fraction 5 (3.7 g) was eluted with CH2Cl2–MeOH (20:1, 10:1, 5:1, 2:1, and 1:1) to obtain five subfractions. Subfraction 5-1 was repeatedly purified by SiO2 CC and recrystallized from MeOH to afford compounds 5 (10.3 mg), 6 (9.3 mg), and 7 (8.5 mg).
Setosphacohol A (1), C16H22O7, white powder; [α]25D –36° (c 0.1, CHCl3). IR (KBr, νmax, cm–1): 3406, 2924, 2850, 1668, 1423, 1276, 1115. For 1H and 13C NMR data, see Table 1. HR-ESI-MS at m/z 349.1241 [M + Na]+ (calcd for C16H22O7Na, 349.1263).
Cytotoxity Assay. The cells were cultured at Roswell Park Memorial Institute (RPMI1640, Hyclone, Logan, UT, USA, MCF-7, H1975) using Dulbecco′s modified Eagle′s medium (DMEM, Hyclone, Logan, UT, USA, MGC-803, HeLa, Huh-7, A549) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS, Hyclone, Logan, UT, USA) at 37°C under an atmosphere of 5% CO2 and were seeded on each well of 96-well plates containing 100 μL of tumor cell suspension (5 × 104 cells/mL). After 48 h, 2 μL (2 μg·mL–1) of the test compounds dissolved in an appropriate amount of DMSO (Sigma, St. Louis, MO, USA) was added to each well to a final concentration of 3.125, 6.25, 12.5, 25, 50, 100 μg·mL–1, with 0.5% DMSO as controls, to eliminate the effect of methanol on cells, and the whole was incubated for another 24 h. Then 20 μL of MTT solution (1 mg·mL–1, Beijing Cellchip Biotechnology Co., Ltd.) was added to each well, and the plate was incubated for 4 h under the same condition. Then 100 μL of SDS-HCl was added to each well and the whole incubated in a carbon dioxide incubator overnight. The absorbance in the control and drug-treated wells was measured using a microplate reader (Thermo Scientific, USA) at 570 nm (emission) wavelength. All experiments were carried out in triplicate and repeated twice. The cytotoxicity was expressed as IC50 value (50% inhibitory concentration calculated by the modified Karber method). The results were analyzed using SPSS 19.0.
References
S. Pal, V. Chatare, and M. Pal, Curr. Org. Chem., 15, 782 (2011).
A. Saeed, Eur. J. Med. Chem., 116, 290 (2016).
W. Zhang, K. Krohn, S. Draeger, and B. Schulz, J. Nat. Prod., 71, 1078 (2008).
T. Tanahashi, M. Kuroishi, A. Kuwahara, N. Nagakura, and N. Hamada, Chem. Pharm. Bull., 45, 1183 (1997).
A. Visconti, A. Bottalico, M. Solfrizzo, and F. Palmisano, Mycotoxin Res., 5, 69 (1989).
X. N. Sang, S. F Chen, X. An, G. Chen, H. F. Wang, and Y. H. Pei, J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res., 19, 436 (2017).
P. A. Onocha, D. A. Okorie, J. D. Connolly, and D. S. Roycroft, Phytochemistry, 40, 1183 (1995).
M. Naganuma, M. Nishida, K. Kuramochi, F. Sugawara, H. Yoshida, and Y. Mizushina, Bioorg. Med. Chem., 16, 2939 (2008).
Y. Kimura, T. Yoshinari, H. Koshino, S. Fujioka, K. Okada, and A. Shimada, Biosci. Biotech. Biochem., 71, 1896 (2007).
Acknowledgment
This work was kindly supported by the Post-graduate′s Innovation Fund Project of Hebei Province (Project CXZZBS2019026), the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2017YFD0201401), and the Central Public-Interest Scientific Institution Basal Research Fund for Chinese Academy of Tropical Agricultural Sciences (17CXTD-15; 1630052016008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Published in Khimiya Prirodnykh Soedinenii, No. 5, September–October, 2020, pp. 688–690.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, SS., Gao, WB., Kang, J. et al. Isolation and Cytotoxicity of Isocoumarins from the Entomogenous Fungus Setosphaeria sp.. Chem Nat Compd 56, 799–802 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10600-020-03155-3
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10600-020-03155-3