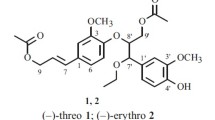
A new lignan (1) was isolated from the flowers of Forsythia koreana along with one known lignan, 4,4′-di-O-β-D-glucosylpinoresinol (2). The molecular structures were determined using spectral methods. These compounds were isolated from F. koreana flowers for the first time.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Forsythia koreana (Oleaceae), a perennial shrub, is widely distributed in China and Korea. It grows up to 1–3 m high and has oblong and ovate-lanceolate leaves [1]. The fruits of F. koreana (Forsythiae fructus), which are known in Korea as “Yeon-kyo,” are used in oriental medicine as an antipyretic medication and a detoxification agent [2]. They also exhibited inhibition effects on inflammatory and asthmatic symptoms [3, 4]. Previous studies isolated numerous phenylethanoids and lignans from Forsythiae fructus [5, 6]. However, phytochemicals present in the flowers of F. koreana have not been well studied. Here, we describe one new lignan of F. koreana flowers.
Dried F. koreana flowers were extracted in aqueous MeOH, and the concentrates were successively partitioned into EtOAc, n-BuOH, and aqueous fractions by polarity according to [7, 8]. Repeated SiO2 column chromatography of the n-BuOH and H2O fractions yielded two lignans. Their chemical structures were determined on the basis of NMR, IR, and FAB-MS data. The known lignan, compound 2, was identified as pinoresinol 4,4′-di-O-β-D-glucoside by comparison with previously reported data [9].

Compound 1 was isolated as a white amorphous powder, with mp of 83–84°C and an [α]D value of –47.8°. The molecular weight was determined to be 524 from the molecular ion peak m/z 547 [M + Na]+ in positive FAB/MS, and the molecular formula was determined to be C26H36O11 according to the highly-resolved molecular ion peak m/z 547.2151 [M + Na]+ (calcd for C26H36O11Na, 547.2155) in positive HR-FAB/MS. IR absorbance bands of hydroxyl (3455 cm–1) and aromatics (1625, 1615, 1525 cm–1) were detected. The 1H NMR signals of six olefine methines [δ 6.59 (1H, dd, J = 8.0, 2.0 Hz, H-6′), 6.71 (1H, d, J = 2.0 Hz, H-2′), 6.86 (1H, d, J = 8.0 Hz, H-5′), 6.63 (1H, dd, J = 8.0, 2.0, H-6), 6.72 (1H, d, J = 2.0, H-2), 7.19 (1H, d, J = 8.0, H-5)] were attributed to two 1,2,4-trisubstituted benzene rings. Proton signals were also observed for two oxygenated methylenes (δ 3.71, overlapped, H-9b, 9′b; 3.81, overlapped, H-9a, 9′a), two methoxyls (δ 3.40 s; 3.43 s), two methylenes (δ 2.74, overlapped, H-7, 7′), and two methines (δ 2.12, m, H-8, 8′). The proton signals of a hemiacetal (δ 5.28, d, J = 6.4 Hz, H-1′′), an oxygenated methylene (δ 4.08, dd, J = 12.0, 5.2 Hz, H-6′′b; 4.27, dd, J = 12.0 Hz, 1.2, H-6′′a), and four oxygenated methines (3.53, overlapped, H-5′′; 3.65, overlapped, H-2′′; 3.69, overlapped, H-4′′; 3.73, overlapped, H-3′′) were attributed to a hexose. The large coupling constant of the anomer proton signal (J = 6.4 Hz) confirmed that both the anomer proton (H-1′′) and the next proton (H-2′′) were in axial positions. The above-mentioned proton signals indicated that compound 1 was an enterodiol-type lignan monoglycoside. The 13C NMR data showed 26 peaks comprising those of one hexose and two methoxyls, confirming that compound 1 is a lignan monoglycoside with two methoxy groups and one hexose. The carbon chemical shifts revealed the hexose to be β-glucopyranose. Four oxygenated olefine quaternaries (δ 146.9, C-4; 149.2, C-4′; 150.2, C-3; 150.7, C-3′), two olefine quaternaries (δ 133.7, C-1; 137.0, C-1′), six olefine methines (δ 114.2, C-2; 114.9, C-2′; 116.9, C-5; 117.2, C-5′; 122.7, C-6; 123.1, C-6′), two oxygenated methylenes (δ 61.7, C-9′; 61.9, C-9), two methoxyls (δC 56.6, C-OCH3 × 2), two methines (δ 44.9, C-8′; 45.1, C-8), and two methylenes (δ 36.4, C-7, 7′) were attributed to the aglycone moiety. The gHMBC correlation between the anomer proton (δ 5.28, H-1′′) and oxygenated olefine quaternary carbon (δ 146.9, C-4) designated the β-glucose to be at C-4. Two methoxy protons signals (δ 3.43; 3.40) correlated with the oxygenated olefine quaternary carbons (δ 149.2, C-4′; 150.2, C-3), indicating two methoxyls to be at C-3 and C-4′. The absolute stereostructures of chiral carbons were determined to be 8R and 8′R from the negative Cotton effect at 239 nm (Δε –2.3) and the positive Cotton effect at 284 nm (Δε +1.3) in the CD spectrum [10]. Taken together, the chemical structure of compound 1 was determined to be a (8R,8′R)-3′-hydroxy-3,4′-dimethoxyenterodiol 4-O-β-D-glucopyranoside, which is a new lignan that we named koreanaside C.
General. Experiments were performed as described previously [11]. Circular dichroism (CD) spectra were obtained with a Chirascan Plus instrument (Applied Photophysics, Surrey, UK).
Plant Material.F. koreana flowers were collected from Kyunghee University Campus, Yong-In, Korea in April 2015 and their identity was confirmed by Prof. D. K. Kim, Woossuk University, Jeonju, Korea. A voucher specimen was lodged with the Natural Product Chemistry Laboratory, Kyunghee University.
Extraction ofF. koreanaFlowers and Isolation of Lignans. F. koreana flowers were dried in the shade for 3 days and stored at 4°C until used for extraction. The dried flowers of F. koreana (962 g) were extracted with 80% aqueous MeOH (33 L × 2) at room temperature for 24 h. The concentrated extracts were poured into H2O (500 mL) and successively extracted with ethyl acetate (EtOAc, 500 mL × 5) and n-butanol (n-BuOH, 500 mL × 4). Separation of each layer and concentration under reduced pressure resulted in an EtOAc fraction (45 g, FKE), n-BuOH fraction (110 g, FKB), and aqueous fraction (213 g, FKH). Fraction FKB (110 g) was subjected to silica gel (SiO2) column chromatography (CC) (∅ 11 × 15 cm) and eluted with CHCl3–MeOH–H2O (30:3:1→20:3:1→10:3:1, 43 L of each) → EtOAc-n-BuOH–H2O (8:10:2, 45 L) by examining the obtained fractions using TLC, yielding 15 fractions (FKB-1–FKB-15). Fraction FKB-6 [elution volume/total volume (Ve/Vt) 0.413–0.486, 3.1 g] was subjected to SiO2 CC (∅ 5 × 17 cm) and eluted with CHCl3–MeOH–H2O (24:6:2, 3.9 L), giving 16 fractions (FKB-6-1–FKB-6-16). Fraction FKB-6-12 (Ve/Vt 0.382–0.547, 1.6 g) was subjected to ODS CC (∅ 4 × 5 cm) and eluted with MeOH–H2O (1:3, 2 L) to give 13 fractions (FKB-6-12-1–FKB-6-12-13), including purified compound 1 [FKB-6-12-9, 55.6 mg, Ve/Vt 0.215–0.600, TLC (Kieselgel 60 F254) Rf 0.51, CHCl3–MeOH–H2O (7:3:1), (RP-18 F254S) 0.55, acetone–H2O (1:3)]. Fraction FKH (213 g) was subjected to Diaion HP-20 CC (∅ 12 × 15 cm) and eluted with 100% H2O (30 L) → 100% MeOH (13 L), yielding six fractions (FKH-1–FKH-6). Fraction FKH-6 (Ve/Vt 0.815–1.000, 30.0 g) was subjected to SiO2 CC (∅ 11 × 15 cm) and eluted with CHCl3–MeOH–H2O (10:3:1→8:3:1→7:3:1, 35 L of each) to give 15 fractions (FKH-6-1–FKH-6-15). Fraction FKH-6-8 (Ve/Vt 0.271–0.486, 816 mg) was subjected to ODS CC (∅ 3 × 5 cm) and eluted with MeOH–H2O (2:3→2:1, 800 mL of both) to give 13 fractions (FKH-6-8-1–FKH-6-8-13). Fraction FKH-6-8-3 (Ve/Vt 0.043–0.077, 325 mg) was subjected to Sephadex LH-20 CC (∅ 2 × 60 cm) and eluted with 100% MeOH (1 L) to give 10 fractions (FKH-6-8-3-1–FKH-6-8-3-10). Fraction FKH-6-8-3-6 (Ve/Vt 0.500–0.515, 119 mg) was subjected to SiO2 CC (∅ 2.5 × 15 cm) and eluted with EtOAc–n-BuOH–H2O (12:3:1→8:3:1, 1.6 L of both) to give 15 fractions (FKH-6-8-3-6-1–FKH-6-8-3-6-15), including purified compound 2 [Fr. FKH-6-8-3-6-13, 14.5 mg, Ve/Vt 0.500–0.646, TLC (Kieselgel 60 F254) Rf 0.35, EtOAc–n-BuOH–H2O (6:3:1), (RP-18 F254S) 0.72, acetone–MeOH–H2O (1:1:2)].
Koreanaside C (1). White amorphous powder (MeOH), mp 83–84°C, [α]D –47.8° (c 0.5, MeOH). HR FAB/MS m/z 547.2151 [M + Na]+ (cacld for C26H36O11Na, 547.2155). IR (KBr, ν, cm–1): 3455, 1625, 1615, 1525. 1H NMR (400 MHz, pyridine-d5, δ, J/Hz): 2.12 (2H, m, H-8, 8′), 2.74 (4H, overlapped, H-7, 7′), 3.40 (3H, s, OCH3), 3.43 (3H, s, OCH3), 3.53 (1H, overlapped, H-5′′), 3.65 (1H, overlapped, H-2′′), 3.69 (1H, overlapped, H-4′′), 3.71 (2H, overlapped, H-9b, 9′b), 3.73 (1H, overlapped, H-3′′), 3.81 (2H, overlapped, H-9a, 9′a), 4.08 (1H, dd, J = 12.0, 5.2, H-6′′b), 4.27 (1H, dd, J = 12.0, 1.2, H-6′′a), 5.28 (1H, d, J = 6.4, H-1′′), 6.59 (1H, dd, J = 8.0, 2.0, H-6′), 6.63 (1H, dd, J = 8.0, 2.0, H-6), 6.71 (1H, d, J = 2.0, H-2′), 6.72 (1H, d, J = 2.0, H-2), 6.86 (1H, d, J = 8.0, H-5′), 7.19 (1H, d, J = 8.0, H-5). 13C NMR (100 MHz, pyridine-d5, δ, ppm): 36.4 (C-7′), 36.4 (C-7), 44.9 (C-8′), 45.1 (C-8), 56.6 (C-OCH3 × 2), 61.7 (C-9′), 61.9 (C-9), 63.0 (C-6′′), 71.9 (C-4′′), 75.5 (C-2′′), 79.0 (C-3′′), 79.3 (C-5′′), 103.4 (C-1′′), 114.2 (C-2), 114.9 (C-2′), 116.9 (C-5), 117.2 (C-5′), 122.7 (C-6), 123.1 (C-6′), 133.7 (C-1), 137.0 (C-1′), 146.9 (C-4), 149.2 (C-4′), 150.2 (C-3), 150.7 (C-3′).
Pinoresinol-4,4′-di-O-β-D-glucopyranoside (2). Colorless needles (MeOH), mp 219–220°C, [α]D –76.4° (c 1.0, MeOH). FAB-MS m/z 683.2 [M + H]+. IR (KBr, ν, cm–1): 3460, 3450, 1597, 1514, 1460.
References
I. R. Kim, Herbal Medicine, Jungumsa, Seoul, 2009, 242 pp.
Y. H. Choi, J. Kim, and K. P. Yoo, Chromatographia, 57, 73 (2003).
H. Lim, J. G. Lee, S. H. Lee, Y. S. Kim, and H. P. Kim, J. Ethnopharmacol., 118, 113 (2008).
J. H. Lee, J. Y. Lee, T. D. Kim, and C. J. Kim, Phytother. Res., 25, 387 (2010).
S. K. El-Desouky and Y. K. Kim, Z. Naturforsch. B, 63, 90 (2008).
U. W. Hawas, A. M. Gamal-Eldeen, S. K. El-Desouky, Y. K. Kim, A. Huefner, and R. Saf, Z. Naturforsch. C, 68, 29 (2013).
Y. S. Baek, N. Y. Song, T. G. Nam, D. O. Kim, H. C. Kang, O. K. Kwon, and N. I. Baek, Appl. Biol. Chem., 58, 787 (2016).
N. T. Nguyen, H. S. Song, E. J. Oh, Y. G. Lee, J. H. Ko, J. E. Kwon, S. C. Kang, D. Y. Lee, I. H. Jung, and N. I. Baek, Appl. Biol. Chem., 60, 527 (2017).
S. X. Qiu, Z. Z. Lu, L. Luyengi, S. K. Lee, J. M. Pezzuto, N. R. Farnsworth, L. U. Thompson, and H. H. S. Fong, Pharm. Biol., 37, 1 (1999).
J. Fritsche, R. Angoelal, and M. Dachtler, J. Chromatogr. A, 972, 195 (2002).
E. J. Oh, J. H. Kwon, S. Y. Kim, S. J. In, D. G. Lee, M. Y. Cha, H. C. Kang, J. H. Bo, Y. H. Lee, I. S. Chung, and N. I. Baek, Appl. Biol. Chem., 59, 567 (2016).
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by the Korean Institute of Planning and Evaluation for Technology in Food, Agriculture, and Forestry (IPET) through the Agri-Bio Industry Technology Development Program, funded by the Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Rural Affairs (MAFRA) (317071-03-1-SB020).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Published in Khimiya Prirodnykh Soedinenii, No. 3, May–June, 2019, pp. 370–372.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, YG., Seo, KH., Gwag, J.E. et al. New Lignan from the Flowers of Forsythia koreana. Chem Nat Compd 55, 432–434 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10600-019-02707-6
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10600-019-02707-6