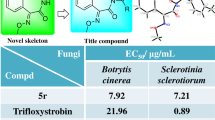
A series of 6H-benzimidazo[1,2-c][1,3]benzoxazin-6-one derivatives were synthesized in moderate to good yield by reaction of 2-(1H-benzimidazol-2-yl)phenols with triphosgene, and the structures of the target compounds were characterized by NMR, IR, and HRMS methods. The fungicidal activity of the compounds was evaluated at 50 μg/ml concentration, and unsubstituted 6H-benzimidazo-[1,2-c][1,3]benzoxazin-6-one showed 75.1% activity against Sclerotinia sclerotium, which was higher than that of chlorothalonil.
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
1,3-Benzoxazinone derivatives have received much attention in the research fields of pharmaceuticals and pesticides because of their broad pharmacological and biological activities such as antibacterial and antifungal,1,2,3 peroxisome proliferator activated receptor (PPAR) agonistic, antidiabetic, antihyperlipidaemic,4 DNA-PK enzyme inhibiting,5,6 anticancer.7,8 1,3-Benzoxazinone derivatives also possess photochromic properties.9,10 Therefore, the studies on 1,3-benzoxazinones raised great interest of chemists. On the other hand, benzimidazoles also have unique activities like insecticidal,11,12 antibacterial and antifungal,13,14,15 herbicidal,16 and antiviral.17 Benzimidazole derivative carbendazim (methyl benzimidazol-2-ylcarbamate) is extensively used as anthelmintic, antiprotozoal agent, and post-harvest fungicide on fruits and vegetables.18 Thiabendazole serves as a common post-harvest pesticide to control the diseases of citrus fruits caused by fungi.19
Recently, we reported series of substituted 1,3-benzoxazines which showed good fungicidal activities.20,21,22
However, to our knowledge, there are few reports on compounds containing both 1,3-benzoxazinone and benzimidazole moieties. Therefore, we designed a new class of 6H-benzimidazo[1,2-c][1,3]benzoxazin-6-one derivatives 4 by the fusion of 1,3-benzoxazinone moiety and benzimidazole structure in order to obtain highly active compounds as our continuous projects aimed at the discovery of new active fungicidies.20,21,22,23 The synthetic route to the target compounds 4a–p is shown in Scheme 1.
The intermediate 2-(1H-benzimidazol-2-yl)phenols 3a–p were synthesized in 38–78% yields (Table 1) by the reaction of substituted salicylaldehydes 1a–h with benzene-1,2-diamine derivatives 2a,b in the presence of NaHSO3 in EtOH24 (Scheme 1). Afterward, to prepare substituted 6H-benzimidazo[1,2-c][1,3]benzoxazin-6-ones 4a–p, we initially screened the reaction conditions using the reaction of 2-(1H-benzimidazol-2-yl)phenol (3a) with triphosgene25 as a model reaction (Table 2). It was found that in the absence of a base the reaction gave the desired product 4a in only 8% yield (Table 2, entry 1). In the search of an appropriate base (Table 2, entries 2–6), Et3N was found to be the most suitable for the reaction as shown by yield of 75% (Table 2, entry 7). Then, we investigated the effect of the ratio of reactants, temperature, and reaction time on the yield of the reaction (Table 2, entries 8–18, 20) and obtained the optimized reaction conditions: the molar ratio of compound 3a : triphosgene : Et3N = 1:0.65:2, temperature 100°C, time 22 h, in which the desired product 4a was produced in 83% yield (Table 2, entry 19).
Under the optimized reaction conditions 6H-benzimidazo-[1,2-c][1,3]benzoxazin-6-ones 4a–p were prepared in 38–83% yields (Table 1). It can be seen that the yield of compound 4a without the substituents in 1,3-benzoxazinone and benzimidazole is higher than the yields of compounds with any R = Me (Table 1, entries 1–4). Moreover, the position of methyl or methoxy group on the phenyl ring has influence on the reaction yield following the order of position 6 > position 7 > position 8 regardless of the nature of the substituent.
The structures of compounds 4a–p were characterized by IR, 1H and 13C NMR spectra, and HRMS. This can be illustrated with compound 4b. In 1H NMR spectrum, signals at 8.26–7.30 ppm correspond to the protons of the phenyl group, and the single peak at 2.48 ppm – to the protons of the methyl group. In 13C NMR spectrum, the peak at 149.4 ppm belongs to the carbonyl carbon, the signals at 146.1–111.9 ppm correspond to the carbons of the phenyl group. The signal at 143.7 ppm corresponds to carbon atom linked to the N=C double bond, and signal at 15.6 ppm – to the methyl carbon.
According to the standard method NY/T1156.5-2006,20,21,22 the in vitro fungicidal activity of compounds 4a–p against Sclerotinia sclerotium, Phytophthora capsici, Botrytis cinerea, Rhizoctonia solani, Gibberella zeae, and Magnaporthe oryzae was evaluated at the 50 μg/ml concentration, employing the mycelium growth rate test method with chlorothalonil as the reference compound. As shown in Table 3, compounds 4a–p exhibited moderate to good fungicidal activity against the tested fungi. In general, the fungicidal activity against Sclerotinia sclerotium was the best, and the activities of compounds 4a,c,h,n were 75.1, 63.6, 56.9, and 58.8%, respectively, which are all higher than that of chlorothalonil. For Gibberella zeae, Phytophthora capsici, Sclerotinia sclerotium, and Magnaporth oryzae, compound 4a without substituents on the phenyl
ring demonstrated higher activity than those with substituents. For Rhizoctonia solani, compounds 4h,p with electron-withdrawing group (R1 = Br) showed higher activity than those with electron-donating group or hydrogen. For Gibberella zeae, compounds with methyl group as a substituent exhibited higher activity than those with methoxy group regardless of the position of these groups, and for Botrytis cinerea, when any R = Me, the fungicidal activity of compounds abided the same rule.
In conclusion, we have prepared a variety of substituted 1,3-benzoxazinobenzimidazoles in moderate to good yields, and the fungicidal activity of the compounds was evaluated. 6H-Benzimidazo[1,2-c][1,3]benzoxazin-6-one showed 75.1% activity against Sclerotinia sclerotium, which was higher than that of the reference compound chlorothalonil.
Experimental
IR spectra of compounds were recorded for samples in KBr pellets on a Nicolet 6700 FT-IR instrument. 1H and 13C NMR spectra (500 and 125 MHz, respectively) were recorded on a Bruker Avance spectrometer in DMSO-d6 or CDCl3 using TMS as internal standard. HRMS were recorded on a Waters UPLC/XevoQTof LC/MS instrument (ESI). Melting points were determined on a WRS-1B digital melting point apparatus and were uncorrected. Column chromatography was carried out using silica gel (200–300 mesh).
Reagents were purchased from Meryer Chemical Technology Co., Ltd. and Energy & Chemicals Company (China) of analytical grades and used without further purification. All anhydrous solvents were dried by standard procedures.
Synthesis of substituted 2-(1 H -benzimidazol-2-yl)-phenols 3а–p 24 (General method). Salicylaldehyde 1a–h (10 mmol) and NaHSO3 (1.56 g, 15 mmol) were added into a 100-ml round-bottomed flask containing EtOH (30 ml), and the mixture was stirred at room temperature for 4 h. Then the corresponding benzene-1,2-diamine 2a,b (10 mmol) was added and the solution was heated at 75°C for 3 h (checked by TLC). After the reaction was completed, the reaction solution was poured into cold H2O (100 ml), and a large amount of precipitate formed. After standing, the solid was filtered off, washed with EtOAc, and the obtained crude product was purified by column chromatography, eluent EtOAc – petroleum ether, 1:4.
2-(1 H -Benzimidazol-2-yl)phenol (3a). Yield 1.618 g (77%), white solid, mp 251–252°C. IR spectrum, ν, cm–1: 3325 (NH), 1632 (C=N), 1594 (C=C). 1H NMR spectrum (DMSO-d6), δ, ppm (J, Hz): 13.13 (2H, s, OH, NH); 8.02 (1H, dd, J = 7.8, J = 1.4, H Ar); 7.67 (1H, d, J = 6.7, H Ar); 7.57 (1H, s, H Ar); 7.34 (1H, s, H Ar); 7.24 (2H, s, H Ar); 7.01–6.98 (2H, m, H Ar). 13C NMR spectrum (DMSO-d6), δ, ppm: 158.0 (C–OH); 151.7 (C=N); 140.9; 133.2; 131.7; 126.2; 123.3; 122.4; 119.1; 117.9; 117.2; 112.6; 111.5. Found, m/z: 210.0798 [M+H]+. C13H10N2O. Calculated, m/z: 210.0793.
2-(1 H -Benzimidazol-2-yl)-6-methylphenol (3b). Yield 1.390 g (62%), yellow solid, mp 218–220°C. IR spectrum, ν, cm–1: 3239 (NH), 1626 (C=N), 1596 (C=C). 1H NMR spectrum (DMSO-d6), δ, ppm (J, Hz): 13.55 (1H, s, NH); 13.27 (1H, s, OH); 7.92 (1H, d, J = 7.8, H Ar); 7.75 (1H, d, J = 7.8, H Ar); 7.63 (1H, d, J = 7.8, H Ar); 7.34–7.29 (3H, m, H Ar); 6.95 (1H, s, H Ar); 2.29 (3H, s, CH3). 13C NMR spectrum (DMSO-d6), δ, ppm: 156.5 (C–OH); 152.2 (C=N); 140.8; 133.2; 132.6; 125.8; 123.7; 123.4; 122.5; 118.6; 117.9; 111.6; 111.5; 15.9 (CH3). Found, m/z: 224.0955 [M+H]+. C14H12N2O. Calculated, m/z: 224.0950.
2-(1 H -Benzimidazol-2-yl)-5-methylphenol (3c). Yield 1.570 g (70%), yellow solid, mp 237–239°C. IR spectrum, ν, cm–1: 3254 (NH), 1634 (C=N), 1587 (C=C). 1H NMR spectrum (DMSO-d6), δ, ppm (J, Hz): 13.13 (2H, s, OH, NH); 7.97 (1H, d, J = 8.0, H Ar); 7.68 (2H, d, J = 3.3, H Ar); 7.30–7.29 (2H, m, H Ar); 6.90 (1H, s, H Ar); 6.87 (1H, d, J = 8.0, H Ar); 2.35 (3H, s, CH3). 13C NMR spectrum (DMSO-d6), δ, ppm: 158.0 (C–OH); 151.9 (C=N); 142.0; 126.0 (2C); 122.5; 120.1 (2C); 117.8; 117.4 (2C); 111.4; 110.0; 21.1 (CH3). Found, m/z: 224.0944 [M+H]+. C14H12N2O. Calculated, m/z: 224.0950.
2-(1 H -Benzimidazol-2-yl)-4-methylphenol (3d). Yield 1.637 g (73%), yellow solid, mp 247–248°C. IR spectrum, ν, cm–1: 3289 (NH), 1637 (C=N), 1586 (C=C). 1H NMR spectrum (DMSO-d6), δ, ppm (J, Hz): 13.16 (1H, s, NH); 12.94 (1H, s, OH); 7.91 (1H, s, H Ar); 7.72 (1H, s, H Ar); 7.64 (1H, s, H Ar); 7.29 (2H, s, H Ar); 7.20 (1H, d, J = 8.3, H Ar); 6.97 (1H, d, J = 8.3, H Ar); 2.35 (3H, s, CH3). 13C NMR spectrum (DMSO-d6), δ, ppm: 155.9 (C–OH); 151.8 (C=N); 141.0; 133.2; 132.4; 127.6; 126.2; 123.1; 122.3; 117.9; 117.0; 112.2; 111.5; 20.2 (CH3). Found, m/z: 224.0942 [M+H]+. C14H12N2O. Calculated, m/z: 224.0950.
2-(1 H -Benzimidazol-2-yl)-6-methoxyphenol (3e). Yield 1.754 g (73%), white solid, mp 217–218°C. IR spectrum, ν, cm–1: 3335 (NH), 1626 (C=N), 1593 (C=C). 1H NMR spectrum (DMSO-d6), δ, ppm (J, Hz): 13.28 (2H, s, OH, NH); 7.76–7.69 (3H, m, H Ar); 7.32 (2H, s, H Ar); 7.09 (1H, d, J = 7.9, H Ar); 6.98 (1H, t, J = 8.0, H Ar); 3.87 (3H, s, OCH3). 13C NMR spectrum (DMSO-d6), δ, ppm: 152.0 (C–OH); 148.6 (C=N); 148.4; 140.8; 133.1; 123.3; 122.5; 118.7; 118.0; 117.6; 113.9; 112.6; 111.6; 55.7 (OCH3). Found, m/z: 240.0895 [M+H]+. C14H12N2O2. Calculated, m/z: 240.0899.
2-(1 H -Benzimidazol-2-yl)-5-methoxyphenol (3f). Yield 1.850 g (77%), white solid, mp 238–239°C. IR spectrum, ν, cm–1: 3347 (NH), 1619 (C=N), 1590 (C=C). 1H NMR spectrum (DMSO-d6), δ, ppm (J, Hz): 13.46 (1H, s, NH); 13.08 (1H, s, OH); 8.02 (1H, d, J = 8.6, H Ar); 7.70 (1H, s, H Ar); 7.62 (1H, s, H Ar); 7.28 (2H, d, J = 4.3, H Ar); 6.67 (2H, dt, J = 6.3, J = 2.4, H Ar); 3.84 (3H, s, OCH3). 13C NMR spectrum (DMSO-d6), δ, ppm: 162.2 (C–OH); 160.0 (C=N); 152.1; 140.8; 127.3; 122.8; 122.2; 117.5 (2C); 111.2; 106.5; 105.7; 101.5; 55.3 (OCH3). Found, m/z: 240.0899 [M+H]+. C14H12N2O2. Calculated, m/z: 240.2573.
2-(1 H -Benzimidazol-2-yl)-4-methoxyphenol (3g). Yield 1.874 g (78%), white solid, mp 283–284°C. IR spectrum, ν, cm–1: 3314 (NH), 1612 (C=N), 1590 (C=C). 1H NMR spectrum (DMSO-d6), δ, ppm (J, Hz): 13.14 (1H, s, NH); 12.77 (1H, s, OH); 7.71 (3H, d, J = 1.7, H Ar); 7.32–7.30 (2H, m, H Ar); 7.04–7.00 (2H, m, H Ar); 3.84 (3H, s, OCH3). 13C NMR spectrum (DMSO-d6), δ, ppm: 152.0 |(C–OH); 151.9 (C=N); 150.8; 139.6; 132.1; 131.6; 130.9; 118.3; 118.0; 117.8; 112.5; 111.4; 109.7; 55.7 (OCH3). Found, m/z: 240.0899 [M+H]+. C14H12N2O2. Calculated, m/z: 240.2573.
2-(1 H -Benzimidazol-2-yl)-4-bromophenol (3h). Yield 1.157 g (40%), white solid, mp 220–221°C. IR spectrum, ν, cm–1: 3346 (NH), 1636 (C=N), 1582 (C=C). 1H NMR spectrum (DMSO-d6), δ, ppm (J, Hz): 13.29 (2H, s, OH, NH); 8.29 (1H, s, H Ar); 7.70 (1H, s, H Ar); 7.64 (1H, s, H Ar); 7.51 (1H, d, J = 8.4, H Ar); 7.29 (2H, s, H Ar); 7.01 (1H, d, J = 8.7, H Ar). 13C NMR spectrum (DMSO-d6), δ, ppm: 157.2 (C–OH, C=N); 150.3 (2C); 133.9 (2C); 128.4 (2C); 123.1; 119.4 (2C); 114.6; 110.1. Found, m/z: 287.9891 [M+H]+. C13H9BrN2O. Calculated, m/z: 287.9898.
2-(5,6-Dimethyl-1 H -benzimidazol-2-yl)phenol (3i). Yield 1.763 g (74%), white solid, mp 238–239°C. IR spectrum, ν, cm–1: 3256 (NH), 1636 (C=N), 1590 (C=C). 1H NMR spectrum (DMSO-d6), δ, ppm (J, Hz): 13.24 (1H, s, NH); 12.94 (1H, s, OH); 8.00 (1H, d, J = 7.6, H Ar); 7.46 (1H, s, H Ar); 7.34 (2H, t, J = 7.7, H Ar); 6.99 (2H, m, H Ar); 2.33 (6H, s, 2CH3). 13C NMR spectrum (DMSO-d6), δ, ppm: 157.9 (C–OH); 150.8 (C=N); 131.3 (2C); 125.9 (2C); 119.0 (2C); 117.9; 117.1 (2C); 112.8; 111.5; 20.0 (2CH3). Found, m/z: 238.1101 [M+H]+. C15H14N2O. Calculated, m/z: 238.1106.
2-(5,6-Dimethyl-1 H -benzimidazol-2-yl)-6-methylphenol (3j). Yield 1.539 g (61%), yellow solid, mp 297–298°C. IR spectrum, ν, cm–1: 3342 (NH), 1632 (C=N), 1601 (C=C). 1H NMR spectrum (DMSO-d6), δ, ppm (J, Hz): 13.64 (1H, s, NH); 13.00 (1H, s, OH); 7.91 (1H, d, J = 7.6, H Ar); 7.55 (1H, s, H Ar); 7.42 (1H, s, H Ar); 7.30 (1H, d, J = 7.2, H Ar); 6.96 (1H, t, J = 7.6, H Ar); 2.42 (3H, s, CH3); 2.40 (3H, s, CH3); 2.32 (3H, s, CH3). 13C NMR spectrum (DMSO-d6), δ, ppm: 156.2 (C–OH); 151.2 (C=N); 139.3; 132.1; 132.0; 131.6; 130.8; 125.5; 123.3; 118.4; 117.9; 111.8; 111.4; 20.0 (CH3); 19.9 (CH3); 15.8 (CH3). Found, m/z: 252.1257 [M+H]+. C16H16N2O. Calculated, m/z: 252.1263.
2-(5,6-Dimethyl-1 H -benzimidazol-2-yl)-5-methylphenol (3k). Yield 1.716 g (68%), yellow solid, mp 238–239°C. IR spectrum, ν, cm–1: 3235 (NH), 1648 (C=N), 1585 (C=C). 1H NMR spectrum (DMSO-d6), δ, ppm (J, Hz): 13.24 (1H, s, NH); 12.91 (1H, s, OH); 7.95 (1H, d, J = 7.0, H Ar); 7.56–7.42 (2H, m, H Ar); 6.97–6.81 (2H, m, H Ar); 2.39 (6H, s, 2CH3); 2.38 (3H, s, CH3). 13C NMR spectrum (DMSO-d6), δ, ppm: 157.8 (C–OH); 151.1 (C=N); 141.5; 139.4; 131.8; 131.5; 130.7; 125.7; 120.0; 117.8; 117.3; 111.3; 110.2; 21.1 (CH3); 20.0 (CH3); 19.9 (CH3). Found, m/z: 252.1256 [M+H]+. C16H16N2O. Calculated, m/z: 252.1263.
2-(5,6-Dimethyl-1 H -benzimidazol-2-yl)-4-methylphenol (3l). Yield 1.791 g (71%), yellow solid, mp 244–246°C. IR spectrum, ν, cm–1: 3278 (NH), 1637 (C=N), 1581 (C=C). 1H NMR spectrum (DMSO-d6), δ, ppm (J, Hz): 13.03 (1H, s, NH); 12.91 (1H, s, OH); 7.86 (1H, s, H Ar); 7.48 (1H, s, H Ar); 7.38 (1H, s, H Ar); 7.17 (1H, d, J = 7.6, H Ar); 6.94 (1H, d, J = 8.0, H Ar); 2.34 (9H, s, 3CH3). 13C NMR spectrum (DMSO-d6), δ, ppm: 155.8 (C–OH); 150.9 (C=N); 132.0 (2C); 127.5 (2C); 125.8 (2C); 117.9; 116.8 (2C); 112.4; 111.4; 20.2 (CH3); 19.9 (2CH3). Found, m/z: 252.1268 [M+H]+. C16H16N2O. Calculated, m/z: 252.1263.
2-(5,6-Dimethyl-1 H -benzimidazol-2-yl)-6-methoxyphenol (3m). Yield 1.851 g (69%), yellow solid, mp 239–241°C. IR spectrum, ν, cm–1: 3318 (NH), 1637 (C=N), 1592 (C=C). 1H NMR spectrum (DMSO-d6), δ, ppm (J, Hz): 13.47 (1H, s, NH); 13.00 (1H, s, OH); 7.67 (1H, d, J = 7.9, H Ar); 7.56 (1H, s, H Ar); 7.42 (1H, s, H Ar); 7.11 (1H, d, J = 7.8, H Ar); 6.99 (1H, t, J = 8.0, H Ar); 3.90 (3H, s, OCH3); 2.40 (6H, s, 2CH3). 13C NMR spectrum (DMSO-d6), δ, ppm: 151.1 (C–OH); 148.6 (C=N); 148.2; 139.3; 132.1; 131.5; 130.9; 118.5; 117.9; 117.4; 113.6; 112.7; 111.4; 55.7 (OCH3); 19.9 (2CH3). Found, m/z: 268.1207 [M+H]+. C16H16N2O2. Calculated, m/z: 268.1212.
2-(5,6-Dimethyl-1 H -benzimidazol-2-yl)-5-methoxyphenol (3n). Yield 1.958 g (73%), yellow solid, mp 294–295°C. IR spectrum, ν, cm–1: 3257 (NH), 1616 (C=N), 1591 (C=C). 1H NMR spectrum (DMSO-d6), δ, ppm (J, Hz): 13.44 (1H, s, NH); 12.80 (1H, s, OH); 7.91 (1H, d, J = 8.7, H Ar); 7.36 (2H, s, H Ar); 6.60–6.56 (2H, m, H Ar); 3.78 (3H, s, OCH3); 2.30 (6H, s, 2CH3). 13C NMR spectrum (DMSO-d6), δ, ppm: 161.9 (2C); 159.8 (2C); 151.3 (2C); 126.9; 106.3 (2C); 106.0 (2C); 101.5 (2C); 55.3 (OCH3); 20.0 (2CH3). Found, m/z: 268.1206 [M+H]+. C16H16N2O2. Calculated, m/z: 268.1212.
2-(5,6-Dimethyl-1 H -benzimidazol-2-yl)-4-methoxyphenol (3o). Yield 2.039 g (76%), yellow solid, mp 292–294°C. IR spectrum, ν, cm–1: 3259 (NH), 1639 (C=N), 1581 (C=C). 1H NMR spectrum (DMSO-d6), δ, ppm (J, Hz): 12.87 (1H, s, NH); 12.78 (1H, s, OH); 7.61 (1H, s, H Ar); 7.43 (1H, s, H Ar); 7.38 (1H, s, H Ar); 6.94 (2H, s, H Ar); 3.79 (3H, s, OCH3); 2.32 (6H, s, 2CH3). 13C NMR spectrum (DMSO-d6), δ, ppm: 152.0 (C–OH); 151.9 (C=N); 150.8; 139.6; 118.2 (2C); 117.8 (2C); 112.5; 111.4; 111.3; 109.7 (2C); 55.7 (OCH3); 19.9 (2CH3). Found, m/z: 268.1218 [M+H]+. C16H16N2O2. Calculated, m/z: 268.1212.
4-Bromo-2-(5,6-dimethyl-1 H -benzimidazol-2-yl)phenol (3p). Yield 1.205 g (38%), yellow solid, mp 200–202°C. IR spectrum, ν, cm–1: 3281 (NH), 1633 (C=N), 1580 (C=C). 1H NMR spectrum (DMSO-d6), δ, ppm (J, Hz): 13.40 (1H, s, NH); 13.02 (1H, s, OH); 8.23 (1H, s, H Ar); 7.45 (3H, m, H Ar); 6.98 (1H, d, J = 8.7, H Ar); 2.32 (6H, s, 2CH3). 13C NMR spectrum (DMSO-d6), δ, ppm: 157.0 (2C, C–OH, C=N); 149.3; 133.5 (2C); 128.0 (2C); 119.3 (2C); 118.0; 114.8; 111.6; 110.0; 19.9 (2CH3). Found, m/z: 316.0205 [M+H]+. C15H13BrN2O. Calculated, m/z: 316.0211.
Synthesis of substituted 6 H -benzimidazo[1,2- c ][1,3]-benzoxazin-6-ones 4а–p (General method). A mixture of substituted 2-(benzimidazolyl)phenol 3a–p (2 mmol) and Et3N (0.405g, 4 mmol) was added into a 100-ml threenecked round-bottom flask containing PhMe (30 ml), then PhMe solution of triphosgene (0.386g, 1.3 mmol) was slowly added. The formed reaction mixture was stirred at 0°C for 1.5 h. Then, the mixture was heated at 100°C for 22 h under nitrogen atmosphere. After the reaction was completed (TLC control), the reaction mixture was diluted with EtOAc (30 ml), filtered, and concentrated under the reduced pressure. The crude product was purified by column chromatography (eluent EtOAc – petroleum ether, 1:6), affording the desired products as white solids.
6 H -Benzimidazo[1,2- c ][1,3]benzoxazin-6-one (4a). Yield 0.392 g (83%), mp 200–202°C. IR spectrum, ν, cm–1: 1771 (C=O), 1628 (C=N), 1588 (C=C). 1H NMR spectrum (CDCl3), δ, ppm (J, Hz): 8.37 (1H, d, J = 7.8, H Ar); 8.31 (1H, d, J = 7.4, H Ar); 7.89–7.88 (1H, m, H Ar); 7.65 (1H, d, J = 7.3, H Ar); 7.53–7.44 (4H, m, H Ar). 13C NMR spectrum (CDCl3), δ, ppm: 151.4 (C=O); 146.2; 144.0 (C=N); 143.3; 133.5; 130.7; 126.6; 126.4; 125.9; 125.3; 120.3; 117.3; 115.2; 112.6. Found, m/z: 237.0657 [M+H]+. C14H9N2O2. Calculated, m/z: 237.0664.
4-Methyl-6 H -benzimidazo[1,2- c ][1,3]benzoxazin-6-one (4b). Yield 0.340 g (68%), mp 191–193°C. IR spectrum, ν, cm–1: 1765 (C=O), 1630 (C=N), 1608 (C=C). 1H NMR spectrum (CDCl3), δ, ppm (J, Hz): 8.26 (1H, d, J = 7.4, H Ar); 8.12 (1H, d, J = 7.7, H Ar); 7.82 (1H, d, J = 7.8, H Ar); 7.50–7.45 (2H, m, H Ar); 7.44–7.40 (1H, m, H Ar); 7.30 (1H, t, J = 7.6, H Ar); 2.48 (3H, s, CH3). 13C NMR spectrum (CDCl3); δ, ppm: 149.4 (C=O); 146.1; 143.7 (C=N); 142.9; 134.4; 130.2; 126.6; 126.2; 125.5; 125.3; 122.4; 119.8; 114.7; 111.9; 15.6 (CH3). Found, m/z: 251.0828 [M+H]+. C15H11N2O2. Calculated, m/z: 251.0821.
3-Methyl-6 H -benzimidazo[1,2- c ][1,3]benzoxazin-6-one (4c). Yield 0.360 g (72%), mp 214–216°C. IR spectrum, ν, cm–1: 1766 (C=O), 1629 (C=N), 1576 (C=C). 1H NMR spectrum (CDCl3), δ, ppm (J, Hz): 8.23 (1H, d, J = 7.5, H Ar); 8.14 (1H, d, J = 8.0, H Ar); 7.80 (1H, d, J = 7.8, H Ar); 7.46 (2H, t, J = 7.7, H Ar); 7.21 (1H, d, J = 8.0, H Ar); 7.16 (1H, s, H Ar); 2.45 (3H, s, CH3). 13C NMR spectrum (CDCl3), δ, ppm: 151.1 (C=O); 146.0; 144.6 (C=N); 143.7; 143.0; 130.3; 127.2; 126.2; 125.2; 124.5; 119.8; 116.9; 114.7; 109.5; 21.8 (CH3). Found, m/z: 251.0815 [M+H]+. C15H11N2O2. Calculated, m/z: 251.0821.
2-Methyl-6 H -benzimidazo[1,2- c ][1,3]benzoxazin-6-one (4d). Yield 0.380 g (76%), mp 186–188°C. IR spectrum, ν, cm–1: 1780 (C=O), 1627 (C=N), 1594 (C=C). 1H NMR spectrum (CDCl3), δ, ppm (J, Hz): 8.23 (1H, d, J = 7.5, H Ar); 8.05 (1H, s, H Ar); 7.80 (1H, d, J = 7.4, H Ar); 7.46 (2H, t, J = 6.8, H Ar); 7.36 (1H, d, J = 8.4, H Ar); 7.24 (1H, d, J = 8.5, H Ar); 2.42 (3H, s, CH3). 13C NMR spectrum (CDCl3), δ, ppm: 149.1 (C=O); 145.8; 143.6 (C=N); 142.9; 136.1; 134.0; 130.3; 126.1; 125.4; 124.5; 119.9; 116.5; 114.7; 111.7; 20.7 (CH3). Found, m/z: 251.0817 [M+H]+. C15H11N2O2. Calculated, m/z: 251.0821.
4-Methoxy-6 H -benzimidazo[1,2- c ][1,3]benzoxazin-6-one (4e). Yield 0.373 g (70%), mp 231–232°C. IR spectrum, ν, cm–1: 1766 (C=O), 1630 (C=N), 1592 (C=C). 1H NMR spectrum (DMSO-d6), δ, ppm (J, Hz): 8.15 (1H, s, H Ar); 7.85 (1H, s, H Ar); 7.76 (1H, s, H Ar); 7.51 (2H, s, H Ar); 7.42–7.39 (2H, m, H Ar); 3.95 (3H, s, OCH3). 13C NMR spectrum (DMSO-d6), δ, ppm: 147.0 (C=O); 146.6; 143.4 (C=N); 142.8; 140.6; 130.4; 126.0; 125.8; 125.0; 119.7; 115.4; 115.2; 114.3; 113.2; 56.3 (OCH3). Found, m/z: 267.0776 [M+H]+. C15H11N2O3. Calculated, m/z: 267.0770.
3-Methoxy-6 H -benzimidazo[1,2- c ][1,3]benzoxazin-6-one (4f). Yield 0.421 g (79%), mp 188–190°C. IR spectrum, ν, cm–1: 1770 (C=O), 1632 (C=N), 1580 (C=C). 1H NMR spectrum (CDCl3), δ, ppm (J, Hz): 8.18 (1H, d, J = 7.5, H Ar); 8.12 (1H, d, J = 8.6, H Ar); 7.75 (1H, d, J = 7.5, H Ar); 7.45–7.38 (2H, m, H Ar); 6.91 (1H, d, J = 8.2, H Ar); 6.79 (1H, s, H Ar); 3.85 (3H, s, OCH3). 13C NMR spectrum (CDCl3), δ, ppm: 163.9 (C=O); 152.9; 146.3 (C=N); 144.0; 143.3; 130.4; 126.4; 126.2; 125.2; 119.8; 114.8; 114.0; 105.2; 101.3; 56.1 (OCH3). Found, m/z: 267.0765 [M+H]+. C15H11N2O3. Calculated, m/z: 267.0770.
2-Methoxy-6 H -benzimidazo[1,2- c ][1,3]benzoxazin-6-one (4g). Yield 0.442 g (83%), mp 191–192°C. IR spectrum, ν, cm–1: 1772 (C=O), 1625 (C=N), 1580 (C=C). 1H NMR spectrum (CDCl3), δ, ppm (J, Hz): 8.32–8.27 (1H, m, H Ar); 8.14 (1H, s, H Ar); 7.86 (1H, d, J = 7.0, H Ar); 7.53–7.46 (2H, m, H Ar); 7.42 (1H, dd, J = 8.5, J =1.8, H Ar); 7.31 (1H, d, J = 8.5, H Ar); 2.47 (3H, s, OCH3). 13C NMR spectrum, δ, ppm: 157.5 (C=O); 146.2; 145.6 (C=N); 143.9; 143.3; 130.7; 126.5; 125.8; 122.0; 120.2; 118.5; 115.1; 112.8; 106.1; 56.3 (OCH3). Found, m/z: 267.0763 [M+H]+. C15H11N2O3. Calculated, m/z: 267.0770.
2-Bromo-6 H -benzimidazo[1,2- c ][1,3]benzoxazin-6-one (4h). Yield 0.315 g (50%), mp 259–261°C. IR spectrum, ν, cm–1: 1781 (C=O), 1626 (C=N), 1584 (C=C). 1H NMR spectrum (DMSO-d6), δ, ppm (J, Hz): 8.36 (1H, d, J = 2.3, H Ar); 8.20–8.18 (1H, m, H Ar); 7.93–7.90 (2H, m, H Ar); 7.60–7.54 (3H, m, H Ar). 13C NMR spectrum (CDCl3), δ, ppm: 150.4 (C=O); 145.4; 143.3 (C=N); 142.7; 135.7; 130.4; 126.3; 126.0; 125.4; 119.9; 119.3; 117.6; 114.7; 114.3. Found, m/z: 314.9762 [M+H]+. C14H8BrN2O3. Calculated, m/z: 314.9769.
9,10-Dimethyl-6 H -benzimidazo[1,2- c ][1,3]benzoxazin-6-one (4i). Yield 0.412 g (78%), mp 262–263°C. IR spectrum, ν, cm–1: 1768 (C=O), 1622 (C=N), 1589 (C=C). 1H NMR spectrum (DMSO-d6), δ, ppm (J, Hz): 8.24 (1H, d, J = 7.4, H Ar); 7.95 (1H, s, H Ar); 7.71 (1H, t, J = 7.7, H Ar); 7.64 (1H, s, H Ar); 7.55 (1H, d, J = 8.1, H Ar); 7.51 (1H, t, J = 7.5, H Ar); 2.40 (3H, s, CH3); 2.38 (3H, s, CH3). 13C NMR spectrum (CDCl3), δ, ppm: 151.0 (C=O); 145.1; 143.1 (C=N); 142.1; 135.6; 135.2; 132.8; 128.7; 126.0; 124.9; 120.1; 116.9; 115.0; 112.5; 20.5 (CH3); 20.5 (CH3). Found, m/z: 265.0972 [M+H]+. C16H13N2O2. Calculated, m/z: 265.0977.
4,9,10-Trimethyl-6 H -benzimidazo[1,2- c ][1,3]benzoxazin-6-one (4j). Yield 0.351 g (63%), mp 257–258°C. IR spectrum, ν, cm–1: 1768 (C=O), 1625 (C=N), 1563 (C=C). 1H NMR spectrum (CDCl3), δ, ppm (J, Hz): 8.10 (1H, s, H Ar); 8.02 (1H, s, H Ar); 7.57 (1H, s, H Ar); 7.39 (1H, dd, J = 8.5, 1.6, H Ar); 7.29–7.27 (1H, m, H Ar); 2.46 (3H, s, CH3); 2.42 (3H, s, CH3); 2.40 (3H, s, CH3). 13C NMR spectrum (CDCl3), δ, ppm: 149.1 (C=O); 145.2; 143.2 (C=N); 142.1; 136.0; 135.4; 135.0; 133.7; 128.7; 124.5; 120.0; 116.6; 114.9; 112.1; 20.8 (CH3); 20.5 (2CH3). Found, m/z: 279.1128 [M+H]+. C17H15N2O2. Calculated, m/z: 279.1134.
3,9,10-Trimethyl-6 H -benzimidazo[1,2- c ][1,3]benzoxazin-6-one (4k). Yield 0.379 g (68%), mp 234–235°C. IR spectrum, ν, cm–1: 1766 (C=O), 1627 (C=N), 1586 (C=C). 1H NMR spectrum (CDCl3), δ, ppm (J, Hz): 8.20 (1H, d, J = 7.9, H Ar); 8.05 (1H, s, H Ar); 7.60 (1H, s, H Ar); 7.26 (1H, d, J = 4.6, H Ar); 7.22 (1H, s, H Ar); 2.50 (3H, s, CH3); 2.44 (3H, s, CH3); 2.42 (3H, s, CH3). 13C NMR spectrum (CDCl3), δ, ppm: 151.1 (C=O); 145.4; 144.2 (C=N); 143.3; 142.3; 135.4; 134.9; 128.7; 127.2; 124.5; 120.0; 117.0; 115.0; 109.9; 29.7 (CH3); 21.9 (CH3); 20.5 (CH3). Found, m/z: 279.1140 [M+H]+. C17H15N2O2. Calculated, m/z: 279.1134.
2,9,10-Trimethyl-6 H -benzimidazo[1,2- c ][1,3]benzoxazin- 6-one (4l). Yield 0.395 g (71%), mp 260–261°C. IR spectrum, ν, cm–1: 1764 (C=O), 1627 (C=N), 1598 (C=C). 1H NMR spectrum (CDCl3), δ, ppm (J, Hz): 8.15 (1H, d, J = 7.3, H Ar); 8.03 (1H, s, H Ar); 7.58 (1H, s, H Ar); 7.44 (1H, d, J = 7.0, H Ar); 7.34–7.30 (1H, m, H Ar); 2.52 (3H, s, CH3); 2.43 (3H, s, CH3); 2.41 (3H, s, CH3). 13C NMR spectrum (CDCl3), δ, ppm: 149.4 (C=O); 145.5; 143.1 (C=N); 142.2; 135.5; 135.0; 134.1; 128.6; 126.6; 125.5; 122.4; 120.0; 114.9; 112.3; 20.5 (CH3); 20.5 (CH3); 15.7 (CH3). Found, m/z: 279.1129 [M+H]+. C17H15N2O2. Calculated, m/z: 279.1134.
4-Methoxy-9,10-dimethyl-6 H -benzimidazo[1,2- c ][1,3]-benzoxazin-6-one (4m). Yield 0.388 g (66%), mp 278–279°C. IR spectrum, ν, cm–1: 1764 (C=O), 1615 (C=N), 1587 (C=C). 1H NMR spectrum (CDCl3), δ, ppm (J, Hz): 8.10 (1H, s, H Ar); 7.92 (1H, dd, J = 7.9, J = 1.0, H Ar); 7.63 (1H, s, H Ar); 7.39 (1H, t, J = 8.1, H Ar); 7.18–7.16 (1H, m, H Ar); 4.02 (3H, s, OCH3); 2.45 (3H, s, CH3); 2.43 (3H, s, CH3). 13C NMR spectrum (CDCl3), δ, ppm: 147.6 (C=O); 145.2; 142.7 (C=N); 142.1; 140.7; 135.6; 135.2; 128.7; 126.1; 120.1; 115.8; 115.0; 114.5; 113.4; 56.4 (OCH3); 29.7 (CH3); 20.5 (CH3). Found, m/z: 295.1077 [M+H]+. C17H15N2O2. Calculated, m/z: 295.1083.
3-Methoxy-9,10-dimethyl-6 H -benzimidazo[1,2- c ][1,3]-benzoxazin-6-one (4n). Yield 0.406 g (69%), mp 227–228°C. IR spectrum, ν, cm–1: 1766 (C=O), 1623 (C=N), 1585 (C=C). 1H NMR spectrum (CDCl3), δ, ppm (J, Hz): 8.23 (1H, d, J = 8.7, H Ar); 8.02 (1H, s, H Ar); 7.57 (1H, s, H Ar); 7.02 (1H, d, J = 8.4, H Ar); 6.90 (1H, s, H Ar); 3.96 (3H, d, J = 8.4, OCH3); 2.46 (3H, s, CH3); 2.43 (3H, s, CH3). 13C NMR spectrum (CDCl3), δ, ppm: 163.4 (C=O); 152.5; 145.3 (C=N); 143.2; 142.1; 135.3; 134.5; 128.4; 125.9; 119.7; 114.8; 113.7; 105.2; 101.1; 55.9 (OCH3); 29.7 (CH3); 20.4 (CH3). Found, m/z: 295.1088 [M+H]+. C17H15N2O3. Calculated, m/z: 295.1083.
2-Methoxy-9,10-dimethyl-6 H -benzimidazo[1,2- c ][1,3]-benzoxazin-6-one (4o). Yield 0.465 g (79%), mp 247–248°C. IR spectrum, ν, cm–1: 1758 (C=O), 1623 (C=N), 1601 (C=C). 1H NMR spectrum (CDCl3), δ, ppm (J, Hz): 8.04 (1H, s, H Ar); 7.69 (1H, d, J = 3.0, H Ar); 7.58 (1H, s, H Ar); 7.32 (1H, d, J = 9.1, H Ar); 7.15 (1H, dd, J = 9.1, J = 3.0, H Ar); 3.92 (3H, s, OCH3); 2.43 (3H, s, CH3); 2.41 (3H, s, CH3). 13C NMR spectrum (CDCl3), δ, ppm: 157.3 (C=O); 145.2; 145.2 (C=N); 143.2; 142.1; 135.5; 135.1; 128.7; 121.3; 120.0; 118.2; 115.0; 112.8; 105.7; 56.1 (OCH3); 20.5 (2CH3). Found, m/z: 295.1075 [M+H]+. C17H15N2O3. Calculated, m/z: 295.1083.
2-Bromo-9,10-dimethyl-6 H -benzimidazo[1,2- c ][1,3]-benzoxazin-6-one (4p). Yield 0.261 g (38%), mp 282–283°C. IR spectrum, ν, cm–1: 1777 (C=O), 1626 (C=N), 1588 (C=C). 1H NMR spectrum (CDCl3), δ, ppm (J, Hz): 8.33 (1H, s, H Ar); 8.05 (1H, s, H Ar); 7.61 (2H, s, H Ar); 7.44 (1H, d, J = 6.0, H Ar); 2.44 (3H, s, CH3); 2.42 (3H, s, CH3). 13C NMR spectrum (CDCl3), δ, ppm: 149.8 (C=O); 143.7; 142.6 (C=N); 142.1; 135.9; 135.8; 135.5; 128.7; 127.4; 120.3; 119.0; 118.7; 115.0; 114.2; 20.6 (CH3); 20.5 (CH3). Found, m/z: 343.0076 [M+H]+. C16H11BrN2O2 Calculated, m/z: 343.0082.
In vitro fungicidal activity of compounds 4a–p was tested according to the standard method NY/T1156.5-2006.20,21,22 The in vitro inhibition of mycelium growth in the agriculture medium caused by the title compounds against six strains of phytopathogenic fungi was performed. Referencing standard method NY/T1156.5-2006, antifungal activity assays adopted drug-containing medium method. Stock solution of every test compound was prepared in Me2CO and then diluted to the required test concentration (500 μg/ml) with sorporl-144 (concentration 200 μg/ml). Solutions of the test compounds (1 ml) were added to potato dextrose agar (PDA) medium (9 ml, 45°C) to provide the final concentration of 50 μg/ml. The mixed medium without sample was used as the blank control. The inocula, 4 mm in diameter, were removed from the margins of actively growing colonies of mycelium and placed in the centers of the above plates. 4 Replicates per treatment were performed. Percentages of growth inhibition were calculated by comparing the mean value of the diameters of the mycelia in the test plates after placing in 24°C biochemical incubator thermostat for 3 days.
Supplementary information file containing 1H and 13C NMR spectra of the synthesized compounds 4a–p is available at the journal website at http://springerlink.bibliotecabuap.elogim.com/journal/10593.
References
Waisser, K.; Petrlíkova, E.; Peřina, M.; Klimešova, V.; Kuneš, J.; Palát, K., Jr.; Kaustová, J.; Dahse, H. M.; Möllmann, U. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 45, 2719.
Velappan, A. B.; Kesamsetty, D.; Datta, D.; Ma, R.; Hari, N.; Franzblau, S. G.; Debnath, J. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 208, 112835.
Varshney H.; Ahmad, A.; Rauf, A.; Husain, F. M.; Ahmad, I. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2017, 21, S394.
Madhavan, G. R.; Chakrabarti, R.; Reddy, K. A.; Rajesh, B. M.; Balraju, V.; Rao, P. B.; Rajagopalan, R.; Iqbal, J. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2006, 14, 584.
Ihmaid, S.; Ahmed, H. E. A.; Al-Sheikh Ali, A.; Sherif, Y. E.; Tarazi, H. M.; Riyadh, S. M.; Zayed, M. F.; Abulkhair, H. S.; Rateb, H. S. Bioorg. Chem. 2017, 72, 234.
Morrison R.; Al-Rawi, J. M. A.; Jennings, I. G.; Thompson, P. E.; Angove, M. J. Eur J. Med. Chem. 2016, 110, 326.
Jiang, S.; Awadasseid, A.; Narva, S.; Cao S; Tanaka, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wei, F.; Zhao, X.; Wei, C.; Zhang, W. Life Sci. 2020, 258,118252.
Bari, A.; Khan, Z. A.; Shahzad, S. A.; Naqvi, S. A. R.; Khan, S. A.; Amjad, H.; Iqbal, A.; Yar, M. J. Mol. Struct. 2020, 1214, 128252.
Popov, L. D.; Shcherbakov, I. N.; Bulanov, A. O.; Kobeleva, O. I.; Valova, T. M.; Barachevsky, V. A. Russ. Chem. Bull., Int. Ed 2009, 58, 2418. [Izv. Akad. Nauk, Ser. Khim. 2009, 2340.]
Ozhogin, I. V.; Tkachev, V. V.; Lukyanov, B. S.; Ozhogin, I. V.; Tkachev, V. V.; Lukyanov, B. S.; Mukhanov, E. L.; Rostovtseva, I. A.; Lukyanova, M. B.; Shilov, G. V.; Strekal, N. D.; Aldoshin, S. M.; Minkin, V. I. J. Mol. Struct. 2018, 1161, 18.
Mayence, A.; Vanden Eynde, J. J.; Kaiser, M.; Brun, R.; Yarlett, N.; Huang, T. L. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2011, 19, 7493.
Bandyopadhyay, P.; Sathe, M.; Tikar, S. N.; Yadav, R.; Sharma, P.; Kumar, A.; Kaushik, M. P. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 24, 2934.
Abdel-Motaal, M.; Almohawes, K.; Tantawy, M. A. Bioorg. Chem. 2020, 101, 103972.
Li, Y.; Zhou, X.; Wu, H.; Yu, Z.; Li, H.; Yang, S. Ind. Crops Prod. 2020, 150, 112406.
Meshram, G. A.; Vala, V. A. Chem. Heterocycl. Compd. 2015, 51, 44. [Khim. Geterotsikl. Soedin. 2015, 51, 44.]
Bocion, P. F.; Cattanach, C. J.; Eggenberg, P.; Gressel, J.; Hagmann, M. L.; Malkin, S.; Wenger, J. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 1987, 28, 75.
Akhtar, W.; Khan, M. F.; Verma, G.; Shaquiquzzaman, M.; Rizvi, M. A.; Mehdi, S. H.; Akhter, M.; Alam, M. M. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 126, 705.
Jornet, D.; Castillo, M. A.; Sabater, M. C.; Tormos, R.; Miranda, M. A. J. Photochem. Photobiol., A 2013, 256, 36.
Feng, J.; Hu, Y.; Grant, E.; Lu, X. Food Chem. 2018, 239, 816.
Tang, Z.; Chen, W.; Zhu, Z.; Liu, H. Synth. Commun. 2012, 42, 1372.
Tang, Z.; Chen, W.; Zhu, Z.; Liu, H. J. Heterocycl. Chem. 2011, 48, 255.
Tang, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Xia, Z.; Liu, H.; Chen, J.; Xiao, W.; Ou, X. Molecules 2012, 17, 8174.
Tang, Z.; Li, X.; Yao, Y.; Qi, Y.; Wang, M.; Dai, N.; Wen, Y.; Wan, Y.; Peng, L. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2019, 27, 2572.
Cui, L. J.; Xiao, S.-Y.; Yang, H.-S.; Xu, P.; Cheng, F. S.; Li, Z. H.; Liang, R. H.; Xia, Z. N. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2011, 31, 672.
Dou, G.-L.; Sun, F.; Shi, D.-Q. Tetrahedron 2012, 68, 4852.
Tang, Z. L.; Ma, C. X.; Peng, L. F.; Wan, Y. C.; Li, Y. CN Patent 110218217.
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21877034, 21372070) and the Scientific Research Fund of Hunan Provincial Education Department (No. 17A066).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Published in Khimiya Geterotsiklicheskikh Soedinenii, 2021, 57(5), 581–587
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(PDF 4891 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tan, Y., Tang, Z., Ma, C. et al. Synthesis and fungicidal activity of novel 6H-benzimidazo[1,2-c][1,3]benzoxazin-6-ones. Chem Heterocycl Comp 57, 581–587 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10593-021-02946-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10593-021-02946-y