Abstract
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are a class of non-coding RNAs, containing about 22 nucleotides and having a pivotal function in various cellular processes. The oncogenic and tumor suppressor roles of miRNAs have been identified in cancers especially in gastric cancer, which is one of the most prevalent cancers. MiR-299-5p is located in the imprinted Dlk1-Dio3 region in chromosome 14q32. Aberrant expression of miR-299-5p was determined in solid and blood cancers. The current study was performed to assess the expression pattern of miR-299-5p in intestinal-type gastric adenocarcinoma and compare it with the normal adjacent counterparts. The expression level of miR-299-5p was investigated in forty fresh specimens which were obtained from gastric cancer patients during endoscopy. Moreover, the association of aberrant expression of miR-299-5p and clinicopathological features, as well as the susceptibility of miR-299-5p as a tumor marker, was determined. The result of qRT-PCR revealed the downregulation of miR-299-5p in intestinal-type gastric adenocarcinoma compared with adjacent tumor-free tissues (P < 0.001); this misregulation can be used as a tumor marker. Analysis of miR-299-5p misregulation did not reveal a significant correlation with clinical features. The result obtained from the present study revealed the significant downregulation of miR-299-5p in intestinal-type gastric adenocarcinoma which is consistent with previous studies showing miR-299-5p downregulation in other types of cancers. The data obtained from the current study suggest basic information which can be very helpful for future research in the field of diagnosis and treatment of gastric cancer.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Gastric cancer is one of the most prevalent cancers, especially in developing countries like East Asia, Eastern Europe, and South America (Jemal et al. 2011). In Iran, gastric cancer has a high prevalence both in men and women (Mousavi et al. 2009). Regarding the geographical distribution, northwest and northeast of Iran have the highest rates of gastric cancer (Malekzadeh et al. 2009). East Azerbaijan, located in northwest of Iran, is one of the provinces with a high mortality rate for gastric cancer (Somi et al. 2014). Overall, the incidence rate of gastric cancer in males is two times higher than in females. Histologically, the intestinal and the diffuse types are two major categories of gastric cancer; the incidence of each category differs in men and women. It has been recognized that more men are diagnosed with intestinal type than women (Adachi et al. 2000). Also, the incidence rate of intestinal type is higher in high-risk population (Carcas 2014), which emphasizes the need for further research to identify approaches for early diagnosis prognosis, and treatment of this disease.
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are a subgroup of non-coding RNAs (ncRNA) that regulate gene expression by binding to the UTRs (predominantly act on 3’UTR and rarely on 5’UTR) of mRNAs, and on lncRNAs or pseudogenes (Hafner et al. 2010; Jeggari et al. 2012). Approximately, two decades have passed since the discovery of the first miRNA, lin-4, and now it is recognized that miRNAs have a prominent role in essential cellular processes, including differentiation, proliferation, and apoptosis (Courts and Madea 2010; Kong et al. 2012). Obviously, any alteration in the miRNA expression or mutation in miRNAs will lead to diseases, as researchers have uncovered the role of miRNAs in a number of diseases including cancers (Kong et al. 2012).
MiR-299-5p is located in the DLK1-DIO3 genomic locus at chromosome 14q32.31. Dysregulation of miR-299-5p has been demonstrated in some cancers, including leukemia, colorectal, and breast cancers (Bandres et al. 2006; Marcucci et al. 2011; Yan et al. 2012). However, neither the expression pattern of miR-299, nor the exact function of miR-299 has been determined in gastric cancer. Therefore, the purpose of this study was to quantitatively analyze the expression pattern of miR-299-5p in intestinal-type gastric adenocarcinoma relative to their non-tumor counterparts. Moreover, the association between misregulation of miR-299-5p and clinicopathological outcomes in patients has been examined.
Materials and Methods
Study Population
Fresh-frozen specimens from 40 human gastric tissue samples and normal adjacent tissues were obtained from patients who had undergone endoscopy at the Tabriz Medical University Hospital from 2014 to 2015. The non-tumor counterparts were collected from a region of the resected specimen at the farthest distance from tumor. The median age of patients with gastric cancer was 64.52 ± 10.70 (within the age range of 42–84), and 70 % of the samples were obtained from males and the remainder from females. The Research Ethics Committee of Imam Reza Hospital approved the study in accordance with institutional protocol, and informed consents were obtained from all of the patients. Resected specimens were analyzed by standard histopathological examination and intestinal-type gastric adenocarcinoma was selected for investigation. The clinicopathological data regarding the patients participating in the study are shown in Table 1.
RNA Extraction, Complementary DNA Synthesis
Total RNA was isolated from the gastric cancer and normal gastric tissues using TRIzol (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA) reagent based on the manufacturer’s instructions. The quality and quantity of isolated RNAs were determined by agarose gel electrophoresis and Pico Drop spectrophotometer, respectively. Before synthesizing cDNA, we performed a DNase I treatment reaction to degrade any DNA contamination. The extracted RNAs were reverse-transcribed to cDNA using Prime Script (R) miRNA cDNA Synthesis Kit (Takara) based on the manufacturer’s instructions. Briefly, at first stage, poly A tail was added by poly A polymerase; then, the single-stranded reverse transcriptase was synthesized. The 10 μl RT reaction mixtures were performed at 37 °C for 60 min, at 85 °C for 5 s, and subsequently held at 4 °C.
Real-Time Reverse Transcription PCR
The qRT-PCR reaction was performed using Rotorgene system and the SYBR® Green Suppermix (Takara). The 10 μl qRT-PCR reaction included 1 μl of the diluted RT product, 5 μl SYBR Green suppermix, 0.25 μl primers, and 3.75 μl RNase-free water in the tube. The reactions were run in triplicate using the protocol with 60 s at 95 °C for one cycle, 5 s at 95 °C, followed by 15 s at 60 °C and 72 °C for 30 s for 40 cycles, and 72 °C for 180 s for one cycle; each run included a non-template negative control.
Normalization of Data and Statistical Analysis
Normalization is essential for the compensation of intra- and inter-kinetic RT-PCR variations. Normalization was applied using the housekeeping reference gene, 5srRNA, and adjacent non-tumor tissue was used as a calibrator. \( 2^{{ - \Delta C_{\text{t}} }} \) method was used to analyze the relative expression levels of miR-299-5p in gastric cancer tissues relative to their non-tumor counterparts. Relative Quantification Software Tool (REST) 2009 Software was used to evaluate the statistical differences in miR-299-5p expression in cancer tissues relative to the adjacent non-tumor tissues. The association between miR-299-5p expression and clinicopathological features of the patients was evaluated by a non-parametric test. Analyses were performed with SPSS 22.0 software and P values less than 0.05 were considered to be statistically significant. Data were shown as mean ± SD. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) Sigmaplot 12.5 was used to evaluate the sensitivity and specificity of miR-229-5p dysregulation in gastric cancer and non-tumorous tissues, and P values less than 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
Results
Expression of miR-299-5p in Intestinal-Type Gastric Cancer and Adjacent Normal Tissues
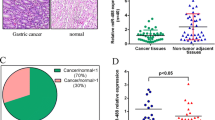
Among the samples obtained from 40 patients with intestinal-type gastric cancer (28 males, 12 females), the relative expression level of miR-299-5p was evaluated by real-time quantitative PCR, and non-tumor tissues were used as control group. The results of using REST software indicated that miR-299-5p expression levels were significantly decreased in tumor tissues compared with their matching non-tumor counterparts as a control group, by a mean factor of 0.159, and S.E. range of 0.041–4.493 (P < 0.03). Compared to normal gastric tissues, miR-299-5p was downregulated in gastric cancer tissues up to twofold. Figure 1 shows the differences between miR-299-5p expression levels.
Association Between Expression Levels of miR-299-5p and Clinicopathological Outcomes
The association between miR-299-5p expression levels and clinicopathological outcomes (including age (P = 0.59), gender (P = 0.47), and grade (P = 0.08)) was pursued in a total of 40 patients with gastric cancer. Variables analyzed using independent t test is shown in Table 1. The results indicated that the downregulation of miR-299-5p did not significantly correlate with clinical features in patients. ROC curves were employed to examine the diagnostic value of miR-299-5p in intestinal-type gastric cancer patients. The results indicated an estimated area under the ROC curve of 0.37 at a cutoff value of 2.25. ROC curve data were shown in Fig. 2.
Discussion
In recent years, the implication of miRNAs, which have a significant role in a wide range of cellular processes, has been recognized in various types of cancer. More research in this field will disclose the involvement of miRNAs in the pathogenesis of gastric cancer and ensure future advances in understanding the pathogenesis and treatment of gastric cancer.
MiR-229-5p is located in one of the largest miRNA-containing clusters of the human genome, a ∼1 Mb spanning DLK1-DIO3 region that harbors 54 miRNA. DLK1-DIO3 region belongs to an imprinted cluster; it was recognized that most imprinted genes function as embryonic and/or placental growth and development (Benetatos et al. 2013). Most of miRNAs in this cluster are expressed from the maternally inherited chromosome, and these miRNA genes are likely involved in transacting and negatively regulating the expression of some paternal genes (Seitz et al. 2004; Zehavi et al. 2012).
Following the previous studies regarding the dysregulation of this miRNA, the present study was conducted to assess the alteration of miR-299-5p expression in intestinal-type gastric adenocarcinoma. The findings demonstrated that miR-299-5p was downregulated in gastric tissues compared to normal gastric tissue. The results of the current study could be a support for the findings of the previous studies regarding the downregulation of miR-299-5p in various types of cancer including Gliomas and melanoma, as this miRNA is located in the largest tumor-suppressor miRNA cluster (Lavon et al. 2010; Zehavi et al. 2012).
Also, the findings of the current study reveal that the dysregulation of miR-299-5p is in line with previous research. In estrogen receptor (ER) status of breast cancer, miR-299 was dysregulated (Lowery et al. 2009). In acute myeloid leukemia (AML), miR-299-5p has an opposed dealing, depending on cytogenetic subtypes of AML. In fact, miR-299-5p was downregulated in patients with t(11q23)/MLL-rearrangement and upregulated in t(15;17) cytogenetic subtypes (Marcucci et al. 2011).
The current study represents the downregulation of miR-299-5p; however, the reason for the misregulation of this miRNA is unclear. Possibly, loss of heterozygosity or epigenetic silencing could be the reasons for this misregulation. Loss of heterozygosity (Benetatos et al.) of a Ch14q32.31 region in many cancers like renal cell carcinoma is identified by microsatellite markers (Alimov et al. 2004). Besides, mir genes in Ch14q32.31 are the miRNAs that were scattered near the fragile sites (Calin et al. 2004).
Studies show the inverse association of miR-299-5p with RAD21 (Yan et al. 2012), BCL6 (B-Cell CLL/Lymphoma 6) (Bae et al. 2011), and osteopontin (OPN) mRNA (Shevde et al. 2010). MiR-299-5p targets the 3 UTR of OPN mRNA (Shevde et al. 2010). OPN is a secreted protein that acts as autocrine and paracrine molecules and involves in the survival of cancer cells and tumor metastasis through cooperation of CD44, OPN receptor on cell surfaces, and promotion of matrix metalloproteinase 2 (MMP-2), respectively (Shevde and Samant 2014). In addition, reports have shown the overexpression of one splice variants of OPN, an oncogenic protein, in gastric cancer (Tang et al. 2013).
Exploring the relation between misregulation of miR-299-5p and pathological features in the present study showed no significant relation between miR-299-5p downregulation and age, gender, and tumor grade.
Overall, the findings of this study demonstrated the expression of miR-299-5p in gastric tissue. Additionally, the findings showed that during the alteration of normal tissue to cancerous one, the expression of miR-299-5p was downregulated. Misregulation of miR-299-5p may provide a basis for further research related to the introduction of miR-299-5p as a potential biomarker in the gastric cancer diagnosis or a novel therapeutic target, but further studies are required to find out the molecular mechanisms as well as targets of miR-299-5p.
References
Adachi Y, Yasuda K, Inomata M, Sato K, Shiraishi N, Kitano S (2000) Pathology and prognosis of gastric carcinoma: well versus poorly differentiated type. Cancer 89(7):1418–1424. doi:10.1002/1097-0142(20001001)89:7<1418:AID-CNCR2>3.0.CO;2-A
Alimov A, Sundelin B, Wang N, Larsson C, Bergerheim U (2004) Loss of 14q31-q32.2 in renal cell carcinoma is associated with high malignancy grade and poor survival. Int J Oncol 25(1):179–185. doi:10.3892/ijo.25.1.179
Bae S, Lee EM, Cha HJ, Kim K, Yoon Y, Lee H, An S (2011) Resveratrol alters microRNA expression profiles in A549 human non-small cell lung cancer cells. Mol Cells 32(3):243–249. doi:10.1007/s10059-011-1037-z
Bandres E, Cubedo E, Agirre X, Malumbres R, Zarate R, Ramirez N, Garcia-Foncillas J (2006) Identification by Real-time PCR of 13 mature microRNAs differentially expressed in colorectal cancer and non-tumoral tissues. Mol Cancer 5:29. doi:10.1186/1476-4598-5-29
Benetatos L, Hatzimichael E, Londin E, Vartholomatos G, Loher P, Rigoutsos I, Briasoulis E (2013) The microRNAs within the DLK1-DIO3 genomic region: involvement in disease pathogenesis. Cell Mol Life Sci 70(5):795–814. doi:10.1007/s00018-012-1080-8
Calin GA, Sevignani C, Dumitru CD, Hyslop T, Noch E, Yendamuri S, Croce CM (2004) Human microRNA genes are frequently located at fragile sites and genomic regions involved in cancers. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101(9):2999–3004. doi:10.1073/pnas.0307323101
Carcas LP (2014) Gastric cancer review. J Carcinog 13:14. doi:10.4103/1477-3163.146506
Courts C, Madea B (2010) Micro-RNA—a potential for forensic science? Forensic Sci Int 203(1–3):106–111. doi:10.1016/j.forsciint.2010.07.002
Hafner M, Landthaler M, Burger L, Khorshid M, Hausser J, Berninger P, Tuschl T (2010) Transcriptome-wide identification of RNA-binding protein and microRNA target sites by PAR-CLIP. Cell 141(1):129–141. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2010.03.009
Jeggari A, Marks DS, Larsson E (2012) miRcode: a map of putative microRNA target sites in the long non-coding transcriptome. Bioinformatics 28(15):2062–2063. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/bts344
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D (2011) Global cancer statistics. Cancer J Clin 61(2):69–90. doi:10.3322/caac.20107
Kong YW, Ferland-McCollough D, Jackson TJ, Bushell M (2012) microRNAs in cancer management. Lancet Oncol 13(6):e249–e258. doi:10.1016/s1470-2045(12)70073-6
Lavon I, Zrihan D, Granit A, Einstein O, Fainstein N, Cohen MA, Siegal T (2010) Gliomas display a microRNA expression profile reminiscent of neural precursor cells. Neuro Oncol 12(5):422–433. doi:10.1093/neuonc/nop061
Lowery AJ, Miller N, Devaney A, McNeill RE, Davoren PA, Lemetre C, Kerin MJ (2009) MicroRNA signatures predict oestrogen receptor, progesterone receptor and HER2/neu receptor status in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res 11(3):R27. doi:10.1186/bcr2257
Malekzadeh R, Derakhshan MH, Malekzadeh Z (2009) Gastric cancer in Iran: epidemiology and risk factors. Arch Iran Med 12(6):576–583
Marcucci G, Mrozek K, Radmacher MD, Garzon R, Bloomfield CD (2011) The prognostic and functional role of microRNAs in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 117(4):1121–1129. doi:10.1182/blood-2010-09-191312
Mousavi SM, Gouya MM, Ramazani R, Davanlou M, Hajsadeghi N, Seddighi Z (2009) Cancer incidence and mortality in Iran. Ann Oncol 20(3):556–563. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdn642
Seitz H, Royo H, Bortolin ML, Lin SP, Ferguson-Smith AC, Cavaille J (2004) A large imprinted microRNA gene cluster at the mouse Dlk1-Gtl2 domain. Genome Res 14(9):1741–1748. doi:10.1101/gr.2743304
Shevde LA, Samant RS (2014) Role of osteopontin in the pathophysiology of cancer. Matrix Biol 37:131–141. doi:10.1016/j.matbio.2014.03.001
Shevde LA, Metge BJ, Mitra A, Xi Y, Ju J, King JA, Samant RS (2010) Spheroid-forming subpopulation of breast cancer cells demonstrates vasculogenic mimicry via hsa-miR-299-5p regulated de novo expression of osteopontin. J Cell Mol Med 14(6b):1693–1706. doi:10.1111/j.1582-4934.2009.00821.x
Somi MH, Golzari M, Farhang S, Naghashi S, Abdollahi L (2014) Gastrointestinal cancer incidence in East Azerbaijan, Iran: update on 5 year incidence and trends. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 15(9):3945–3949
Tang X, Li J, Yu B, Su L, Yu Y, Yan M, Zhu Z (2013) Osteopontin splice variants differentially exert clinicopathological features and biological functions in gastric cancer. Int J Biol Sci 9(1):55–66. doi:10.7150/ijbs.5280
Yan M, Xu H, Waddell N, Shield-Artin K, Haviv I, McKay MJ, Fox SB (2012) Enhanced RAD21 cohesin expression confers poor prognosis in BRCA2 and BRCAX, but not BRCA1 familial breast cancers. Breast Cancer Res 14(2):R69. doi:10.1186/bcr3176
Zehavi L, Avraham R, Barzilai A, Bar-Ilan D, Navon R, Sidi Y, Leibowitz-Amit R (2012) Silencing of a large microRNA cluster on human chromosome 14q32 in melanoma: biological effects of mir-376a and mir-376c on insulin growth factor 1 receptor. Mol Cancer 11:44. doi:10.1186/1476-4598-11-44
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the patients, staff, and nurses in the Endoscopy and the pathology Department of Tabriz Imam Reza hospital who sincerely helped us in conducting this project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There is no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Azarbarzin, S., Hosseinpour Feizi, M.A., Safaralizadeh, R. et al. The Value of miR-299-5p in Diagnosis and Prognosis of Intestinal-Type Gastric Adenocarcinoma. Biochem Genet 54, 413–420 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-016-9728-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-016-9728-y