Abstract
Purpose
Recent studies have shown that circular RNAs (circRNAs) are closely related to the occurrence and development of gastric cancer. In this paper, we analyzed the value of hsa_circ_0003195 in diagnosis and prognosis of gastric cancer.
Methods
Quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) was used to determine the level of hsa_circ_0003195 in 100 paired gastric cancer tissues and paracancerous tissues, 74 paired fasting plasma from gastric cancer patients before and 10 days after operation, and 74 fasting plasmas from healthy controls. A receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was generated to evaluate the diagnostic value. The survival analysis and Cox proportional-hazards model were used to evaluate the efficiency of hsa_circ_0003195 in predicting overall survival (OS) in patients with gastric cancer.
Results
The expression of hsa_circ_0003195 was down-regulated in gastric cancer tissues and plasma from patients with gastric cancer. The expression level of hsa_circ_0003195 was correlated with differentiation, TNM stages, lymphatic metastasis, and distal metastasis. The area under the ROC curve (AUC) of tissue and plasma hsa_circ_0003195 was 0.684 and 0.695, respectively. The plasma hsa_circ_0003195 can be used as predictors of survival of patients with gastric cancer.
Conclusion
Hsa_circ_0003195 may be a new diagnostic and prognostic marker of gastric cancer.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Gastric cancer is a common digestive tract cancer in the world. In 2020, there were 1.089 million new cases of gastric cancer and 769,000 deaths in the world, accounting for 5.6% and 7.7% of all cancer cases and deaths, respectively [1]. The incidence of gastric cancer ranks fifth among all kinds of tumors in the world; and the mortality ranks fourth among all kinds of tumors. The morbidity and mortality of gastric cancer are high in East Asia [1]. Most early gastric cancer is curable, but the early symptoms of gastric cancer are not obvious. The treatment of advanced gastric cancer patients is very difficult [2,3,4]. Therefore, early diagnosis is very important for patients with gastric cancer. Clinically, gastric cancer is usually diagnosed by gastroscopy and pathological examination; but this diagnostic method is invasive [4,5,6,7].
It is important to find new diagnostic markers for gastric cancer. Circular RNAs (circRNAs) are a kind of RNA molecules with closed-ring structure. They are widely distributed in various tissues and cells [8, 9]. Recent studies have found that circRNAs not only regulate gene transcription, but also translate into proteins [10,11,12]. CircRNAs have been proved to play an important role in human diseases [12,13,14]. However, the role of circRNAs in gastric cancer has not been fully elucidated.
In this study, we focused on hsa_circ_0003195 (http://www.circbase.org/cgi-bin/simplesearch.cgi). Its gene is located at chr2:32858942-32865477; its relative gene symbol is TTC27 (tetratricopeptide repeat domain 27). The reason that we chose hsa_circ_0003195 as the target of this study is that it was one of the gastric cancer-associated circRNAs based on our previous microarray screening results (GEO No. GSE89143, Guo, 2016; https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/query/acc.cgi?acc=GSE89143) [16]. In this study, we expanded sample size and further found that hsa_circ_0003195 was aberrantly expressed in gastric cancer tissues and plasma from patients with gastric cancer. More important, hsa_circ_0003195 level was related to main clinicopathological factors of gastric cancer patients, suggesting that it may be a diagnostic biomarker and prognostic factor of gastric cancer.
Methods
Patients and tissue specimens
Gastric cancer patients' tissues group: 100 gastric cancer patients from The Affiliated People’s Hospital, Ningbo University, Ningbo, China, between January 2015 and March 2019. No chemotherapy and other treatments were used when samples were obtained. Small pieces of tissues no more than 0.5 cm thickness were taken intraoperatively in the gastric cancer lesion and corresponding non-tumor normal tissues 5 cm from the lesion, respectively. The removed tissues were put into 1 ml RNAfixer sample preservation solution (Bioteke, Beijing, China) and stored at a − 80 °C freezer till use. All tissue samples were pathologically diagnosed.
Gastric cancer patients' plasma group: 74 gastric cancer patients from The Affiliated People’s Hospital, Ningbo University, Ningbo, China, between January 2015 and July 2019. Total 3 ml fasting peripheral venous blood was collected in ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) anticoagulant tubes before and 10 days after surgery. The blood was first centrifuged at 3000 rpm for 10 min at room temperature. Then the upper plasma layer was transferred to a 2 ml RNase free Eppendorf tube and stored at − 80 °C freezer till use.
Healthy controls: 74 age- and sex-matched healthy individuals from Ningbo No. 1 Hospital who were for health examined in August 2016. Plasma collection and preservation were as the same as described above.
Tumor clinical stages were assessed according to the tumor–node–metastasis (TNM) staging system (8th ed.) [17].
The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Ningbo University School of Medicine (No. 2017022701). Written informed consent was obtained from all the participants.
Total RNA extraction
Total RNA in tissues and plasma was first extracted with TRIzol reagent and TRIzol LS reagent (Invitrogen, Karlsruhe, Germany) following the manufacturer's instructions, respectively. Then, the purity and concentration of total RNA were detected with a SmartSpec Plus Spectrophotometer (Denovix, Hercules, CA, USA).
Reverse transcription of total RNA
Total RNA was reverse transcribed to yield cDNA according to the instructions of the reverse transcription kit from Promega (Promega, Madison, WI, USA) [16].
qRT-PCR detection of hsa_circ_0003195
In the Mx3005p real-time PCR system (Stratagene, La Jolla, CA, USA), GoTaq qPCR Master MX (Promega) was used for real-time quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR). Primers for hsa_circ_0003195 and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH, used as a control) were designed and synthesized by Primer-Blast and BGI-Tech (Shenzhen, China), respectively. The divergent primers’ sequences for hsa_circ_0003195 were 5′-CTACAGCCTGACCTCGAAGC-3′ and 5′-TCAACTGTTGTCTGAATAGCTGTC-3′. The convergent primers’ sequences of GAPDH were 5′-AAGGTGAAGGTCGGAGTCAA-3′ and 5′-AATGAAGGGGTCATTGATGG-3′. The qRT-PCR results were expressed as ΔCq value with calculation formula ΔCq = Cq(circRNA) – Cq(GAPDH). The higher the ΔCq value, the lower the expression level of hsa_circ_0003195.
Statistical analysis
Statistical Program for Social Sciences (SPSS) software 22.0 (IBM Inc., Chicago, IL, USA) and GraghPad Prism 5.0 (GraphPad Software, La Jolla, CA, USA) were used to analyze experimental data. The two-sample t test were used to compare the differences of hsa_circ_0003195 levels between gastric cancer tissues and adjacent tissues; and one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) were used to compare the differences of hsa_circ_0003195 levels among preoperative, postoperative gastric cancer patient plasma, and healthy control plasma. The χ2 test and Mann–Whitney rank test were used to analyze the correlation between the hsa_circ_0003195 levels and clinicopathological factors. The diagnostic value of hsa_circ_0003195 was analyzed by establishing the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve. The prediction efficiency of hsa_circ_0003195 in tissues and plasma for postoperative overall survival (OS) of patients with gastric cancer was evaluated by survival analysis and Cox proportional-hazards model. The value of P < 0.05 can be considered statistically significant.
Results
Down-regulation of hsa_circ_0003195 expression in gastric cancer tissues and plasma of patients with gastric cancer
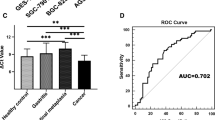
We detected the expression of hsa_circ_0003195 in gastric cancer tissues and plasma of gastric cancer patients. As shown in Fig. 1, the expression of hsa_circ_0003195 in gastric cancer tissues was lower than that in corresponding non-tumor normal tissues (P < 0.001); and the expression of hsa_circ_0003195 in plasma of preoperative patients with gastric cancer was significantly lower than that in healthy subjects (P < 0.001), as well as it also lower than that in postoperative patients (P = 0.005). But through comparing hsa_circ_0003195 expression level of the healthy controls and postoperative patients, the result showed that there was no statistical difference (P = 0.689), meaning most postoperative patients restored plasma hsa_circ_0003195 levels.
The hsa_circ_0003195 expression was detected by qRT-PCR. a Hsa_circ_0003195 expression levels in gastric cancer tissues and corresponding non-tumor normal tissues. P < 0.001, n = 100. b Hsa_circ_0003195 expression levels in plasma from preoperative patients with gastric cancer, postoperative patients with gastric cancer and healthy control. Preoperation vs. Postoperation: P = 0.005; Preoperation vs. Healthy control: P < 0.001; Postoperation vs. Healthy control: P = 0.689. n = 74. The higher ΔCq value means the lower expression
The correlation of hsa_circ_0003195 expression level in gastric cancer tissues and plasma from gastric cancer patients with clinicopathological factors
We first measured the median expression level of hsa_circ_0003195 in gastric cancer tissues or plasma from preoperative gastric cancer, and then divided patients with gastric cancer into two groups. The patients whose expression level of hsa_circ_0003195 were higher and lower than the median were thought as high expression group and low expression group, respectively. Combined with the clinicopathological data of gastric cancer patients studied, we found that the expression level of hsa_circ_0003195 in gastric cancer tissues was related to degree of differentiation (P = 0.024), TNM stage (P = 0.002), lymphatic metastasis (P = 0.009), and distant metastasis (P = 0.041) (Table 1). At the same time, the level of hsa_circ_0003195 in plasma from gastric cancer patients was related to distant metastasis (P = 0.040) (Table 2). According to the results, we were able to learn that, at the tissue aspect, the expression level of hsa_circ_0003195 was affected by differentiation, TNM stage, and lymphatic metastasis, suggesting that hsa_circ_0003195 might have the value of diagnosis of gastric cancer. Meanwhile, at the plasma aspect, the expression level of hsa_circ_0003195 was affected by distant metastasis, suggesting that it is related to postoperative survival.
Using ROC curve to analyze the diagnostic value of hsa_circ_0003195 as a biomarker of gastric cancer
According to the difference of hsa_circ_0003195 expression between gastric cancer tissues and normal tissues, plasma from gastric cancer patients and healthy people, we established ROC curves to analyze the diagnostic value of hsa_circ_0003195. The results showed that the area under the ROC curve (AUC) of hsa_circ_0003195 in tissues was 0.684 (Fig. 2), while the specificity and the sensitivity were 0.420 and 0.910, respectively. The AUC of hsa_circ_0003195 in plasma was 0.695; and the specificity and sensitivity were 0.946 and 0.469, respectively. For the hsa_circ_0003195 in the tissues, we found that 91.00% true positive patients were detected. The probability of correct diagnosis of gastric cancer was 1.57 times the probability of misdiagnosis of gastric cancer, indicating that it may be useful in the diagnosis of patients with suspected gastric cancer. As for hsa_circ_0003195 in plasma, we found that 94.59% true-negative people were detected. The probability of missed diagnosis was 0.56 times the probability of correctly excluding gastric cancer, indicating that it may have certain significance for gastric cancer screening. The reason that the expression levels of cancer and non-cancer hsa_circ_0003195 have a certain degree of overlap may be relative small number of sample.
The possibility of hsa_circ_0003195 as a prognostic indicator
We also measured the median expression level of hsa_circ_0003195 in gastric cancer tissues and divided them into high expression group and low expression group as same as above. In addition, we calculated the ratio of hsa_circ_0003195 in plasma of patients with gastric cancer before and after operation, and then took the patients whose ratio was less than 1 and greater than 1 as recovered group and non-recovered group, respectively.
Through Kaplan–Meier survival analysis, we found that the overall survival (OS) of patients with high expression of hsa_circ_0003195 in gastric cancer tissues was better those patients with low expression (Fig. 3a, P = 0.0006). The 1-year survival rates of high expression group and low expression group were 97.96% and 86.275%; and the 5-year survival rates were 93.83% and 63.05%, respectively. At the same time, we found that the OS rate of the recovery group was better than that of the non-recovery group (Fig. 3b, P = 0.0005). The 1-year survival rates of postoperative recovered group and non-recovered group were 96.30% and 85.00%; and the 5-year survival rates of postoperative recovered group and non-recovered group were, respectively, 92.98% and 60.42%, respectively.
Then, through Cox proportional-hazard model classification, it was found that the expression level of hsa_circ_0003195 in gastric cancer tissues (P = 0.030) (Table 3) and changes of in plasma of gastric cancer patients (P = 0.011) (Table 4) could be used as independent predictors of OS of gastric cancer patients.
Discussion
As an auxiliary tool for cancer diagnosis, tumor biomarkers have always been a hot issue in tumor research. With the development of scientific research and technology, more and more biomarkers, such as CEA [18], CA19-9 [19], CA72-4 [20], CA125 [21], and so on, have been used in the diagnosis of gastric cancer. However, their sensitivity and specificity are not satisfied.
In recent years, the once inconspicuous circRNAs have gradually entered people's field of vision. circRNAs have been gradually studied by researchers because of their good stability [22]. Most circRNAs are produced by reverse splicing of precursor mRNA (pre-mRNA) through non-classical splicing [9]. circRNAs exist widely in human tissues, plasma, and exosomes [8, 23]. Studies have shown that circRNAs are involved in the occurrence, development, and distant metastasis of gastric cancer [8, 15, 16, 23, 24].
In addition, because of circRNAs’ abnormal expression in cancer tissues, researchers began to consider their role in the diagnosis of cancers [8, 23]. In this study, we found that, compared with normal tissues and plasma, the expression of hsa_circ_0003195 was low in gastric cancer tissues and plasma of patients with gastric cancer (Fig. 1). They are consistent between tissue samples and plasma samples. Many studies have showed that the circRNA levels in plasma can indicate the situation of cancer patients [8, 15, 16]. The plasma include exosomes, which are vesicles generated and released by normal and cancer cells. Exosomes, carrying a cargo of DNA, RNA, proteins, lipids, and their derivatives, modulate cells' behaviors, influence the extracellular system, and may be a source of human disease biomarkers [8]. Exosomal circRNAs have unique profiles reflecting the characteristics of tumors [8]. Moreover, the amount of hsa_circ_0003195 in blood was restored after the surgical resection (Fig. 1b). This indicates that most cancer tissues in gastric cancer patients' body had been removed by operation and the hsa_circ_0003195 level in blood went back to normal level as healthy controls. It means that hsa_circ_0003195 may be used to monitor recurrence.
A research showed that the degree of early gastric cancer associated with lymph node metastasis [25]. What’s more, the incidence of gastric cancer increased gradually along with the growth of the age; about 10% of the gastric cancer were found in 45 years of age or younger [26]. In this study, we through the analysis of the correlation between hsa_circ_0003195 expression level and pathological data found that in gastric cancer tissues, the expression level of hsa_circ_0003195 was related to degree of differentiation, TNM stage, lymphatic metastasis, and distant metastasis (Table 1). This suggests that tissue hsa_circ_0003195 may be used in the diagnosis of gastric cancer. It is interesting to note that the distant lymph node metastasis negatively affected the survival rate of patients with gastric cancer [27]. Therefore, distant metastasis is an important prognostic indicator of gastric cancer, with distant lymph node metastasis of gastric cancer patients with poor prognosis. In this study, we found that the level of hsa_circ_0003195 in plasma from gastric cancer patients was related to distant metastasis (Table 2). These indicate that plasma hsa_circ_0003195 may be associated with the prognosis of gastric cancer and may be a prognostic biomarker of gastric cancer.
And the AUC of the hsa_circ_0003195 in tissues and plasma were 0.684 and 0.695, respectively (Fig. 2). The diagnostic efficiency was better than that of CEA and CA19-9 in plasma. It reminds that the use of hsa_circ_0003195 has great potential as a new biomarker for diagnosis of gastric cancer. For prognosis of gastric cancer patients, the expression level of hsa_circ_0003195 in tissues (Table 3) and the postoperative response of hsa_circ_0003195 in plasma (Table 4) can be used as independent predictors of patients with gastric cancer.
Conclusion
According to the above results, we think that hsa_circ_0003195 has clinical significance in the diagnosis of gastric cancer. It is a potential new biomarker for screening and prognosis evaluation of gastric cancer.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel R et al (2021) Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 71(3):209–249
Alshehri A, Alanezi H, Kim B (2020) Prognosis factors of advanced gastric cancer according to sex and age. World J Clin Cases 8(9):1608–1619
Shen Y, Yu X, Ruan Y et al (2021) Global profile of tRNA-derived small RNAs in gastric cancer patient plasma and identification of tRF-33-P4R8YP9LON4VDP as a new tumor suppressor. Int J Med Sci 18(7):1570–1579
Wang F, Shen L, Li J et al (2019) The Chinese society of clinical oncology (CSCO): clinical guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of gastric cancer. Cancer Commun (Lond) 39(1):10
Martin-Richard M, Carmona-Bayonas A, Custodio A et al (2020) SEOM clinical guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of gastric cancer (GC) and gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinoma (GEJA) (2019). Clin Transl Oncol 22(2):236–244
Shen Y, Xie Y, Yu X et al (2021) Clinical diagnostic values of transfer RNA-derived fragment tRF-19-3L7L73JD and its effects on the growth of gastric cancer cells. J Cancer 12(11):3230–3238
Deng G, Mou T, He J et al (2020) Circular RNA circRHOBTB3 acts as a sponge for miR-654-3p inhibiting gastric cancer growth. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 39(1):1
Wang Y, Li Z, Xu S et al (2020) Novel potential tumor biomarkers: circular RNAs and exosomal circular RNAs in gastrointestinal malignancies. J Clin Lab Anal 34(7):e23359
Wang Y, Lu T, Wang Q et al (2018) Circular RNAs: crucial regulators in the human body. Oncol Rep 40(6):3119–3135
Memczak S, Jens M, Elefsinioti A et al (2013) Circular RNAs are a large class of animal RNAs with regulatory potency. Nature 495(7441):333–338
Li Z, Huang C, Bao C et al (2015) Exon-intron circular RNAs regulate transcription in the nucleus. Nat Struct Mol Biol 22(3):256–264
Li Z, Ruan Y, Zhang H et al (2019) Tumor-suppressive circular RNAs: mechanisms underlying their suppression of tumor occurrence and use as therapeutic targets. Cancer Sci 110(12):3630–3638
Cao H, Chen J, Lai X et al (2021) Circular RNA expression profile in human primary multiple intracranial aneurysm. Exp Ther Med 21(3):239
He X, Bao X, Tao Z et al (2021) The microarray identification circular RNA hsa_circ_0105015 up-regulated involving inflammation pathway in essential hypertension. J Clin Lab Anal 35(2):e23603
Ruan Y, Li Z, Shen Y et al (2020) Functions of circular RNAs and their potential applications in gastric cancer. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 14(2):85–92
Shao Y, Li J, Lu R et al (2017) Global circular RNA expression profile of human gastric cancer and its clinical significance. Cancer Med 6(6):1173–1180
Sobin LH, Fleming ID (1997) TNM classification of malignant tumors, fifth edition (1997). Union Internationale Contre le cancer and the American joint committee on cancer. Cancer 80(9):1803–1804
Shimada H, Noie T, Ohashi M et al (2014) Clinical significance of serum tumor markers for gastric cancer: a systematic review of literature by the task force of the Japanese gastric cancer association [J]. Gastric Cancer 17(1):26–33
Gong X, Zhang H (2020) Diagnostic and prognostic values of anti-helicobacter pylori antibody combined with serum CA724, CA19-9, and CEA for young patients with early gastric cancer. J Clin Lab Anal 34(7):e23268
Ubukata H, Katano M, Motohashi G et al (2003) Evaluation of CA72-4 as a tumor marker in patients with gastric cancer. Gan To Kagaku Ryoho 30(11):1821–1824
Zhu X, Zhou W, Chen Y et al (2014) High serum carbohydrate antigen 125 concentration can predict serous effusion but not gastrointestinal malignancy in male patients. Tumor Biol 35(6):5129–5135
Yu X, Ding H, Yang L et al (2020) Reduced expression of circRNA hsa_circ_0067582 in human gastric cancer and its potential diagnostic values. J Clin Lab Anal 34(3):e23080
Tao X, Shao Y, Yan J et al (2021) Biological roles and potential clinical values of circular RNAs in gastrointestinal malignancies. Cancer Biol Med 18(2):437–457
Zhang Y, Xia L, Wu J et al (2020) Hsa_circ_0023642 promotes proliferation, invasion, and migration of gastric cancer by sponging microRNA-223. J Clin Lab Anal 34(10):e23428
Chen R, He Q, Cui J et al (2014) Lymph node metastasis in early gastric cancer. Chin Med J (Engl) 127(3):560–567
Moriguchi S, Odaka T, Hayashi Y et al (1991) Death due to recurrence following curative resection of early gastric cancer depends on age of the patient. Br J Cancer 64(3):555–558
Isozaki H, Okajima K, Ichinona T et al (1997) Distant lymph node metastasis of early gastric cancer. Surg Today 27(7):600–605
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a grant from The National Natural Science Foundation of China (81772279), the K. C. Wong Magna Fund in Ningbo University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YM, ZL, DM, and WS collected clinical information; WS reviewed the pathological diagnosis; YM and JG analyzed the data and wrote the manuscript; ZL, WS, and JG made critical revisions to the manuscript; WS and JG designed the study; JG gave the final approval of the manuscript for publication. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no potential competing interests.
Ethical approval
The authors adhered to institutional ethical standards.
Informed consent
All patients signed an informed consent form for research.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, Y., Li, Z., Ma, D. et al. Hsa_circ_0003195 as a biomarker for diagnosis and prognosis of gastric cancer. Int J Clin Oncol 27, 354–361 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10147-021-02073-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10147-021-02073-w