Abstract
Background and purpose
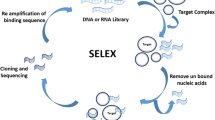
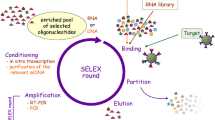
Nucleic acid aptamers are a novel molecular recognition tool that is functionally similar to antibodies but superior to antibodies in terms of thermal stability, structural modification, preparation, and cost, and therefore hold great promise for molecular detection. However, due to the limitations of a single aptamer in molecular detection, the multiple aptamer combination for bioanalysis has received much attention. Here, we reviewed the progress of tumor precision detection based on the combination of multiple nucleic acid aptamers and optical methods and discussed its challenges and prospects.
Methods
The relevant literature in PubMed was collected and reviewed.
Results
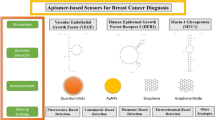
The combination of two or more aptamers with modern nanomaterials and analytical methods allows the fabrication of various detection systems for the simultaneous detection of different structural domains of a substance and/or different substances, including soluble tumor markers, tumor cell surface and intracellular markers, circulating tumor cells, and other tumor-related biomolecules, which has great potential for application in efficient and precise tumor detection.
Conclusion
The combination of multiple nucleic acid aptamers provides a new approach for the precise detection of tumors and will play an important role in precision medicine for tumors.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Bates SE (1991) Clinical applications of serum tumor markers. Ann Intern Med 115(8):623–638. https://doi.org/10.7326/0003-4819-115-8-623
Chang X, Zhang C, Lv C et al (2019) Construction of a multiple-aptamer-based DNA logic device on live cell membranes via associative toehold activation for accurate cancer cell identification. J Am Chem Soc 141(32):12738–12743. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.9b05470
Dai J, Su Y, Zhong S et al (2020) Exosomes: key players in cancer and potential therapeutic strategy. Signal Transduct Target Ther 5(1):145. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-020-00261-0
Dong H, Han L, Wang J et al (2018) In vivo inhibition of circulating tumor cells by two apoptosis-promoting circular aptamers with enhanced specificity. J Control Release 280:99–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2018.05.004
Flanagan SP, Fogel R, Edkins AL et al (2021) Nonspecific nuclear uptake of anti-MUC1 aptamers by dead cells: the role of cell viability monitoring in aptamer targeting of membrane-bound protein cancer biomarkers. Anal Methods 13(9):1191–1203. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0ay01878c
Gao Q, Zhao Y, Xu K et al (2020) Highly specific, single-step cancer cell isolation with multi-aptamer-mediated proximity ligation on live cell membranes. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 59(52):23564–23568. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202011198
Hayes DF, Paoletti C (2013) Circulating tumour cells: insights into tumour heterogeneity. J Intern Med 274(2):137–143. https://doi.org/10.1111/joim.12047
Hofmann A, Gerrits B, Schmidt A et al (2010) Proteomic cell surface phenotyping of differentiating acute myeloid leukemia cells. Blood 116(13):e26–e34. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2010-02-271270
Jia W, Xie D, Li F et al (2021) Evaluation the effect of nanoparticles on the structure of aptamers by analyzing the recognition dynamics of aptamer functionalized nanoparticles. Anal Chim Acta 1183:338976. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2021.338976
Kalluri R, LeBleu VS (2020) The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science 367(6478):eaau6977. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aau6977
Lee J, Kang HJ, Jang H et al (2015) Simultaneous imaging of two different cancer biomarkers using aptamer-conjugated quantum dots. Sensors (basel) 15(4):8595–8604. https://doi.org/10.3390/s150408595.34
Li N, Ebright JN, Stovall GM et al (2009) Technical and biological issues relevant to cell typing with aptamers. J Proteome Res 8(5):2438–2448. https://doi.org/10.1021/pr801048z
Li L, Xu S, Yan H et al (2021) Nucleic acid aptamers for molecular diagnostics and therapeutics: advances and perspectives. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 60(5):2221–2231. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202003563
Lin D, Shen L, Luo M et al (2021) Circulating tumor cells: biology and clinical significance. Signal Transduct Target Ther 6(1):404. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-021-00817-8
Liu Y, Le C, Tyrrell DL et al (2020) Aptamer binding assay for the E antigen of hepatitis B using modified aptamers with G-quadruplex structures. Anal Chem 92(9):6495–6501. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.9b05740
Manochehry S, McConnell EM, Li Y (2019) Unraveling determinants of affinity enhancement in dimeric aptamers for a dimeric protein. Sci Rep 9(1):17824. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-54005-4
Martínez O, Bellard E, Golzio M et al (2014) Direct validation of aptamers as powerful tools to image solid tumor. Nucleic Acid Ther 24(3):217–225. https://doi.org/10.1089/nat.2013.0444
Mattiuzzi C, Lippi G (2019) Current cancer epidemiology. J Epidemiol Glob Health 9(4):217–222. https://doi.org/10.2991/jegh.k.191008.001
Ning CF, Wang L, Tian YF, Yin BC, Ye BC (2020) Multiple and sensitive SERS detection of cancer-related exosomes based on gold-silver bimetallic nanotrepangs. Analyst 145(7):2795–2804. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9an02180a
Pantel K, Alix-Panabières C (2016) Functional studies on viable circulating tumor cells. Clin Chem 62(2):328–334. https://doi.org/10.1373/clinchem.2015.242537
Paoletti C, Hayes DF (2014) Molecular testing in breast cancer. Annu Rev Med 65:95–110. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-med-070912-143853
Qi L, Liu S, Jiang Y, Lin JM, Yu L, Hu Q (2020) Simultaneous detection of multiple tumor markers in blood by functional liquid crystal sensors assisted with target-induced dissociation of aptamer. Anal Chem 92(5):3867–3873. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.9b05317
Vorobyeva M, Vorobjev P, Venyaminova A (2016) Multivalent aptamers: versatile tools for diagnostic and therapeutic applications. Molecules 21(12):1613. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21121613
Wang Y, Tang L, Li Z, Lin Y, Li J (2014) In situ simultaneous monitoring of ATP and GTP using a graphene oxide nanosheet-based sensing platform in living cells. Nat Protoc 9(8):1944–1955. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2014.126
Wang Z, Zong S, Wang Y et al (2018) Screening and multiple detection of cancer exosomes using an SERS-based method. Nanoscale 10(19):9053–9062. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7nr09162a
Wang D, Li S, Zhao Z, Zhang X, Tan W (2021) Engineering a second-order DNA logic-gated nanorobot to sense and release on live cell membranes for multiplexed diagnosis and synergistic therapy. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 60(29):15816–15820. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202103993
Xu S, Feng X, Gao T et al (2017) Aptamer induced multicoloured Au NCs-MoS2 “switch on” fluorescence resonance energy transfer biosensor for dual color simultaneous detection of multiple tumor markers by single wavelength excitation. Anal Chim Acta 983:173–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2017.06.023
Xu Y, Wang H, Luan C, Liu Y, Chen B, Zhao Y (2018) Aptamer-based hydrogel barcodes for the capture and detection of multiple types of pathogenic bacteria. Biosens Bioelectron 100:404–410. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2017.09.032
Xu J, Chen W, Shi M et al (2019) An aptamer-based four-color fluorometic method for simultaneous determination and imaging of alpha-fetoprotein, vascular endothelial growth factor-165, carcinoembryonic antigen and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 in living cells. Mikrochim Acta 186(3):204. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3312-1
Xu X, Ji J, Chen P et al (2020) Salt-induced gold nanoparticles aggregation lights up fluorescence of DNA-silver nanoclusters to monitor dual cancer markers carcinoembryonic antigen and carbohydrate antigen 125. Anal Chim Acta 1125:41–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2020.05.027
Xu L, Zhou Z, Gou X et al (2021) Light up multiple protein dimers on cell surface based on proximity-induced fluorescence activation of DNA-templated sliver nanoclusters. Biosens Bioelectron 179:113064. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2021.113064
Yu W, Hurley J, Roberts D et al (2021) Exosome-based liquid biopsies in cancer: opportunities and challenges. Ann Oncol 32(4):466–477. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.annonc.2021.01.074
Zhang Z, Liu C, Yang C et al (2018) Aptamer-patterned hydrogel films for spatiotemporally programmable capture and release of multiple proteins. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 10(10):8546–8554. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.8b00191
Zhang D, Zheng Y, Lin Z et al (2020a) Equipping natural killer cells with specific targeting and checkpoint blocking aptamers for enhanced adoptive immunotherapy in solid tumors. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 59(29):12022–12028. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202002145
Zhang Q, Wang W, Huang S et al (2020b) Capture and selective release of multiple types of circulating tumor cells using smart DNAzyme probes. Chem Sci 11(7):1948–1956. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9sc04309h.26
Zhang X, Wei X, Men X et al (2021) Dual-multivalent-aptamer-conjugated nanoprobes for superefficient discerning of single circulating tumor cells in a microfluidic chip with inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry detection. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 13(36):43668–43675. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.1c11953
Zhao X, Lis JT, Shi H (2013) A systematic study of the features critical for designing a high avidity multivalent aptamer. Nucleic Acid Ther 23(3):238–242. https://doi.org/10.1089/nat.2012.0410
Zhao B, Wu P, Zhang H, Cai C (2015) Designing activatable aptamer probes for simultaneous detection of multiple tumor-related proteins in living cancer cells. Biosens Bioelectron 68:763–770. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2015.02.004
Zhao L, Tang C, Xu L et al (2016) Enhanced and differential capture of circulating tumor cells from lung cancer patients by microfluidic assays using aptamer cocktail. Small 12(8):1072–1081. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201503188
Zheng F, Cheng Y, Wang J et al (2014) Aptamer-functionalized barcode particles for the capture and detection of multiple types of circulating tumor cells. Adv Mater 26(43):7333–7338. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201403530
Zhong Y, Wang X, Zha R et al (2021) Dual-wavelength responsive photoelectrochemical aptasensor based on ionic liquid functionalized Zn-MOFs and noble metal nanoparticles for the simultaneous detection of multiple tumor markers. Nanoscale 13(45):19066–19075. https://doi.org/10.1039/d1nr05782k
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Project No. 82160494, 82160444) and the Science and Technology Program of Jiangxi Province (Project No. 2019BBG70048).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
DC, GC, TW, and KZ participated in conception and design; DC and GC participated in drafting the manuscript; DC and TW participated in the reference review; DC and KZ participated in the revision of manuscript. DC and GC should be considered co-first author. All authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Informed consent
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Cai, D., Chen, GL., Wang, T. et al. Combination of multiple nucleic acid aptamers for precision detection of tumors based on optical methods. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 149, 7895–7903 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-023-04646-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-023-04646-w