Abstract
Background
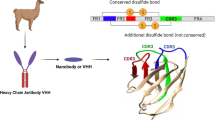
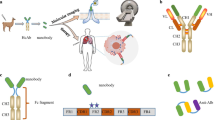
The current progressive increase in the cancer burden of prostate cancer requires the exploration of new diagnostic and therapeutic approaches. Nanobodies are single-domain antibodies with the advantages of small size, high stability, easy processing and modification, which are increasingly used in the treatment of many types of cancer.
Methods
This review analyzed the relevant literature in PubMed and other databases.
Result
In the retrieved literature, nanobodies are widely used in the treatment of prostate cancer. The preparation of nanobodies targeting PSA or PSMA is straightforward. For diagnostic purposes, nanobodies can be used in the preparation of biosensors for more sensitive identification of prostate cancer; for therapeutic purposes, nanobodies are used in the preparation of immunotoxic and ADC drugs. Preclinical in vivo and in vitro experiments have shown that this therapeutic approach is feasible. This article is a review of the above to provide new ideas for the treatment of prostate cancer.
Conclusion
Compared with traditional antibodies, nano-antibodies have the advantages of small size, high stability, and high penetration. These advantages make nano-antibodies worthy to be widely used. Current studies have shown that nanobodies have advantages and future in the diagnosis and treatment of prostate cancer.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Afshar-Oromieh A, Alberts I, Sachpekidis C, Rominger A (2019) Prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA)-based diagnostics and treatment of prostate cancer. Urologe A 58:1429–1434. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00120-019-01067-x
Allegra A, Innao V, Gerace D, Vaddinelli D, Allegra AG, Musolino C (2018) Nanobodies and cancer: current status and new perspectives. Cancer Invest 36:221–237. https://doi.org/10.1080/07357907.2018.1458858
Bagchi S, Yuan R, Engleman EG (2021) Immune checkpoint inhibitors for the treatment of cancer: clinical impact and mechanisms of response and resistance. Annu Rev Pathol 16:223–249. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-pathol-042020-042741
Bannas P, Hambach J, Koch-Nolte F (2017) Nanobodies and nanobody-based human heavy chain antibodies as antitumor therapeutics. Front Immunol 8:1603. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2017.01603
Bastos-Soares EA et al (2020) Single domain antibodies in the development of immunosensors for diagnostics. Int J Biol Macromol 165:2244–2252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.10.031
Belicky S, Damborsky P, Zapatero-Rodriguez J, O’Kennedy R, Tkac J (2017) Full-length antibodies versus single-chain antibody fragments for a selective impedimetric lectin-based glycoprofiling of prostate specific antigen. Electrochim Acta 246:399–405. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2017.06.065
Chaput G, Sumar N (2022) Endocrine therapies for breast and prostate cancers: essentials for primary care. Can Fam Physician 68:271–276. https://doi.org/10.46747/cfp.6804271
Chatalic KL et al (2015) A novel 111 in-labeled anti-prostate-specific membrane antigen nanobody for targeted SPECT/CT imaging of prostate cancer. J Nucl Med 56:1094–1099. https://doi.org/10.2967/jnumed.115.156729
De Genst E et al (2006) Molecular basis for the preferential cleft recognition by dromedary heavy-chain antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:4586–4591. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0505379103
De Munter S et al (2020) Rapid and effective generation of nanobody based CARs using PCR and Gibson assembly. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21030883
Duffy MJ (2020) Biomarkers for prostate cancer: prostate-specific antigen and beyond. Clin Chem Lab Med 58:326–339. https://doi.org/10.1515/cclm-2019-0693
Epstein JI, Egevad L, Amin MB, Delahunt B, Srigley JR, Humphrey PA (2016) The 2014 international society of urological pathology (ISUP) consensus conference on Gleason grading of prostatic carcinoma. Am J Surg Pathol 40(2):244–252
Evazalipour M et al (2014) Generation and characterization of nanobodies targeting PSMA for molecular imaging of prostate cancer. Contrast Media Mol Imaging 9:211–220. https://doi.org/10.1002/cmmi.1558
Goulet DR, Atkins WM (2020) Considerations for the design of antibody-based therapeutics. J Pharm Sci 109:74–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.xphs.2019.05.031
Hamers-Casterman C et al (1993) Naturally occurring antibodies devoid of light chains. Nature 363:446–448. https://doi.org/10.1038/363446a0
Huang L et al (2005) Prostate-specific antigen immunosensing based on mixed self-assembled monolayers, camel antibodies and colloidal gold enhanced sandwich assays. Biosens Bioelectron 21:483–490. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2004.11.016
Khongorzul P, Ling CJ, Khan FU, Ihsan AU, Zhang J (2020) Antibody-drug conjugates: a comprehensive review. Mol Cancer Res 18:3–19. https://doi.org/10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-19-0582
Liu X, Wang D, Chu J, Xu Y, Wang W (2018) Sandwich pair nanobodies, a potential tool for electrochemical immunosensing serum prostate-specific antigen with preferable specificity. J Pharm Biomed Anal 158:361–369. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2018.06.021
Luo G et al (2019) Slp-coated liposomes for drug delivery and biomedical applications: potential and challenges. Int J Nanomedicine 14:1359–1383. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S189935
Maass DR, Sepulveda J, Pernthaner A, Shoemaker CB (2007) Alpaca (Lama pacos) as a convenient source of recombinant camelid heavy chain antibodies (VHHs). J Immunol Methods 324:13–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jim.2007.04.008
Maniam S, Maniam S (2021) Small molecules targeting programmed cell death in breast cancer cells. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22189722
McMurphy T (2014) The anti-tumor activity of a neutralizing nanobody targeting leptin receptor in a mouse model of melanoma. PLoS ONE 9(2):e89895
Mir MA, Mehraj U, Sheikh BA, Hamdani SS (2020) Nanobodies: the “magic bullets” in therapeutics, drug delivery and diagnostics. Hum Antibodies 28:29–51. https://doi.org/10.3233/HAB-190390
Moradi A, Srinivasan S, Clements J, Batra J (2019) Beyond the biomarker role: prostate-specific antigen (PSA) in the prostate cancer microenvironment. Cancer Metastasis Rev 38:333–346. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10555-019-09815-3
Nessler I et al (2020) Increased tumor penetration of single-domain antibody-drug conjugates improves in vivo efficacy in prostate cancer models. Cancer Res 80:1268–1278. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-19-2295
Petrylak DP et al (2020) PSMA ADC monotherapy in patients with progressive metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer following abiraterone and/or enzalutamide: efficacy and safety in open-label single-arm phase 2 study. Prostate 80:99–108. https://doi.org/10.1002/pros.23922
Pleschberger M, Saerens D, Weigert S, Sleytr UB, Muyldermans S, Sara M, Egelseer EM (2004) An S-layer heavy chain camel antibody fusion protein for generation of a nanopatterned sensing layer to detect the prostate-specific antigen by surface plasmon resonance technology. Bioconjug Chem 15:664–671. https://doi.org/10.1021/bc049964w
Powles T et al (2022) Atezolizumab with enzalutamide versus enzalutamide alone in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer: a randomized phase 3 trial. Nat Med 28:144–153. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-021-01600-6
Ricciuti B et al (2021) Antibody-drug conjugates for lung cancer in the era of personalized oncology. Semin Cancer Biol 69:268–278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcancer.2019.12.024
Roointan A et al (2019) Early detection of lung cancer biomarkers through biosensor technology: a review. J Pharm Biomed Anal 164:93–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2018.10.017
Ruigrok E et al (2021) Extensive preclinical evaluation of lutetium-177-labeled PSMA-specific tracers for prostate cancer radionuclide therapy. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 48:1339–1350. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-020-05057-6
Saerens D, Kinne J, Bosmans E, Wernery U, Muyldermans S, Conrath K (2004) Single domain antibodies derived from dromedary lymph node and peripheral blood lymphocytes sensing conformational variants of prostate-specific antigen. J Biol Chem 279:51965–51972. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M409292200
Schumacher D, Helma J, Schneider A, Leonhardt H, Hackenberger C (2018) Nanobodies: chemical functionalization strategies and intracellular applications. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 57:2314–2333. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201708459
Shajari S, Farajollahi MM, Behdani M, Tarighi P (2022) Production and conjugation of truncated recombinant diphtheria toxin to VEGFR-2 Specific nanobody and evaluation of its cytotoxic effect on PC-3 cell line. Mol Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-022-00485-1
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, Jemal A (2022) 2022 Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 72:7–33. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21708
Trilling AK et al (2014) Orientation of llama antibodies strongly increases sensitivity of biosensors. Biosens Bioelectron 60:130–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2014.04.017
Wang F, Li Z, Feng X, Yang D, Lin M (2022) Advances in PSMA-targeted therapy for prostate cancer. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis 25:11–26. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41391-021-00394-5
Xing Y et al (2021) A single-domain antibody-based anti-PSMA recombinant immunotoxin exhibits specificity and efficacy for prostate cancer therapy. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22115501
Yi-kai B, Hao-fei H, Jie S, Zhi-fang Z, Zhi-meng W (2022) Development and biological activity analysis of PSMA specific multivalent nanobodies China. Biotechnology 42:37–45
Funding
This project was supported by the Tianjin Science and Technology Program (Tianjin Natural Science Foundation Project), 19JCZDJC37000.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. This article was co-authored by JS and XL. They are co-first authors; SG and JZ collected the relevant data; XW created the graphs needed for the article; XL reviewed the full text and is the corresponding author of this article.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Not applicable.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent for participation
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Su, J., Liu, X., Guo, S. et al. Nanobodies: a new potential for prostate cancer treatment. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 149, 6703–6710 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-022-04515-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-022-04515-y