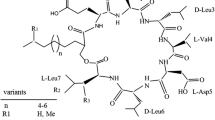
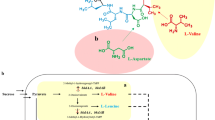
Abstract
Surfactin is a lipopeptide which has attracted massive attention due to its versatile bioactive properties, although it has less commercial application due to its low yield in wild strains. The B. velezensis Bs916 has enable commercial production of surfactin due to its outstanding capacity to synthesize lipopeptides and amenable to genetically engineering. In this study, 20 derivatives with high surfactin production were obtained firstly by transposon mutagenesis and knockout techniques, and the surfactin yield of the derivative H5 (△GltB) was increased approximately 7-folds, reaching to 1.48 g/L. The molecular mechanism of high yielding surfactin in △GltB was investigated by the transcriptomic and KEGG pathway analysis. The results indicated that △GltB enhanced its ability to synthesize surfactin mainly by promoting transcription of the srfA gene cluster and inhibiting degradation of some key precursors such as fatty acid. Secondly, we obtained a triple mutant derivative BsC3 by cumulative mutagenesis of the negative genes GltB, RapF, and SerA, and it could increase the surfactin titer by twofold, reaching to 2.98 g/L. Thirdly, we achieved overexpression of two key rate-limiting enzyme genes, YbdT, and srfAD, and the derivative BsC5 which further increased the surfactin titer by 1.3-fold, reaching to 3.79 g/L. Finally, the yield of surfactin by derivatives was significantly increased under the optimal medium, particularly the BsC5 increased the surfactin titer to 8.37 g/L. To the best of our knowledge, this is one of the highest yields that have been reported. Our work may pave way for large scale production of surfactin by B. velezensis Bs916.
Key points
• Elucidation of the molecular mechanism of surfactin high-yielding transposon mutant.
• Genetically engineering of B. velezensis Bs916 surfactin titer to 8.37 g/L for large scale preparation.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Arnaouteli S, Bamford NC, Stanley-Wall NR, Kovács ÁT (2021) Bacillus subtilis biofilm formation and social interactions. Nat Rev Microbiol 19:600–614. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41579-021-00540-9
Auchtung JM, Lee CA, Grossman AD (2006) Modulation of the ComA-dependent quorum response in Bacillus subtilis by multiple rap proteins and Phr peptides. J Bacteriol 188:5273–5285. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.00300-06
Bartal A, Vigneshwari A, Bóka B, Vörös M, Takács I, Kredics L, Manczinger L, Varga M, Vágvölgyi C, Szekeres A (2018) Effects of different cultivation parameters on the production of surfactin variants by a bacillus subtilis strain. Molecules 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23102675
Boyle EI, Weng S, Gollub J, Jin H, Botstein D, Cherry JM, Sherlock G (2004) GO::TermFinder—open source software for accessing Gene Ontology information and finding significantly enriched Gene Ontology terms associated with a list of genes. Bioinformatics 20(18):3710–3715. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bth456
Breton Le Y, Mohapatra NP, Haldenwang WG (2006) In vivo random mutagenesis of. Society 72:327–333. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.72.1.327
Chen XH, Vater J, Piel J, Franke P, Scholz R, Schneider K, Koumoutsi A, Hitzeroth G, Grammel N, Strittmatter AW, Gottschalk G, Süssmuth RD, Borriss R (2006) Structural and functional characterization of three polyketide synthase gene clusters in Bacillus amyloliquefaciens FZB 42. J Bacteriol 188:4024–4036. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.00052-06
Hu F, Liu Y, Li S (2019) Rational strain improvement for surfactin production: enhancing the yield and generating novel structures. Microb Cell Fact 18:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-019-1089-x
Jiao S, Li X, Yu H, Yang H, Li X, Shen Z (2017) In situ enhancement of surfactin biosynthesis in Bacillus subtilis using novel artificial inducible promoters. Biotechnol Bioeng 114:832–842. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.26197
Klausmann P, Hennemann K, Hoffmann M, Treinen C, Aschern M, Lilge L, Morabbi Heravi K, Henkel M, Hausmann R (2021) Bacillus subtilis high cell density fermentation using a sporulation-deficient strain for the production of surfactin. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 105:4141–4151. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-021-11330-x
Klausmann P, Lilge L, Aschern M, Hennemann K, Henkel M, Hausmann R, Morabbi Heravi K (2021b) Influence of B. subtilis 3NA mutations in spo0A and abrB on surfactin production in B. subtilis 168. Microb Cell Fact 20. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-021-01679-z
Kraas FI, Helmetag V, Wittmann M, Strieker M, Marahiel MA (2010) Functional dissection of surfactin synthetase initiation module reveals insights into the mechanism of lipoinitiation. Chem Biol 17:872–880. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chembiol.2010.06.015
Li D, Nie F, Wei L, Wei B, Chen Z (2007) Screening of high-yielding biocontrol bacterium Bs-916 mutant by ion implantation. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 75:1401–1408. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-007-0951-7
Liu JF, Mbadinga SM, Yang SZ, Gu JD, Mu BZ (2015) Chemical structure, property and potential applications of biosurfactants produced by Bacillus subtilis in petroleum recovery and spill mitigation. Int J Mol Sci 16:4814–4837. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms16034814
López D, Kolter R (2010) Extracellular signals that define distinct and coexisting cell fates in Bacillus subtilis. FEMS Microbiol Rev 34:134–149. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6976.2009.00199.x
Luo C, Liu X, Zhou H, Wang X (2015) Nonribosomal peptide synthase gene clusters for lipopeptide biosynthesis in Bacillus subtilis 916 and their phenotypic functions. Appl Environ Microbiol 81:422–431. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.02921-14
Luo C, Zhou H, Zou J, Wang X, Zhang R, Xiang Y, Chen Z (2015) Bacillomycin L and surfactin contribute synergistically to the phenotypic features of Bacillus subtilis 916 and the biocontrol of rice sheath blight induced by Rhizoctonia solani. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99:1897–1910. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-6195-4
Luo C, Chen Y, Liu X, Wang X, Wang X, Li X, Zhao Y, Wei L (2019) Engineered biosynthesis of cyclic lipopeptide locillomycins in surrogate host Bacillus velezensis FZB42 and derivative strains enhance antibacterial activity. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 103:4467–4481. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-019-09784-1
Mandal SM, Barbosa AEAD, Franco OL (2013) Lipopeptides in microbial infection control: scope and reality for industry. Biotechnol Adv 31:338–345. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2013.01.004
Nakano MM, Xia L, Zuber P (1991) Transcription initiation region of the srfA operon, which is controlled by the comP-comA signal transduction system in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol 173:5487–5493
Ongena M, Jacques P (2008) Bacillus lipopeptides: versatile weapons for plant disease biocontrol. Trends Microbiol 16:115–125
Pirri G, Giuliani A, Nicoletto S, Pizzuto L, Rinaldi A (2009) Lipopeptides as anti-infectives: a practical perspective. Cent Eur J Biol 4:258–273. https://doi.org/10.2478/s11535-009-0031-3
Roggiani M, Dubnau D (1993) ComA, a phosphorylated response regulator protein of Bacillus subtilis, binds to the promoter region of srfA. J Bacteriol 175:3182–3187
Romero D, de Vicente A, Rakotoaly RH, Dufour SE, Veening J-W, Arrebola E, Cazorla FM, Kuipers OP, Paquot M, Pérez-García A (2007) The iturin and fengycin families of lipopeptides are key factors in antagonism of Bacillus subtilis toward Podosphaera fusca. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 20:430–440
Sen R (2010) Surfactin: Biosynthesis, genetics and potential applications. Adv Exp Med Biol 672:316–323. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4419-5979-9_24
Shaligram NS, Singhal RS (2010) Surfactin — a review on biosynthesis, fermentation, purification and applications. Food Technol Biotechnol 48:119–134. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erf089
Shank EA, Kolter R (2011) Extracellular signaling and multicellularity in Bacillus subtilis. Curr Opin Microbiol 14:741–747. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mib.2011.09.016
Stein T (2005) Bacillus subtilis antibiotics: structures, syntheses and specific functions. Mol Microbiol 56:845–857
Steller S, Sokoll A, Wilde C, Bernhard F, Franke P, Vater J (2004) Initiation of surfactin biosynthesis and the role of the SrfD-thioesterase protein. Biochemistry 43:11331–11343. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi0493416
Strauch MA, Bobay BG, Cavanagh J, Yao F, Wilson A, Le Breton Y (2007) Abh and AbrB control of Bacillus subtilis antimicrobial gene expression. J Bacteriol 189:7720–7732. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.01081-07
Sun H, Bie X, Lu F, Wu Y, Lu Z (2009) Enhancement of surfactin production of Bacillus subtilis fmbR by replacement of the native promoter with the Pspac promoter. Can J Microbiol 55:1003–1006
Tsuge K, Ohata Y, Shoda M (2001) Gene yerP, involved in surfactin self-resistance in Bacillus subtilis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 45:3566–3573. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.45.12.3566-3573.2001
Wang C, Cao Y, Wang Y, Sun L, Song H (2019) Enhancing surfactin production by using systematic CRISPRi repression to screen amino acid biosynthesis genes in Bacillus subtilis. Microb Cell Fact 18:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-019-1139-4
Wang M, Yu H, Shen Z (2019) Antisense RNA-based strategy for enhancing surfactin production in Bacillus subtilis TS1726 via overexpression of the unconventional biotin carboxylase II to enhance ACCase activity. ACS Synth Biol 8:251–256. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssynbio.8b00459
Wang X, Onchari MM, Yang X, Xu L, Yin X, Wan F, Chen Y, Guan M, Li B, Luo C (2022) Genome analysis of Bacillus subtilis JCL16 and the synergistic relationship among its metabolites reveal its potential for biocontrol of Nocardia seriolae. Biol Control 167:104855. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocontrol.2022.104855
Willenbacher J, Mohr T, Henkel M, Gebhard S, Mascher T, Syldatk C, Hausmann R (2016) Substitution of the native srfA promoter by constitutive Pveg in two B. Subtilis strains and evaluation of the effect on Surfactin production. J Biotechnol 224:14–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2016.03.002
Willenbacher J, Yeremchuk W, Mohr T, Syldatk C, Hausmann R (2015) Enhancement of Surfactin yield by improving the medium composition and fermentation process. AMB Express 5. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13568-015-0145-0
Wu Q, Zhi Y, Xu Y (2019) Systematically engineering the biosynthesis of a green biosurfactant surfactin by Bacillus subtilis 168. Metab Eng 52:87–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2018.11.004
Yaseen Y, Diop A, Gancel F, Béchet M, Jacques P, Drider D (2018) Polynucleotide phosphorylase is involved in the control of lipopeptide fengycin production in Bacillus subtilis. Arch Microbiol 0:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-018-1483-5
Yi Z, Zhang T, Xie J, Zhu Z, Luo S, Zhou K, Zhou P, Chen W, Zhao X, Sun Y, Xia L, Ding X (2021) iTRAQ analysis reveals the effect of gabD and sucA gene knockouts on lysine metabolism and crystal protein formation in Bacillus thuringiensis. Environ Microbiol 23:2230–2243. https://doi.org/10.1111/1462-2920.15359
Youssef NH, Wofford N, McInerney MJ (2011) Importance of the long-chain fatty acid beta-hydroxylating cytochrome P450 Enzyme YbdT for lipopeptide biosynthesis in Bacillus subtilis strain OKB105. Int J Mol Sci 12:1767–1786. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms12031767
Zhang F, Huo K, Song X, Quan Y, Wang S, Zhang Z, Gao W, Yang C (2020) Engineering of a genome-reduced strain Bacillus amyloliquefaciens for enhancing surfactin production. Microb Cell Fact 19:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-020-01485-z
Zhao H, Shao D, Jiang C, Shi J, Li Q, Huang Q, Rajoka MSR, Yang H, Jin M (2017) Biological activity of lipopeptides from Bacillus. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 101:5951–5960. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-017-8396-0
Zhi Y, Wu Q, Xu Y (2017) Genome and transcriptome analysis of surfactin biosynthesis in Bacillus amyloliquefaciens MT45. Sci Rep 7:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep40976
Funding
This work was supported by the Agricultural Science and Technology Innovation Fund (CX(21)3127) and Jiangsu Provincial Key Research and Development Program (Modern Agriculture, BE2021324).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
C. L. and X. W. conceived and designed the research. K. L. and H. Z. performed the Bs916 derivatives construction and write the paper, and contributed equally to this work. X. Q. and Y. C. screened the Bs916 mutants and fermentation. M. O. and X. Y. revised the manuscript and mutant construction. X. L. and S. Z. performed the HPLC–MS analysis of surfactin. B. T. performed the bioinformation analysis. X. C. and H. C. performed the strains culture and surfactin extraction.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethical statement
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Luo, K., Chen, Y., Qian, X. et al. Enhancing surfactin production in B. velezensis Bs916 combined cumulative mutagenesis and expression key enzymes. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 107, 4233–4244 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-023-12590-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-023-12590-5