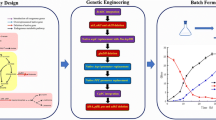
Abstract
β-alanine has been used in food and pharmaceutical industries. Although Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 (EcN) is generally considered safe and engineered as living therapeutics, engineering EcN for producing industrial metabolites has rarely been explored. Here, by protein and metabolic engineering, EcN was engineered for producing β-alanine from glucose. First, an aspartate-α-decarboxylase variant ADCK43Y with improved activity was identified and over-expressed in EcN, promoting the titer of β-alanine from an undetectable level to 0.46 g/L. Second, directing the metabolic flux towards L-aspartate increased the titer of β-alanine to 0.92 g/L. Third, the yield of β-alanine was elevated to 1.19 g/L by blocking conversion of phosphoenolpyruvate to pyruvate, and further increased to 2.14 g/L through optimizing culture medium. Finally, the engineered EcN produced 11.9 g/L β-alanine in fed-batch fermentation. Our work not only shows the potential of EcN as a valuable industrial platform, but also facilitates production of β-alanine via fermentation.
Key points
• Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 (EcN) was engineered as a β-alanine producing cell factory
• Identification of a decarboxylase variant ADC K43Y with improved activity
• Directing the metabolic flux to L-ASP and expressing ADC K43Y elevated the titer of β-alanine to 11.9 g/L






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors declare that all the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article and its supplementary information files: construction of recombinant plasmids and strains; primer pairs used in this study; analyzing the expression of genes; analyzing of β-alanine production by shake-flask fermentation; the ADC genes used in the study; primer pairs used in the study. All the data generated or analyzed during this study are included in the published article.
References
Bavelloni A, Piazzi M, Raffini M, Faenza I, Blalock WL (2015) Prohibitin 2: at a communications crossroads. IUBMB Life 67(4):239–254
Bo Z, Zhou N, Liu YM, Liu C, Liu SJ (2015) Ribosome binding site libraries and pathway modules for shikimic acid synthesis with Corynebacterium glutamicum. Microb Cell Fact 14(1):71
Datsenko KA, Wanner BL (2000) One-step inactivation of chromosomal genes in Escherichia coli K-12 using PCR products. Proc Natl Acad Sci 97(12):6640–6645
Dean RT (1943) Preparation of beta-alanine. (Doctoral dissertation, US)
Datta P, Fu L, Brodfuerer P, Dordick JS, Linhardt RJ (2021) High density fermentation of probiotic E coli Nissle 1917 towards heparosan production, characterization, and modification. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 105(3):1051–1062
Fei M, Mao X, Chen Y, Lu Y, Wang L, Yang J, Qiu J, Sun D (2020) Development of a dual-fluorescence reporter system for high-throughput screening of L-aspartate-α-decarboxylase. Acta Bioch Biophy Sin 52(12):1420–1426
Ford J (1945) The alkaline hydrolysis of β-aminopropionitrile. J Am Chem Soc 67:876–877
Fouad WM, Rathinasabapathi B (2006) Expression of bacterial L-aspartate-alpha-decarboxylase in tobacco increases beta-alanine and pantothenate levels and improves thermotolerance. Plant Mol Biol 60(4):495–505
Hu S, Zhao L, Hu L, Xi X, Zhang Y, Wang Y, Chen J, Chen J, Kang Z (2022) Engineering the probiotic bacterium Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 as an efficient cell factory for heparosan biosynthesis. Enzyme Microb Technol 158:110038
Jr CJ (1980) Beta-alanine synthesis in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 141(3):1291–7
Könst PM, Franssen MCR, Scott EL, Sanders JPM (2009) A study on the applicability of L-aspartate α-decarboxylase in the biobased production of nitrogen containing chemicals. Green Chem 11(10):1646–1652
Li Y, Wei H, Wang T, Xu Q, Zhang C, Fan X, Ma Q, Chen N, Xie X (2017) Current status on metabolic engineering for the production of L-aspartate family amino acids and derivatives. Bioresour Technol 245(Pt B):1588–1602
Li H, Lu X, Chen K, Yang J, Zhang A, Wang X, Ouyang P (2018) β-alanine production using whole-cell biocatalysts in recombinant Escherichia coli. Mol Catal 449:93–98
Li B, Zhang B, Wang P, Cai X, Chen YY, Yang YF, Liu ZQ, Zheng YG (2022) Rerouting fluxes of the central carbon metabolism and relieving mechanism-based inactivation of L-aspartate-alpha-decarboxylase for fermentative production of beta-alanine in Escherichia coli. ACS Synth Biol 11(5):1908–1918
Lynch JP, Goers L, Lesser CF (2022) Emerging strategies for engineering Escherichia coli Nissle 1917-based therapeutics. Trends Pharmacol Sci S0165–6147(22):00026–00028
Medici R, de Maria PD, Otten LG, AJJ S (2011) A high-throughput screening assay for amino acid decarboxylase activity. Adv Synth Catal 353:2369–2376
Miao Y, Liu J, Wang X, Liu B, Liu W, Tao Y (2022) Fatty acid feedstocks enable a highly efficient glyoxylate-TCA cycle for high-yield production of β-alanine. MLife 1(2):171–182
Mo Q, Mao A, Li Y, Shi G (2019) Substrate inactivation of bacterial L-aspartate alpha-decarboxylase from Corynebacterium jeikeium K411 and improvement of molecular stability by saturation mutagenesis. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 35(4):62
Ou B, Yang Y, Tham WL, Chen L, Guo J, Zhu G (2016) Genetic engineering of probiotic Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 for clinical application. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100(20):8693–8699
Parthasarathy A, Savka MA, Hudson AO (2019) The synthesis and role of beta-alanine in plants. Front Plant Sci 10:921
Pei W, Zhang J, Deng S, Tigu F, Li Y, Li Q, Cai Z, Li Y (2017) Molecular engineering of L-aspartate-alpha-decarboxylase for improved activity and catalytic stability. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 101(15):6015–6021
Piao X, Wang L, Lin B, Chen H, Liu W, Tao Y (2019) Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for production of L-aspartate and its derivative beta-alanine with high stoichiometric yield. Metab Eng 54:244–254
Qi B, Wang J, Ma YB, Wu SG, Qi GH, Zhang HJ (2018) Effect of dietary beta-alanine supplementation on growth performance, meat quality, carnosine content, and gene expression of carnosine-related enzymes in broilers. Poult Sci 97(4):1220–1228
Qian Y, Lu C, Liu J, Song W, Chen X, Luo Q, Liu L, Wu J (2020) Engineering protonation conformation of L-aspartate-alpha-decarboxylase to relieve mechanism-based inactivation. Biotechnol Bioeng 117(6):1607–1614
Raman SB, Rathinasabapathi B (2004) Pantothenate synthesis in plants. Plant Sci 167(5):961–968
Schneider F, Kramer R, Burkovski A (2004) Identification and characterization of the main beta-alanine uptake system in Escherichia coli. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 65(5):576–582
Sebastian J, Hegde K, Kumar P, Rouissi T, Brar SK (2019) Bioproduction of fumaric acid: an insight into microbial strain improvement strategies. Crit Rev Biotechnol 39(6):817–834
Shen H, Zhao Z, Zhao Z, Chen Y, Zhang L (2022) Native and engineered probiotics: promising agents against related systemic and intestinal diseases. Int J Mol Sci 23(2):594
Song CW, Lee SY (2015) Combining rational metabolic engineering and flux optimization strategies for efficient production of fumaric acid. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99(20):8455–8464
Song CW, Lee J, Ko YS, Lee SY (2015) Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for the production of 3-aminopropionic acid. Metab Eng 30:121–129
Sonnenborn U (2016) Escherichia coli strain Nissle 1917-from bench to bedside and back: history of a special Escherichia coli strain with probiotic properties. FEMS Microbiol Lett
Steunenberg P, Könst PM, Scott EL, Franssen MCR, Zuilhof H, Sanders JPM (2013) Polymerisation of β-alanine through catalytic ester–amide exchange. Europ Polymer J 49(7):1773–1781
Suwanvichanee C, Sinpru P, Promkhun K, Kubota S, Riou C, Molee W, Yongsawatdigul J, Thumanu K, Molee A (2022) Effects of beta-alanine and L-histidine supplementation on carnosine contents in and quality and secondary structure of proteins in slow-growing Korat chicken meat. Poult Sci 101(5):101776
Tadi SRR, Nehru G, Limaye AM, Sivaprakasam S (2022) High-level expression and optimization of pantoate-beta-alanine ligase in Bacillus megaterium for the enhanced biocatalytic production of D-pantothenic acid. J Food Sci Technol 59(3):917–926
Tan Y, Shen J, Si T, Ho CL, Li Y, Dai L (2020) Engineered live biotherapeutics: progress and challenges. Biotechnol J 15(10):e2000155
Tigu F, Zhang J, Liu G, Cai ZYL (2018) A highly active pantothenate synthetase from Corynebacterium glutamicum enables the production of D-pantothenic acid with high productivity. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 102:6039–6046
Toshihiro O, YMS, Akio J (1998) Production of beta-alanine by microorganism. JP Patent 10042886
Wang L, Piao X, Cui S, Hu M, Tao Y (2020) Enhanced production of beta-alanine through co-expressing two different subtypes of L-aspartate-alpha-decarboxylase. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 47(6–7):465–474
Wang L, Mao Y, Wang Z, Ma H, Chen T (2021a) Advances in biotechnological production of beta-alanine. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 37(5):79
Wang P, Zhou HY, Li B, Ding WQ, Liu ZQ, Zheng YG (2021b) Multiplex modification of Escherichia coli for enhanced beta-alanine biosynthesis through metabolic engineering. Bioresour Technol 342:126050
White WH, Gunyuzlu PL, Toyn JH (2001) Saccharomyces cerevisiae is capable of de novo pantothenic acid biosynthesis involving a novel pathway of β-alanine production from spermine. J Biol Chem 276(14):10794–10800
Yan H, Bao F, Zhao L, Yu Y, Tang J, Zhou X (2015) Cyclic AMP (cAMP) receptor protein-cAMP complex regulates heparosan production in Escherichia coli strain Nissle 1917. Appl Environ Microbiol 81(22):7687–7696
Yin J, Wei Y, Liu D, Hu Y, Lu Q, Ang EL, Zhao H, Zhang Y (2019) An extended bacterial reductive pyrimidine degradation pathway that enables nitrogen release from β-alanine. J Biol Chem 294(43):15662–15671
Yu X, Lin C, Yu J, Qi Q, Wang Q (2020) Bioengineered Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 for tumour-targeting therapy. Microb Biotechnol 13(3):629–636
Zhang T, Zhang R, Xu M, Zhang X, Yang T, Liu F, Yang S, Rao Z (2018) Glu56Ser mutation improves the enzymatic activity and catalytic stability of Bacillus subtilis L-aspartate α-decarboxylase for an efficient β-alanine production. Process Biochem 70:117–123
Zhao L, Yin G, Zhang Y, Duan C, Wang Y, Kang Z (2022) A comparative study on the genomes, transcriptomes, and metabolic properties of Escherichia coli strains Nissle 1917, BL21(DE3), and MG1655. Eng Microbiol 2(1)
Zou X, Guo L, Huang L, Li M, Zhang S, Yang A, Zhang Y, Zhu L, Zhang H, Zhang J, Feng Z (2020) Pathway construction and metabolic engineering for fermentative production of beta-alanine in Escherichia coli. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 104(6):2545–2559
Acknowledgements
We would like to acknowledge Prof. Juanping Qiu, Prof. Tingheng Zhu, and Prof. Jian Xu (College of Biotechnology and Bioengineering, Zhejiang University of Technology, Hangzhou, China) for providing useful suggestions; senior technician Haichan Huang (College of Biotechnology and Bioengineering, Zhejiang University of Technology, Hangzhou, China) for providing technical assistance.
Funding
This work was supported by the grants from the Key Research and Development Program of Zhejiang Province (No. 2020C02031), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31670084), and the State Key Laboratory for Managing Biotic and Chemical Threats to the Quality and Safety of Agro-products (2021DG700024-KF202105).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
S. H. designed and performed the experiments, data curation, formal analysis, and draft manuscript preparation; M. F. designed the experiments, analyzed the data, and edited the manuscript; B. F. performed the experiments; M. Y. performed the experiments and analyzed the data; B. T. and H. Y. edited the manuscript, and D. S. conducted the conceptualization, wrote, reviewed, and edited the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
ASSOCIATED CONTENT
The Supporting Information is available online free of charge.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, S., Fei, M., Fu, B. et al. Development of probiotic E. coli Nissle 1917 for β-alanine production by using protein and metabolic engineering. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 107, 2277–2288 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-023-12477-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-023-12477-5