Abstract
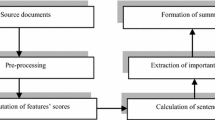
In the era of information overload, need for applications to comb through huge number of documents to extract important information is increasing. This information is helpful in assessing whether or not a document is relevant. Automatic text summarization is one of the solutions to the problem of extracting useful information from huge collection of textual data. A summarizer converts a lengthy document into a short summary by extracting important sentences from it without losing the crucial information. A summarizer can be either abstractive or extractive. An extractive summarizer relies on the statistical features of the input text to create a summary by merely copying the important sentences, whereas an abstractive summarizer tries to understand the context of the document and generates a summary which may contain new sentences not part of the original document. This paper focuses on extractive summarization technique. An approach for generating short and precise summary from a single document using weighted average of feature scores has been proposed. Sentences are ranked based on their scores, and top 40% sentences are selected to form the summary. Experiments were carried out on 250 documents from BBC News summary dataset. The results were compared with existing online summarizers and the proposed summarizer gave better average recall, precision and F-measure values.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Luhn HP (1958) The automatic creation of literature abstracts. IBM J Res Develop
Baxendale P (1958) Machine-made index for technical literature—an experiment. IBM J Res Develop 2(4):354–361
Edmundson HP (1969) New methods in automatic extracting. J ACM 16(2):264–285
Jones KS (1972) A statistical interpretation of term specificity and its application in retrieval. J Document 28(1):11–21
Lee GG, Seo J, Lee S, Jung H (2001) SiteQ: engineering high performance QA system using Lexico-semantic pattern matching and shallow NLP. In: Text retrieval conference (TREC)
Hu M, Lim EP, Sun A (2007) Comment-oriented blog summarization by sentence extraction. In: Proceedings of the 16th ACM conference on information and knowledge management, CIKM
Seki Y (2003) Sentence extraction by TF-IDF and position weighting from newspaper articles. In: Proceedings of the third NTCIR workshop
Babar SA, Patil PD (2014) Improving performance of text summarization. In: International conference on information and communication technologies
Natural Language Toolkit. https://www.nltk.org/
BBC Datasets. https://mlg.ucd.ie/datasets/bbc.html
Lin C-Y (2004) ROUGE: a package for automatic evaluation of summaries. In: Proceedings of the ACL workshop: text summarization braches out 2004
Josef Steinberger KJ (2009) Evaluation measures for text summarization. Comput Inform 28
TextTeaser. https://pypi.org/project/textteaser/
Sumy: simple library and command line utility for extracting summary. https://pypi.org/project/sumy/
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Nadaf, S., Hemadri, V.B. (2021). Extractive Summarization of Text Using Weighted Average of Feature Scores. In: Agrawal, S., Kumar Gupta, K., H. Chan, J., Agrawal, J., Gupta, M. (eds) Machine Intelligence and Smart Systems . Algorithms for Intelligent Systems. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-33-4893-6_20
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-33-4893-6_20
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-33-4892-9
Online ISBN: 978-981-33-4893-6
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)