Abstract
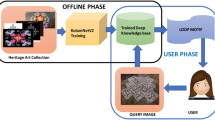
Culture and arts are integral parts of human society and evolution. We find ancient cave paintings which prove even our early ancestors were thinking similar to modern human. Any civilized society creates arts and monuments to reflect their beliefs and ideas. Today’s vibrant culture is tomorrow’s archaeology due to the natural or human-made destruction of the sites. The human race must preserve the current and the prior arts and artifacts from such damage and illegal means of trade. To do so, we need a considerable number of skilled human resources as well as person-hours. Photography plays a vital role in monitoring and cataloging such arts and sculptures in real-time. However, it requires specialized human interventions, which are not always possible. The alternative is an automated deep learning-based image classification technique to discriminate different arts and sculptures more efficiently. Real-time classification and recognition can be used to identify and preserve arts and sculptures in a more efficient way. Here, we have used different deep learning-based transfer learning models to classify the Indic, Egyptian, and Italian sculpture images. We have examined our techniques on popular Kaggle Arts-Image dataset to distinguish five types of arts: drawings, engraving, iconography, painting, and sculpture. Our trained models achieve 98.15% and 97.36% accuracies for the aforementioned sculptures and Kaggle datasets, respectively.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
- 1.
References
Awakening AC (2019) Art crime: exposing a panoply of theft, fraud and plunder. The Palgrave Handbook on Art Crime p 1
Martsiushevskaya E, Ostroga V (2017) Smuggling as a crime of international character: concept, characteristics, qualifications
Zubrow EB (2016) Archaeological cultural heritage: a consideration of loss by smuggling, conflict or war. In: The artful economist. Springer, pp 215–226
Ollus N (2018) The united nations protocol to prevent, suppress and punish trafficking in persons, especially women and children: a tool for criminal justice personnel. Resour Mater Ser 62
Allain J (2015) No effective trafficking definition exists: domestic implementation of the palermo protocol. In: The law and slavery. Brill Nijhoff, pp 265–294
Gaffney V (2017) In the kingdom of the blind: visualization and e-science in archaeology, the arts and humanities. In: The virtual representation of the past. Routledge, pp 125–133
Mitchell J, Odio S, Garcia DH (2015) Computer-vision content detection for sponsored stories. US Patent 9135631
Albrecht CM, Fisher C, Freitag M, Hamann HF, Pankanti S, Pezzutti F, Rossi F (2019) Learning and recognizing archeological features from lidar data. In: 2019 IEEE international conference on big data (Big Data). IEEE, pp 5630–5636
Khaloo A, Lattanzi D (2015) Extracting structural models through computer vision. Struct Congr, 538–548
Pelagotti A, Del Mastio A, De Rosa A, Piva A (2008) Multispectral imaging of paintings. IEEE Sig Process Mag 25(4):27–36
Barni M, Pelagotti A, Piva A (2005) Image processing for the analysis and conservation of paintings: opportunities and challenges. IEEE Sig Process Mag 22(5):141–144
Berezhnoy I, Postma E, van den Herik J (2007) Computer analysis of van gogh’s complementary colours. Pattern Recognit Lett 28(6):703–709
Li J, Yao L, Hendriks E, Wang JZ (2011) Rhythmic brushstrokes distinguish van gogh from his contemporaries: findings via automated brushstroke extraction. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 34(6):1159–1176
Johnson CR, Hendriks E, Berezhnoy IJ, Brevdo E, Hughes SM, Daubechies I, Li J, Postma E, Wang JZ (2008) Image processing for artist identification. IEEE Sig Process Mag 25(4):37–48
Graham DJ, Friedenberg JD, Rockmore DN, Field DJ (2010) Mapping the similarity space of paintings: image statistics and visual perception. Vis Cognit 18(4):559–573
van den Herik HJ, Postma EO (2000) Discovering the visual signature of painters. In: Future directions for intelligent systems and information sciences. Springer, pp 129–147
Yelizaveta M, Tat-Seng C, Ramesh J (2006) Semi-supervised annotation of brushwork in paintings domain using serial combinations of multiple experts. In: Proceedings of the 14th ACM international conference on Multimedia, pp 529–538
Carneiro G, Da Silva NP, Del Bue A, Costeira JP (2012) Artistic image classification: an analysis on the printart database. In: European conference on computer vision. Springer, pp 143–157
Tan C, Sun F, Kong T, Zhang W, Yang C, Liu C (2018) A survey on deep transfer learning. In: International conference on artificial neural networks. Springer, pp 270–279
Huh M, Agrawal P, Efros AA (2016) What makes imagenet good for transfer learning? arXiv preprint arXiv:1608.08614
Zoph B, Yuret D, May J, Knight K (2016) Transfer learning for low-resource neural machine translation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1604.02201
Howard AG, Zhu M, Chen B, Kalenichenko D, Wang W, Weyand T, Andreetto M, Adam H (2017) Mobilenets: Efficient convolutional neural networks for mobile vision applications. arXiv preprint arXiv:1704.04861
Sandler M, Howard A, Zhu M, Zhmoginov A, Chen LC (2018) Mobilenetv2: inverted residuals and linear bottlenecks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 4510–4520
Shorten C, Khoshgoftaar TM (2019) A survey on image data augmentation for deep learning. J Big Data 6(1):60
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Chatterjee, R., Chatterjee, A., Halder, R. (2021). Impact of Deep Learning on Arts and Archaeology: An Image Classification Point of View. In: Prateek, M., Singh, T.P., Choudhury, T., Pandey, H.M., Gia Nhu, N. (eds) Proceedings of International Conference on Machine Intelligence and Data Science Applications. Algorithms for Intelligent Systems. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-33-4087-9_65
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-33-4087-9_65
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-33-4086-2
Online ISBN: 978-981-33-4087-9
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)