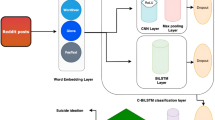
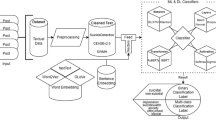
Abstract
In present-day society, the major critical issues are mental health problems which eventually turn out to be suicidal ideation. Premature detection of suicidal thoughts among people is the solution to avoid suicide in the latter times. With each passing year, the growth rate of suicides is abruptly increasing. The social media platform is the key from which people around the world come across and share their feelings, emotions, and reaction to what they are going through in their lives. The data which is available on social media can be used for the identification and detection of suicidal ideation among people, on social media forums like Twitter, Reddit, Tumblr, Facebook, and Instagram. Natural Language Processing has come a long way in the research of finding the sentiment of individuals and checking the linguistic patterns of text shared by the people. Effective to carry out the research by using machine learning, deep learning, and transfer learning algorithms on the online forum data of people. Algorithms such as SVM, Logistic Regression, Naive Bayes, Convolution Neural Network, Recurrent Neural Network, Bidirectional Long Short-Term Memory, BERT, and RoBERTa, respectively, were enforced to classify or detect the suicides in the social media data.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chang Q, Yip PSF, Chen Y-Y (2019) Gender inequality and suicide gender ratios in the world. J Affect Disorders 243:297–304
Lewis SP, Heath NL, Sornberger MJ, Arbuthnott AE (2012) Helpful or harmful? An examination of viewers’ responses to nonsuicidal self-injury videos on YouTube. J Adolescent Health 51(4):380–385
Suicides in India. https://ncrb.gov.in/sites/default/files/adsi2020_Chapter-2-Suicides.pdf. 20 Mar 2022
Rahat AM, Kahir A, Masum AKM (2019) Comparison of Naive Bayes and SVM algorithm based on sentiment analysis using review dataset. In: 2019 8th international conference system modeling and advancement in research trends (SMART). IEEE, pp 266–270
De Choudhury M, Gamon M, Counts S, Horvitz E (2013) Predicting depression via social media. In: Seventh international AAAI conference on weblogs and social media
Burnap P, Colombo G, Amery R, Hodorog A, Scourfield J (2017) Multi-class machine classification of suicide-related communication on Twitter. Online Soc Netw Media 2:32–44
O’dea B, Wan S, Batterham PJ, Calear AL, Paris C, Christensen H (2015) Detecting suicidality on Twitter. Internet Intervent 2(2):183–188
Chadha A, Kaushik B (2021) A Survey on prediction of suicidal ideation using machine and ensemble learning. Comput J 64(11):1617–1632
Description of CNN. https://iq.opengenus.org/text-classification-using-cnn/. 19 Mar 2022
Tadesse MM, Lin H, Xu B, Yang L (2019) Detection of suicide ideation in social media forums using deep learning. Algorithms 13(1):7
Chadha A, Kaushik B (2022) Performance evaluation of learning models for identification of suicidal thoughts. Comput J 65(1):139–154
Wang D, Song Y, Li J, Qin J, Yang T, Zhang M, Chen X, Boucouvalas AC (2020) Data-driven optical fiber channel modeling: a deep learning approach. J Lightwave Technol 38(17):4730–4743
Devlin J, Chang M-W, Lee K, Toutanova K (2018) Bert: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. arXiv preprint arXiv:1810.04805
Description of BERT. https://ai.googleblog.com/2018/11/open-sourcing-bert-state-of-art-pre.html. 21 Mar 2022
Liu Y, Ott M, Goyal N, Du J, Joshi M, Chen D, Levy O, Lewis M, Zettlemoyer L, Stoyanov V (2019) Roberta: a robustly optimized Bert pretraining approach. arXiv preprint arXiv:1907.11692
Zogan H, Razzak I, Jameel S, Xu G (2021) DepressionNet: a novel summarization boosted deep framework for depression detection on social media. arXiv preprint arXiv:2105.10878
Tsugawa S, Kikuchi Y, Kishino F, Nakajima K, Itoh Y, Ohsaki H (2015) Recognizing depression from Twitter activity. In: Proceedings of the 33rd annual ACM conference on human factors in computing systems, pp 3187–3196
Vioules MJ, Moulahi B, Azé J, Bringay S (2018) Detection of suicide-related posts in Twitter data streams. IBM J Res Dev 62(1):7–1
Rao G, Zhang Y, Zhang L, Cong Q, Feng Z (2020) MGL-CNN: a hierarchical posts representations model for identifying depressed individuals in online forums. IEEE Access 8:32395–32403
Ji S, Li X, Huang Z, Cambria E (2021) Suicidal ideation and mental disorder detection with attentive relation networks. Neural Comput Appl 1–11
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Sharma, A., Kaushik, B. (2023). Systematic Review of Learning Models for Suicidal Ideation on Social Media. In: Singh, Y., Singh, P.K., Kolekar, M.H., Kar, A.K., Gonçalves, P.J.S. (eds) Proceedings of International Conference on Recent Innovations in Computing. Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering, vol 1001. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-9876-8_7
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-9876-8_7
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-19-9875-1
Online ISBN: 978-981-19-9876-8
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)