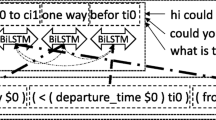
Abstract
Neural networks have been shown to replicate neural processing and in some cases intrinsically show features of semantic insight. It all starts with a word; a semantic parser converts words into meaning. Accurate parsing requires lexicons and grammar, two kinds of intelligence that machines are just starting to gain. As the neural networks get better and better, there will be more demand for machines to parse words into meaning through a system like this. The goal of this paper is to introduce the reader to a new method of semantic parsing with the use of vanilla or ordinary recurrent neural networks. This paper briefly discusses how mathematical formulation for recurrent neural networks (RNNs) could be utilized for tackling sparse matrices. Understanding how neural networks work is key to handling some of the most common errors that might come up with semantic parsers. This is because decisions are generated based on data from text inputs. At first, we present a copying method to speed up semantic parsing and then support it with data augmentation.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li Z, Wu Y, Peng B, Chen X, Sun Z, Liu Y, Paul D (2022) Setransformer: a transformer-based code semantic parser for code comment generation. IEEE Trans Reliab
Sales N, Efson J (2022) An explainable semantic parser for end-user development. Ph.D. dissertation, Universität Passau
Demlew G (2022) Amharic semantic parser using deep learning. In: Proceeding of the 2nd deep learning Indaba-X Ethiopia conference 2021
Rongali S, Arkoudas K, Rubino M, Hamza W (2022) Training naturalized semantic parsers with very little data. arXiv preprint arXiv:2204.14243
Li B, Fan Y, Sataer Y, Gao Z, Gui Y (2022) Improving semantic dependency parsing with higher-order information encoded by graph neural networks. Appl Sci 12(8):4089
Arakelyan S, Hakhverdyan A, Allamanis M, Hauser C, Garcia L, Ren X (2022) Ns3: neuro-symbolic semantic code search. arXiv preprint arXiv:2205.10674
Lam MS, Campagna G, Moradshahi M, Semnani SJ, Xu S (2022) Thingtalk: an extensible, executable representation language for task-oriented dialogues. arXiv preprint arXiv:2203.12751
Lukovnikov D (2022) Deep learning methods for semantic parsing and question answering over knowledge graphs. Ph.D. dissertation, Universitäts und Landesbibliothek Bonn, 2022
Marton G, Bilotti MW, Tellex S. Why names and numbers need semantics
Yang L, Liu Z, Zhou T, Song Q (2022) Part decomposition and refinement network for human parsing. IEEE/CAA J Automatica Sinica 9(6):1111–1114
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Jain, S., Bhardwaj, Y. (2023). Semantic Parser Using a Sequence-to-Sequence RNN Model to Generate Logical Forms. In: Reddy, K.A., Devi, B.R., George, B., Raju, K.S., Sellathurai, M. (eds) Proceedings of Fourth International Conference on Computer and Communication Technologies. Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems, vol 606. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-8563-8_27
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-8563-8_27
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-19-8562-1
Online ISBN: 978-981-19-8563-8
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)