Abstract
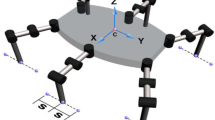
Aiming at the manipulation problem of a hexapod robot with backbone joint, this paper studies the related problems of its two-arm mode. In this mode, the four middle and rear legs are used for support, and the backbone joint and two front legs are used for manipulation. For precise control in the actual scene, the composite motion of the backbone joint and the front legs is first simplified based on the D-H method, and the D-H parameters are obtained. The forward and inverse solutions of its kinematics are derived. Then its workspace is drawn using the Monte Carlo method. Then, the variation range of the centroid of the hexapod robot in this working mode is analyzed. And the requirements for stable work of the robot on flat ground are given. Finally, the correctness of the results and the superiority of the working mode are verified by designing a task scenario and conducting a real machine test.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hirose, S.: Three basic types of locomotion in mobile robots. In: International Conference on Advanced Robotics. IEEE Xplore (1991)
Akizono, J., et al.: Field test of aquatic walking robot for underwater inspection. In: 7th International Symposium on Automation and Robotics in Construction (1990)
Bhavanibhatlaa, K., Pratiharb, D.K.: Kinematic Analysis of Legged Mobile Manipulator. ICTACEM 2017 (2017)
Bhavanibhatla, K., Suresh-Fazeela, S., Pratihar, D.K.: A study on determining optimal base location of a serial manipulator mounted on a hexapod mobile robot. J. Brazilian Society Mechanical Sci. Eng. 43(4), 110 (2021)
Arai, T., Koyachi, N., Ad Achi, H., et al.: Integrated arm and leg mechanism and its kinematic analysis. In: IEEE International Conference on Robotics & Automation. IEEE (1995)
Koyachi, N., Arai, T., Adachi, H., et al.: Hexapod with integrated limb mechanism of leg and arm. In: Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Robotics & Automation. IEEE (1995)
Koyachi, N., Arai, T., Adachi, H., et al.: Design and control of hexapod with integrated limb mechanism: MELMANTIS. In: IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots & Systems. IEEE (2002)
Koyachi, N., Adachi, H., Izumi, M., et al.: Control of walk and manipulation by a hexapod with integrated limb mechanism: MELMANTIS-1. In: IEEE International Conference on Robotics & Automation. IEEE (2002)
Ding, X., Fan, Y.: Study on hexapod robot manipulation using legs. Robotica 34(2), 1–14 (2016)
Hua, D., Gxab, C., Gza, B., et al.: Object carrying of hexapod robots with integrated mechanism of leg and arm. Robotics Computer-Integrated Manufacturing 54, 145–155 (2018)
Inoue, K., Ooe, K., Lee, S.: Pushing methods for working six-legged robots capable of locomotion and manipulation in three modes. In: IEEE International Conference on Robotics & Automation. IEEE (2010)
Chen, W.H., Ren, G.J., Wang, J.H., et al.: An adaptive locomotion controller for a hexa-pod robot: CPG, kinematics and force feedback. Science China Inf. Sci. 57(11), 1–18 (2014)
Goldschmidt, D., Hesse, F., Wörgötter, F., et al.: Biologically inspired reactive climbing behavior of hexapod robots, in 2012 IEEE. In: RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems. pp. 4632–4637 (2012)
Acknowledgements
This research was funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 61603020, No. 61620106012), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. YWF-21-BJ-J-923), and the Foundation of Strengthening Program Technology Fund Projects (No. 2019-JCJQ-JJ-268).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Xu, Q., Zhang, J., Lyu, Z., Zhou, Q., Yue, H., Chen, W. (2023). Kinematics and Stability Analysis of a Hexapod Robot with Backbone Joint. In: Yan, L., Duan, H., Deng, Y. (eds) Advances in Guidance, Navigation and Control. ICGNC 2022. Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering, vol 845. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-6613-2_205
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-6613-2_205
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-19-6612-5
Online ISBN: 978-981-19-6613-2
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)