Abstract
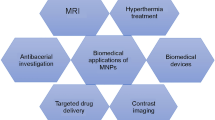
Iron oxide-based nanoparticles have great interest in biomedicine, due to their wide range of applications. The synthesis of iron oxide-based nanoparticles is a very important procedure so both physical and chemical properties of the nanoparticles must be controlled with different analyses. The properties of the synthesized nanoparticles are determined by these analyzes, energy dispersive X-ray (EDX) spectroscopy, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), infrared (IR) absorption spectroscopy, atomic force microscopy (AFM), dynamic light scattering (DLS), hydrophobic interaction chromatography, vibrating sample magnetometry (VSM), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and transmission electron microscopy (TEM), etc. Nanoparticles that are successfully synthesized and optimized can be used safely and allowing widespread biomedical uses such as targeted drug delivery, bioimaging, hyperthermia, biosensors. This chapter focuses on synthesis and characterization methods of iron oxide-based nanoparticles and also includes in future perspectives in iron oxide-based cancer therapy.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AFM :
-
atomic force microscopy
- ATR :
-
attenuated total reflection
- CPT :
-
coprecipitation
- DLS :
-
dynamic light scattering
- DLS :
-
dynamic light scattering
- EBL :
-
electron beam lithography
- EDX :
-
energy dispersive x-ray
- ESEM :
-
environmental SEM
- FCS :
-
fluorescence correlation spectroscopy
- FT-IR :
-
Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy
- GISANS :
-
grazing-incidence small-angle neutron scattering
- GISAXS :
-
grazing-incidence small-angle x-ray scattering
- IONs :
-
iron oxide nanoparticles
- IR :
-
infrared
- İron oxide-based nanoparticles :
-
nanoparticles
- MRI :
-
magnetic resonance imaging
- MS :
-
mass spectroscopy
- MTB :
-
magnetotactic bacteria
- NMR :
-
nuclear magnetic resonance
- NSOM :
-
near-field scanning optical microscopy
- PVD :
-
physical vapor deposition
- RS :
-
Raman scattering
- SANS :
-
small-angle neutron scattering
- SAXS :
-
small-angle x-ray scattering
- SEM :
-
scanning electron microscopy
- SERS :
-
surface-enhanced Raman scattering
- SPIONs :
-
superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles
- STM :
-
scanning tunneling microscopy
- TEM :
-
transmission electron microscopy
- TERS :
-
tip-enhanced Raman spectroscopy
- TGA :
-
thermal gravimetric analysis
- VSM :
-
vibrating sample magnetometry
- XPS :
-
x-ray photoelectron spectroscopy
- XRD :
-
x-ray diffraction analysis
- α :
-
alpha
- γ :
-
gamma
- emu :
-
electromagnetic unit
- eV :
-
electronvolt
- g :
-
gram
- 3D :
-
three dimensional
- NH 4 OH :
-
ammonium hydroxide
- O :
-
oxygen
- Fe :
-
iron
- nm :
-
nanometer
- K :
-
kelvin
- psi :
-
pound-force per square inch
- Cl − :
-
chlorides
- w/o :
-
water-in-oil
- o/w :
-
oil-in-water
References
Abdolmaleki A, Mallakpour S, Karshenas A (2017a) Synthesis and characterization of new nanocomposites films using alanine-Cu-functionalized graphene oxide as nanofiller and PVA as polymeric matrix for improving of their properties. J Solid State Chem 253:398–405
Abdolmaleki A, Mallakpour S, Mahmoudian M (2017b) Preparation and evaluation of edge selective sulfonated graphene by chlorosulfuric acid as an active metal-free electrocatalyst for oxygen reduction reaction in alkaline media. ChemistrySelect 34:11211–11217
Abdolmaleki A, Mallakpour S, Karshenas A (2017c) Facile synthesis of glucose-functionalized reduced graphene oxide (GFRGO)/poly(vinyl alcohol) nanocomposites for improving thermal and mechanical properties. Mater Sci Eng B 217:26–35
Abushrida A, Elhuni I, Taresco V, Marciani L, Stolnik S, Garnett MC (2020) A simple and efficient method for polymer coating of iron oxide nanoparticles. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol 55:101460
Ahrberg CD, Choi JW, Chung BG (2020) Automated droplet reactor for the synthesis of iron oxide/gold core-shell nanoparticles. Sci Rep 10:1737
Ali A, Zafar H, Zia M, Haq I, Phull AR, Ali JS, Hussain A (2016) Synthesis, characterization, applications, and challenges of iron oxide nanoparticles. Nanotechnol Sci Appl 9:49–67
Babay S, Mhiri T, Toumi M (2015) Synthesis, structural and spectroscopic characterizations of maghemite g-Fe2O3 prepared by one-step coprecipitation route. J Mol Struct 1085:286–293
Bahadar H, Maqbool F, Niaz K, Abdollahi M (2016) Toxicity of nanoparticles and an overview of current experimental models. Iran Biomed J 20(1):1–11
Bayda S, Adeel M, Tuccinardi T, Cordani M, Rizzolio F, Baeza A (2020) The history of nanoscience and nanotechnology: from chemical-physical applications to nanomedicine. Molecules 25(1):112
Bharde A, Rautaray D, Bansal V, Ahmad A, Sarkar I, Yusuf SM, Sanyal M, Sastry M (2006) Extracellular biosynthesis of magnetite using fungi. Small 2(1):135–141
Campos EA, Pinto DVBS, Sampaio de Oliveira JI, Mattos EC, Dutra RCL (2015) Synthesis, characterization and applications of ıron oxide nanoparticles. J Aerosp Technol Manag 7(3):267–276
Chen Z, Wu C, Zhang Z, Wu W, Wang X, Yu Z (2018) Synthesis, functionalization, and nanomedical applications of functional magnetic nanoparticles. Chin Chem Lett 29:1601–1608
Cuenya BR (2010) Synthesis and catalytic properties of metal nanoparticles: size, shape, support, composition, and oxidation state effects. Thin Solid Films 518(12):3127–3150
Dobson P (2019) Nanoparticle. In: Encyclopaedia Britannica Inc (ed) Encyclopaedia Britannica
Dulinska-Litewka J, Lazarczyk A, Halubiec P, Szafranski O, Karnas K, Karewicz A (2019) Superparamagnetic Iron oxide nanoparticles-current and prospective medical applications. Materials 12:617
Feynman RP (1960) There’s plenty of room at the bottom. Eng Sci 23:22–36
Gonzalez-Rodriguez R, Campbell E, Naumov A (2019) Multifunctional graphene oxide/iron oxide nanoparticles for magnetic targeted drug delivery dual magnetic resonance/fluorescence imaging and cancer sensing. PLoS One 14(6):e0217072
Gubin SP (2009) Magnetic nanoparticles. Wiley-VCH. ISBN:978-3-527-40790-3
Hasan S (2015) A review on nanoparticles: their synthesis and types. Res J Recent Sci 4:9–11
Hernández-Hernández AA, Aguirre-Álvarez G, Cariño-Cortés R, Mendoza-Huizar LH, Jiménez-Alvarado R (2020) Iron oxide nanoparticles: synthesis, functionalization, and applications in diagnosis and treatment of cancer. Chem Pap 74:3809–3824
Huber DL (2005) Synthesis, properties, and applications of iron nanoparticles. Small 1(5):482–501
Hussain CM (2018) Handbook of nanomaterials for industrial applications. Elsevier
Hussain CM (2020a) The ELSI handbook of nanotechnology: risk, safety, ELSI and commercialization. Wiley
Hussain CM (2020b) Handbook of functionalized nanomaterials for industrial applications. Elsevier
Hussain CM (2020c) Handbook of manufacturing applications of nanomaterials. Elsevier
Hussain CM (2020d) Handbook of polymer nanocomposites for industrial applications. Elsevier
Hussain CM, Mishra AK (2019) Nanotechnology in environmental science, 2 vols. Wiley
Kharey P, Dutta SB, Manikandan M, Palani IA, Majumder SK, Gupta S (2019) Green synthesis of near-infrared absorbing eugenate capped iron oxide nanoparticles for photothermal application. Nanotechnology 31(9):095705
Kojima K, Miyazaki M, Mizukami F, Maeda K (1997) Selective formation of spinel iron oxide in thin films by complexing agent-assisted sol-gel processing. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 8(1–3):77–81
Lin XM, Samia AC (2006) Synthesis, assembly and physical properties of magnetic nanoparticles. J Magn Magn Mater 305(1):100–109
Ling D, Hyeon T (2013) Chemical design of biocompatible iron oxide nanoparticles for medical applications. Small 9(9–10):1450–1466
Liveri VT (2006) Controlled synthesis of nanoparticles in microheterogeneous systems. Springer
Lowell S, Shields JE (1984) Powder surface area and porosity. Chapman & Hall, London/New York
Machala L, Tucek J, Zboril R (2011) Polymorphous transformations of nanometric iron (III) oxide: a review. Chem Mater 23(14):3255–3272
Mallakpour S, Behranvand V (2018) Synthesis of mesoporous recycled poly(ethylene terephthalate)/MWNT/carbon quantum dot nanocomposite from sustainable materials using ultrasonic waves: application for methylene blue removal. J Clean Prod 190:525–537
Mallakpour S, Khadem E (2016) Carbon nanotube–metal oxide nanocomposites: fabrication, properties and applications. Chem Eng J 302:344–367
Mallakpour S, Khadem E (2018) Construction of crosslinked chitosan/nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dot nanocomposite for hydroxyapatite biomimetic mineralization. Int J Biol Macromol 120:1451–1460
Mallakpour S, Khadem E (2019a) Linear and nonlinear behavior of crosslinked chitosan/N-doped graphene quantum dot nanocomposite films in cadmium cation uptake. Sci Total Environ 690:1245–1253
Mallakpour S, Khadem E (2019b) Chapter 8: Carbon nanotubes for heavy metals removal. In: Kyzas G, Mitrpoulos AC (eds) Composite nanoadsorbents. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 181–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-814132-8.00009-5. eBook ISBN:9780128141335
Mallakpour S, Khodadadzadeh L (2018) Chapter 7: Biocompatible and biodegradable chitosan nanocomposites loaded with carbon nanotubes. In: Shimpi NG (ed) Biodegradable and biocompatible polymer composites processing, properties and applications. Elsevier, Woodhead Publishing, Sawston, pp 187–221. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-08-100970-3.00007-9
Mallakpour S, Rashidimoghadam R (2019) Chapter 9: Carbon nanotubes for dyes removal. In: Kyzas G, Mitrpoulos AC (eds) Composite nanoadsorbents. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 211–244. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-814132-8.00010-1. eBook ISBN:9780128141335
Mallakpour S, Rashidimoghadam S (2021) Chapter 29: Utilization of starch and starch/carbonaceous nanocomposites for removal of pollutants from wastewater. In: Hussain CM (ed) Handbook of polymer nanocomposites for industrial applications
Mallakpour S, Abdolmaleki A, Borandeh (2017a) Fabrication of amino acid-based graphene-zinc oxide (ZnO) hybrid and its application for poly(ester–amide)/graphene-ZnO nanocomposite synthesis. J Thermoplast Compos Mater 30:358–380
Mallakpour S, Abdolmaleki A, Karshenas A (2017b) Graphene oxide supported copper coordinated amino acids as novel heterogeneous catalysts for epoxidation of norbornene. Catal Commun 92:109–113
Mallakpour S, Abdolmaleki A, Mahmoudian M, Ensafi AA, Abarghoui M (2017c) Synergetic effect of synthesized sulfonated polyaniline/quaternized graphene and its application as a high-performance supercapacitor electrode. J Mater Sci 52:9683–9695
Mallakpour S, Behranvand V, Mallakpour F (2019) Synthesis of alginate/carbon nanotube/carbon dot/fluoroapatite/TiO2 beads for dye photocatalytic degradation under ultraviolet light. Carbohydr Polym 224:115138
Mallakpour S, Azadi E, Hussain CM (2020a) Environmentally benign production of cupric oxide nanoparticles and various utilizations of their polymeric hybrids in different technologies. Coord Chem Rev 419:213378
Mallakpour S, Hatami M, Hussain CM (2020b) Recent innovations in functionalized layered double hydroxides: fabrication, characterization, and industrial applications. Adv Colloid Interface Sci:102216
Mannheimer WA (2002) Chapter V: Microscopia dos materiais: uma introdução. In: Microscopia eletrônica de transmissão. E-papers, Rio de Janeiro, p V.1
Narayanan KB, Sakthivel N (2010) Biological synthesis of metal nanoparticles by microbes. Adv Colloid Interf Sci 156(1–2):1–13
Nawaz M, Sliman Y, Ercan I, Lima-Tenório MK, Tenório-Neto ET, Kaewsaneha C, Elaissari A (2019) Magnetic and pH-responsive magnetic nanocarriers. Adv Nanocarr Ther Woodhead Publ Ser Biomater 2:37–85
Nowrouzi A, Meghrazi K, Golmohammadi T, Golestani A, Ahmadian S, Shafiezadeh M, Oliveira LCA, Fabris JD, Pereira MC (2013) Óxidos de ferro e suas aplicações em processos catalíticos: uma revisão. Quím Nova 36(1):123–130
Park J, Kadasala NR, Abouelmagd SA, Castanares MA, Collins DS, Wei A, Yeo Y (2016) Polymer-iron oxide composite nanoparticles for EPR-independent drug delivery. Biomaterials 101:285–295
Rego GNA, Mamani JB, Souza TKF, Nucci MP, Silva HRD, Gamarra LF (2019) Therapeutic evaluation of magnetic hyperthermia using Fe3O4-aminosilane-coated iron oxide nanoparticles in glioblastoma animal model. Einstein (Sao Paulo) 17(4):eAO4786
Roth WL (1958) Magnetic structures of MnO, FeO, CoO, and NiO. Phys Rev 110:1333–1341
Sakka S (2016) History of the sol-gel chemistry and technology. In: Klein L et al (eds) Handbook of sol-gel science and technology
Salazar-Alvarez G, Muhammed M, Zagorodni AA (2006) Novel flow injection synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles with narrow size distribution. Chem Eng Sci 61(14):4625–4633
Srivastava M, Chaubey A, Ojha AK (2009) Investigation on size dependent structural and magnetic behavior of nickel ferrite nanoparticles prepared by sol-gel and hydrothermal methods. Mater Chem Phys 118(1):174–180
Starmans LW, Burdinski D, Haex NP, Moonen RP, Strijkers GJ, Nicolay K, Grüll H (2013) Iron oxide nanoparticle-micelles (ION-micelles) for sensitive (molecular) magnetic particle imaging and magnetic resonance imaging. PLoS One 8(2):e57335
Sun S, Zeng H (2002) Size-controlled synthesis of magnetite nanoparticles. J Am Chem Soc 124(28):8204–8205
Swihart MT (2003) Vapor-phase synthesis of nanoparticles. Curr Opin Colloid Interface Sci 8:127–133
Tarantash M, Nosrati H, Kheiri MH, Baradar KA (2018) Preparation, characterization and in vitro anticancer activity of paclitaxel conjugated magnetic nanoparticles. Drug Dev Ind Pharm 44:1895–1903
Tartaj P, del Puerto MM, Veintemillas-Verdaguer S, González-Carreño T, Serna CJ (2003) The preparation of magnetic nanoparticles for applications in biomedicine. J Phys D Appl Phys 36(13):R182
Thorek DL, Chen AK, Czupryna J, Tsourkas A (2006) Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticle probes for molecular imaging. Ann Biomed Eng 34(1):23–38
Unsoy G, Yalcin S, Khodadust R, Gunduz G, Gunduz U (2012) Synthesis optimization and characterization of chitosan-coated iron oxide nanoparticles produced for biomedical applications. J Nanopart Res 14(11):1–13
Vargas G, Cypriano J, Correa T, Leão P, Bazylinski DA, Abreu F (2018) Applications of magnetotactic bacteria, magnetosomes and magnetosome crystals in biotechnology and nanotechnology: mini-review. Molecules 23(10):2438
Wajnberg E, Rossi AL, Esquivel DMS (2017) Titanium and iron titanium oxide nanoparticles in antennae of the migratory ant Pachycondyla marginata: an alternative magnetic sensor for magnetoreception? Biometals 30(4):541–548
Wierzbinski KR, Szymanski T, Rozwadowska N, Rybka JD, Zimna A, Zalewski T, Nowicka-Bauer K, Malcher A, Nowaczyk M, Krupinski M, Fiedorowicz M, Bogorodzki P, Grieb P, Giersig M, Kurpisz MK (2018) Potential use of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for in vitro and in vivo bioimaging of human myoblasts. Sci Rep 8(1):3682
Woo K, Hong J, Choi S, Lee HW, Ahn JP, Kim CS, Lee SW (2004) Easy synthesis and magnetic properties of iron oxide nanoparticles. Chem Mater 16(14):2814–2818
Wu S, Sun A, Zhai F, Wang J, Xu W, Zhang Q, Volinsky AA (2011) Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles synthesis from tailings by ultrasonic chemical co-precipitation. Mater Lett 65(12):1882–1884
Wu W, Wu Z, Yu T, Jiang C, Kim WS (2015) Recent progress on magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: synthesis, surface functional strategies and biomedical applications. Sci Technol Adv Mater 16(2):023501
Xu H, Wang X, Zhang L (2008) Selective preparation of nanorods and micro-octahedrons of Fe2O3 and their catalytic performances for thermal decomposition of ammonium perchlorate. Powder Technol 185(2):176–180
Xu H, Zeigera BW, Suslick KS (2013) Sonochemical synthesis of nanomaterials. Chem Soc Rev 42:2555–2567
Yalcin S (2019) Dextran-coated iron oxide nanoparticle for delivery of miR-29a to breast cancer cell line. Pharm Dev Technol 24(8):1032–1037
Yalcin S, Gündüz U (2018) The magnetic nanobased strategies to overcome drug resistance in breast cancer therapy. In: Handbook of nanomaterials for industrial applications. Elsevier, pp 577–586
Yalcin S, Gündüz U (2019) Iron oxide-based polymeric magnetic nanoparticles for drug and gene delivery: in vitro and in vivo applications in cancer. In: Handbook of polymer and ceramic nanotechnology, pp 1–22
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this entry
Cite this entry
Ata, F.K., Yalçınkaya, S., Yalcin, S. (2022). The Design, Synthesis, and Characterization of Iron Oxide-Based Coating-Based Nanoproducts. In: Handbook of Consumer Nanoproducts. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-8698-6_56
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-8698-6_56
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-16-8697-9
Online ISBN: 978-981-16-8698-6
eBook Packages: Chemistry and Materials ScienceReference Module Physical and Materials ScienceReference Module Chemistry, Materials and Physics