Abstract
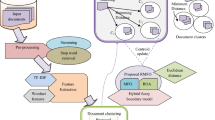
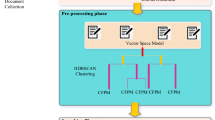
Annotation is the process of adding notes about an entity such as documents, attributes, data repositories and data spaces to make them more visible and expressive. In probabilistic data models, it is used for generating values for attributes which could be used for generating a range of queries which are matched with a database schema. The proposed fuzzy document localization model (FDLM) lists out the top-k attributes by deriving a monotone fuzzy rank function based on query value \(Q_\mathrm{val}\) and content value \(C_\mathrm{val}\). The newly arrived documents are processed with the annotated documents which are conditionally modeled with ground truth attributes in a dynamic document categorization process. The semantic matches of attributes are identified by a pre-processed conceptualization framework this in turn increases the cardinality of result set. The system is biased with a biasing parameter \(\beta \) in order to maintain a balance with workload-based query value and database-oriented content value to set a selection bound over the range of accurate and approximate matches.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Helm, D. J., & Thompson, B. W. (2001). An approach for totally dynamic forms processing in web-based applications. In ICEIS (pp. 974–977).
Tornqvist, N. C., & Johnson, A. M. (1999). XML and Objects-the Future of the E-forms on the Web (pp. 303–308).
Jeffery, S. R., Franklin, M. J., & Halevy, A. Y. (2008). Pay-as-you-go user feedback for dataspace systems (pp. 847–860).
Li, C., Sun, A., Weng, J., & He, Q. (2015). Tweet segmentation and its application to named entity recognition. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 27(2), 558–570.
Yu, Z., Wang, H., Lin, X., & Wang, M. (2016). Understanding short texts through semantic enrichment and hashing. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 28(2), 566–579.
Schmidt, A., Kersten, M., & Windhouwer, M. (2001). Querying XML documents made easy: Nearest concept queries (pp. 321–329).
Fuhr, N., & Grosjohann, K. (2001). XIRQL: A query language for information retrieval in XML documents (pp. 172–180).
Schutze, H., Manning, C. D., & Raghavan, P. (2008). Introduction to information retrieval, 39.
Chen, S. F., & Goodman, J. (1999). An empirical study of smoothing techniques for language modeling. Computer Speech Language, 13(4), 359–394.
Ruiz, E. J., Hristidis, V., & Ipeirotis, P. G. (2014). Facilitating document annotation using content and querying value. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 26(2), 336–349.
Mikolov, T., Chen, K., Corrado, G., & Dean, J. (2013). Efficient estimation of word representations in vector space. Cornell University Library.
Sijin, P., Champa, H., & Venugopal, K. (2017). A survey on intent-based diversification for fuzzy keyword search. International Journal of Computer Science and Information Technologies, 8(6), 602–618.
Liu, J., & Yan, D. (2016). Answering approximate queries over XML data. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 24(2), 288–305.
Li, J., Liu, C., & Yu, J. X. (2015). Context-based diversification for keyword queries over XML data. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 27(3), 660–672.
Wang, L. (2017). Heterogeneous data and big data analytics. Automatic Control and Information Sciences, 3(1), 8–15.
Chiang, I. J., Liu, C. C. H., Tsai, Y. H., & Kumar, A. (2015). Discovering latent semantics in web documents using fuzzy clustering. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 23(6), 2122–2134.
Sestakova, E., & Janousek, J. (2018). Automata approach to XML data indexing. Information, 9(1), 12.
Dou, Z., Jiang, Z., Hu, S., Wen, J.-R., & Song, R. (2016). Automatically mining facets for queries from their search results. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 28(2), 385–397.
Zhao, R., & Mao, K. (2017). Fuzzy bag-of-words model for document representation. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems.
Kusner, M., Sun, Y., Kolkin, N., & Weinberger, K. (2015). From word embeddings to document distances (pp. 957–966).
Liu, J., Wang, K., & Fung, B. C. (2016). Mining high utility patterns in one phase without generating candidates. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 28(5), 1245–1257.
Tseng, V. S., Wu, C.-W., Fournier-Viger, P., & Philip, S. Y. (2016). Efficient algorithms for mining top-k high utility itemsets. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 28(1), 54–67.
Suma, V., & Hills, S. M. (2020). Data mining based prediction of demand in Indian market for refurbished electronics. Journal of Soft Computing Paradigm (JSCP), 2(03), 153–159.
Raj, J. S. (2020). Machine learning implementation in cognitive radio networks with game-theory technique. Journal: IRO Journal on Sustainable Wireless Systems, 2020(2), 68–75.
Koshti, S., Sen, A., & Jadhav, V. (2017). Dynamic Query Forms (DQF) using ranking models for database queries (pp. 365–370).
Jayapandian, M., & Jagadish, H. (2008). Automated Creation of a Forms-based Database Query Interface. Proceedings of the VLDB Endowment, 1(1), 695–709.
Jain, A., & Ipeirotis, P. G. (2009). A quality-aware optimizer for information extraction. ACM Transactions on Database Systems, 34(1), 1–48.
Rahm, E., & Bernstein, P. A. (2001). A Survey of Approaches to Automatic Schema Matching. the VLDB Journal, 10(4), 334–350.
Ponte, J. M., & Croft, W. B. (1998). A language modeling approach to information retrieval (pp. 275–281).
Sijin, P., & Champa, H. (2020). Fuzzy conceptualization model for document representation. In IEEE International Conference on Electronics, 2020, Computing and Communication Technologies (pp. 1–4).
Cohen, W. W., Ravikumar, P., Fienberg, S. E., et al. (2003). A comparison of string distance metrics for. Name-Matching Tasks, 2003, 73–78.
Ney, H., Essen, U., & Kneser, R. (1994). On structuring probabilistic dependences in stochastic language modelling. Computer Speech and Language, 8(1), 1–38.
Fagin, R., Lotem, A., & Naor, M. (2003). Optimal aggregation algorithms for middleware. Journal of Computer and System Sciences, 66(4), 614–656.
Fagin, R. (1999). Combining fuzzy information from multiple systems. Journal of Computer and System Sciences, 58(1), 83–99.
Zadeh, L. A. (1965). Fuzzy Sets. Information and Control, 8(3), 338–353.
Dong, X. L., Halevy, A., & Yu, C. (2009). Data integration with uncertainty. The VLDB Journal, 18(2), 469–500.
Clemen, R. T., & Winkler, R. L. (1990). Unanimity and compromise among probability forecasters. Management Science, 36(7), 767–779.
Chang, K. C.-C., & Hwang, S.-w. (2002). Minimal probing: Supporting expensive predicates for top-k queries (pp. 346–357).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Sijin, P., Champa, H.N. (2022). Dynamic Document Localization for Efficient Mining. In: Shakya, S., Balas, V.E., Kamolphiwong, S., Du, KL. (eds) Sentimental Analysis and Deep Learning. Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, vol 1408. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-5157-1_2
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-5157-1_2
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-16-5156-4
Online ISBN: 978-981-16-5157-1
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)