Abstract
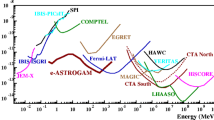
ASTROGAM is a concept for a breakthrough observatory space mission, with a detector composed of a silicon tracker, a calorimeter, and an anticoincidence system, dedicated to the study of the nonthermal Universe in the photon energy range from fractions of an MeV to a few GeV. The instrument measures simultaneously the energy and direction of gamma rays by combining a Compton and a pair-production detector. It consists of a telescope made of tens of planes of silicon, a calorimeter made of scintillation detectors, and an anticoincidence detector to veto the background. All of the required detector technology is nowadays well proven. Thanks to its performance in the largely unknown MeV-GeV domain, ASTROGAM can open a new window on the nonthermal Universe, making pioneering observations of the most powerful Galactic and extragalactic sources, elucidating the nature of their relativistic outflows and their effects on their surroundings. With a line sensitivity in the MeV energy range one to two orders of magnitude better than previous generation instruments, ASTROGAM can determine the origin of key isotopes fundamental for our understanding of supernova explosions and the chemical evolution of our Galaxy. The mission can provide unique data of significant interest to a broad astronomical community, complementary to powerful observatories operating at different wavelengths and in a multimessenger context, as well as to the particle physics community.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Ackermann et al., Astrophys. J. 799, 1 (2015)
A. De Angelis, M. Pimenta, Introduction to Particle and Astroparticle Physics: Multimessenger Astronomy and its Particle Physics Foundations (Springer Nature, Heidelberg, 2018)
A. De Angelis, V. Tatischeff et al., The e-ASTROGAM mission (exploring the extreme Universe with gamma rays in the MeV-GeV range). Exp. Astron. 44, 25–82 (2016)
A. De Angelis, V. Tatischeff et al., Science with e-ASTROGAM (A space mission for MeV-GeV gamma-ray astrophysics). J. High Energy Astrophys. 19, 1–106 (2018). https://arxiv.org/abs/1711.01265
A. Goldstein, P. Veres, E. Burns et al., Astrophys. J. Lett. 848, L14 (2017)
J. Greiner et al., GRIPS – Gamma-ray imaging, polarimetry and spectroscopy. Exp. Astron. 34, 551–582 (2012)
G. Kanbach et al., MEGA – a new telescope for medium energy gamma-ray astronomy. International School of Space Science, L’Aquila, Italy, 2001. Frascati Phys. Ser. 24, 409–416 (2001)
G. Kanbach et al., The MEGA project. NewAR 48, 275–280 (2004)
J. McEnery, D. Thompson et al., AMEGO white paper (2019). https://arxiv.org/abs/1907.07558
A.A. Moiseev et al. (2007). arXiv:1508.07349
A. Moiseev et al., Compton-pair production space telescope (ComPair) for MeV gamma-ray astronomy (2015). https://arxiv.org/abs/1508.07349
A. Morselli, M. Tavani et al., Gamma-light: high-energy astrophysics above 10 MeV. Nucl. Phys. B (Proc. Suppl.) 239–240, 193–198 (2013)
T. Takahashi, Y. Uchiyama, Ł. Stawarz, Astropart. Phys. 43, 142 (2013)
V. Tatischeff et al., COCOTE – a compact Compton telescope for gamma-ray astrophysics in the MeV range (2013). Unpublished
M. Tavani, V. Tatischeff, P. von Ballmoos et al., Unpublished (presented to ESA) (2014)
X. Wu et al., PANGU: a high resolution gamma-ray space telescope. Proc. SPIE Int. Soc. Opt. Eng. 9144, 91440F (2014). arXiv:1407.0710
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Section Editor information
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this entry
Cite this entry
De Angelis, A. (2023). The ASTROGAM Concept. In: Bambi, C., Santangelo, A. (eds) Handbook of X-ray and Gamma-ray Astrophysics. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-4544-0_167-1
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-4544-0_167-1
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-16-4544-0
Online ISBN: 978-981-16-4544-0
eBook Packages: Springer Reference Physics and AstronomyReference Module Physical and Materials ScienceReference Module Chemistry, Materials and Physics