Abstract
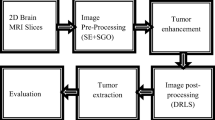
Alzheimer’s disease (AZD) is considered as the most common neurodegenerative disease that generally affects people older than 65 years. It causes irreversible brain commotion that belatedly partitions the memory and thinking abilities on progressively collapsing the capability of accomplishing daily activities. Early detection of AZD symptoms slows down its progression to the next stage and eventually protects the patient from severity of the disease. It is evidenced from various research studies that, application of nature-inspired algorithms in the context of image processing, have depicted decent results in analyzing complex image datasets related to the medical domain. This paper presents a modified BAT optimization algorithm integrated with a novel histogram model to extract ROI (Region of Interest) from brain scan MRIs (Magnetic Resonance Images) to automatically detect and predict the progression of AZD. The experimental analysis presented in the paper indicates that the proposed modified BAT algorithm outperforms state-of-art optimization algorithms.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Frisoni GB, Fox NC, Jack CR, Scheltens P, Thompson PM (2010) The clinical use of structural MRI in Alzheimer disease. Nat Rev Neurol. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrneurol.2009.215
Younes L, Albert M, Miller MI (2014) Inferring change point times of medial temporal lobe morphometric change in preclinical Alzheimer’s dis- ease. Neuro Image Clin. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nicl.2014.04.009
Kurban T, Civicioglu P, Kurban R, Besdok E (2014) Comparison of evo- lutionary and swarm based computational techniques for multilevel color image thresholding. Appl Soft Comput J. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2014.05.037
Yang XS, Deb S (2009) Cuckoo search via Levy flights, in: 2009 World Congr. Nat Biol Inspired Comput NABIC 2009 – Proc. http://dx.doi.org/10. 1109/NABIC.2009.5393690
Suresh S, Lal S (2016) An efficient cuckoo search algorithm based multi- level thresholding for segmentation of satellite images using different objective functions. Expert Syst Appl. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2016.03.032
Oliva D, Cuevas E, Pajares G, Zaldivar D, Perez-Cisneros M (2013) Multilevel thresholding segmentation based on harmony search opti- mization. J Appl Math 2013(1–24):230
Oliva D, Cuevas E, Pajares G, Zaldivar D, Osuna V (2014) A multi- level thresholding algorithm using electromagnetism optimization. Neurocomputing 139:357–381
Mousavirad SJ, Ebrahimpour-Komleh H (2017) Multilevel image thresholding using entropy of histogram and recently developed pop- ulation-based metaheuristic algorithms. Evolut Intell 10(1–2):45–75
Sarkar S, Das S, Paul S, Polley S, Burman R, Chaudhuri SS (2013) Multi-level image segmentation based on fuzzy-Tsallis entropy and diferential evolution. In: 2013 IEEE Int Conf Fuzzy Syst (FUZZ). IEEE, pp. 1–8
Bhandari AK, Kumar A, Singh GK (2015) Modifed artifcial bee col- ony based computationally efcient multilevel thresholding for satellite image segmentation using Kapur’s, Otsu and Tsallis functions. Expert Syst Appl 42(3):1573–1601
Zhang J, Li H, Tang Z, Lu Q, Zheng X, Zhou J (2014) An improved quantum-inspired genetic algorithm for image multilevel thresholding segmentation. Math Probl Eng 2014:1–12
Mala C, Sridevi M (2016) Multilevel threshold selection for image segmentation using soft computing techniques. Soft Comput 20(5):1793–1810
Singh VK, Rashwan HA, Akram F, Pandey N, Sarker MM, Saleh A, Abdulwahab S, Maaroof N, Torrents-Barrena J, Rom- ani S, Puig D (2018) Retinal optic disc segmentation using con- ditional generative adversarial network. CCIA
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Nasina, S.S., Reddy, A.R.M. (2021). A Modified BAT Optimization Algorithm to Segment MRIs of Brain Subregions for Early Detection of Alzheimer’s Disease. In: Jyothi, S., Mamatha, D.M., Zhang, YD., Raju, K.S. (eds) Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Computational and Bio Engineering . Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems, vol 215. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-1941-0_32
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-1941-0_32
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-16-1940-3
Online ISBN: 978-981-16-1941-0
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)