Abstract
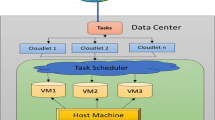
Cloud computing usually needs to process a large number of computing tasks, and task scheduling strategies play a key role in determining the efficiency of cloud computing. How to allocate computing resources reasonably and schedule task operations effectively so that the time and cost required to complete all tasks are shorter is an important issue. This paper proposes an Improved Genetic Algorithm (I-GA) that considers time and cost constraints. The result of scheduling by this algorithm can not only make the task completion time shorter, but also cost less. Through experiments, I-GA is compared with Genetic Algorithm (T-GA) considering time constraints and Genetic Algorithm (C-GA) considering cost constraints. The experimental results show that this algorithm is an effective task scheduling algorithm in cloud computing.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jakobik et al.: Non-deterministic security driven meta scheduler for distributed cloud organization. Simul. Model Pract. Theory 67–81 (2017)
Douglas et al.: Experimental assessment of routing for grid and cloud. In: 10th International Conference on Networks pp. 341–346 (2011)
Alhakami et al.: Comparison between cloud and grid computing: review paper. Int. J. Cloud Comput. 2(4) 1–21 (2012)
Hao, Y, et al.: An adaptive algorithm for scheduling parallel jobs in meteorological Cloud. Knowl. Based Syst. (2016) 226–240
Khorandi et al.: Scheduling of online compute-intensive synchronized jobs on high performance virtual clusters. J. Comput. Syst. Sci. 1–17 (2017)
Chongdarakul et al.: Efficient task scheduling based on theoretical scheduling pattern constrained on single I/O port collision avoidance. Simul. Model. Pract. 171–190 (2016)
Cao, Q., et al.: An optimized algorithm for task scheduling based on activity based costing in cloud computing. In: 3rd International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedical Engineering, pp. 34–37 (2009)
Guo, L., et al.: Task scheduling optimization in cloud computing based on heuristic algorithm. J. Netw. 547–553 (2012)
Buyya, R., et al.: GridSim: a toolkit for the modeling and simulation of distributed resource management and scheduling for grid computing. J. Concurr. Comput. 13–15 (2002)
Calheiros, R.N., et al.: CloudSim: a novel framework for modeling and simulation of cloud computing infrastructures and services. Technical Report, GRIDS-TR-2009-1, Grid Computing and Distributed Systems Laboratory (2009)
Buyya, R. et al.: Calheiros, modeling and simulation of scalable cloud computing environments and the CloudSim toolkit: challenges and opportunities. High Perform. Comput. Simul. 1–11 (2009)
Zhong-wen, G., et al.: The Research on cloud computing resource scheduling method based on Time-Cost-Trust model. In: 2nd International Conference on Computer Science and Network Technology (ICCSNT), p. 10 (2009)
Wu, H., et al.: A priority constrained scheduling strategy of multiple workflows for cloud computing. In: 14th International Conference on Advanced Communication Technology (2012)
Zhang, X., et al.: Locality-aware allocation of multi-dimensional correlated files on the cloud platform. J. Distrib. Parallel Databases 33(3), 353–380 (2015)
Mukundan, et al.: Efficient integrity verification of replicated data in cloud using homomorphic encryption. In: J. Distrib. Parallel Databases 32(3), 507–534 (2014)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Pabboju, S.S., Adilakshmi, T. (2021). Task Scheduling in Cloud Using Improved Genetic Algorithm. In: Satapathy, S.C., Bhateja, V., Favorskaya, M.N., Adilakshmi, T. (eds) Smart Computing Techniques and Applications. Smart Innovation, Systems and Technologies, vol 224. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-1502-3_25
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-1502-3_25
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-16-1501-6
Online ISBN: 978-981-16-1502-3
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)