Abstract
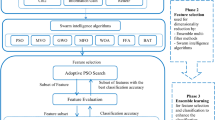
Cancer is a genetic disease characterized by various types of changes in the activity of genes at cell level. The molecules produced by activity of genes are captured by the expression values of genes as obtained by genome sequencing technologies like microarray technology. This gene expression data can be computationally analyzed to detect abnormalities in one or more genes of an organism. Thus, diseases like cancer can be successfully diagnosed and classified into subtypes by analyzing gene expression datasets. Since this data is very high dimensional and very few genes are associated with incidence of a type of cancer. Therefore, many methods have been proposed for selecting subset of most relevant genes for classification task. In this paper, we have proposed a method for feature selection from cancer gene expression data based on binary particle swarm optimization and logistic regression. The ensemble consists of binary particle swarm optimization and logistic regression classifier. The proposed method was compared to existing feature selection-classification approaches and the results show the proposed method to perform better with respect to classification accuracy and learning rate.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R.C. Eberhart, J. Kennedy, A new optimizer using particle swarm theory, in Proceedings of the 6th International Symposium on Micro Machine and Human Science (Nagoya, Japan, Mar 13–16, 1995), pp. 39–43
M.S. Mohamad, S. Omatu, S. Deris, M. Yoshioka, A. Abdullah, Z. Ibrahim, An enhancement of binary particle swarm optimization for gene selection in classifying cancer classes. Algorithms Mole. Biol. 8(15) (2013). https://www.almob.org/content/8/1/15
M.S. Mohamad, S. Omatu, S. Deris et al., Particle swarm optimization for gene selection in classifying cancer classes. Artif. Life Robotics 14, 16–19 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10015-009-0712-z
Q. Shen, W.M. Shi, W. Kong, Hybrid particle swarm optimization and tabu search approach for selecting genes for tumor classification using gene expression data. Comput. Biol. Chem. 32(5), 3–60 (2008)
Q. Shen, W.M. Shi, W. Kong, B.X. Ye, A combination of modified particle swarm optimization algorithm and support vector machine for gene selection and tumor classification. Talanta 71(4), 1679–1683 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2006.07.047
I. Jain, V.K. Jain, R. Jain, Correlation feature selection based improved-binary particle swarm optimization for gene selection and cancer classification. Appl. Soft Comput. 62, 203–215 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2017.09.038
S.A. Wang, W. Kong, W. Zeng, X. Hong, Hybrid binary imperialist competition algorithm and tabu search approach for feature selection using gene expression data. Biomed. Res. Int. 9721713 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/9721713
L.Y. Chuang, H.W. Chang, C.J. Tu et al., Improved binary PSO for feature selection using gene expression data. Comput. Biol. Chem. 32, 29–38 (2008)
L.Y. Chuang, C.H. Yang, K.C. Wu, C.H. Yang, A hybrid feature selection method for DNA microarray data. Comput. Biol. Med. 41(4), 228–237 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2011.02.004
F. Pedregosa et al., Logistic regression. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 12, 2825–2830 (2011)
https://datam.i2r.astar.edu.sg/datastes/krbd/ColonTumor/ColonTumor.html
T.R. Golub, D.K. Slonim, P. Tamayo et al., Molecular classification of cancer: class discovery and class prediction by gene expression monitoring. Science 286(5439), 531–537 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.286.5439.531
Acknowledgements
Authors would like to thank Department of Science and Technology (DST), Government of India, for supporting this research work under the grant DST-ICPS 2019.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Koul, N., Manvi, S.S. (2021). Colon Cancer Classification Using Binary Particle Swarm Optimization and Logistic Regression. In: Tavares, J.M.R.S., Chakrabarti, S., Bhattacharya, A., Ghatak, S. (eds) Emerging Technologies in Data Mining and Information Security. Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems, vol 164. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-9774-9_20
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-9774-9_20
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-15-9773-2
Online ISBN: 978-981-15-9774-9
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)