Abstract
Based on research of experiences of risk management and delicacy management in large cities at home and abroad, the concept of delicacy management for urban risk prevention is put forward in this paper. That is, under the current severe situation of urban safety management and the requirements of delicacy management, urban safety management must be carried out in a delicate way, which is the inevitable trend of urban safety management in the future and is different from the previous extensive management mode. In the delicacy mode, urban risk prevention should start from two aspects: the short-term work should be done by assessing the current risk points (identifying external risk factors), and combining delicacy management ideas with scientific urban management technology to ensure city safety. In the long run, it should be based on the construction of a scientific delicacy management system (to improve the city internal safety abilities). The two aspects work is consistent with the theory of urban operation risk.
Access provided by Autonomous University of Puebla. Download conference paper PDF
Similar content being viewed by others
Keywords
1 Introduction
With the rapid advancement of urbanization, various types of risks in the city continue to accumulate, posing a serious threat to urban public safety, which need to be pay attention to in a more careful and delicate way. At the National Conference in 2017, Xi Jinping put forward the general requirement that “urban management should be as fine as embroidery”. Under the current severe situation of urban safety management and the requirements of delicacy management, urban risk prevention must be carried out with an embroidered and delicacy model, which is totally different from the previous mode of extensive management. The delicacy management mode for urban risk prevention is an important way to realize the urban security.
2 New Trend of Urban Risk Prevention
Urban risks include ecological risks, economic risks, technology risks, political risks and infrastructure lifeline risks etc. [1]. Urban risks are characterized by having many sources, difficult to be identified, dynamic changeable, etc. [2]. Furthermore, large volume of potential and uncertain risks often exist everywhere in large cities.
According to the theoretical formula of urban operation risk,
Risk of urban operation (Risk) = Hazards affecting urban operations × Vulnerability of urban operating systems.
In this formula, “the dangerous factors affecting urban operation”, that is, the external factors refer to the risks faced by the city. It is necessary to conduct an in-depth evaluation to find out the real situations; “the fragility of the urban operating system” refers to the internal capabilities, that is, the city's current ability to resist risks and the status quo. Therefore, in the prevention of urban operational safety risks, we should first understand the current risk points (identify external risk factors), and then construct a scientific risk prevention and management system based on current capabilities and current conditions (improving urban endurance and improving the fragility of urban operating systems).
At present, many Chinese cities are moving towards a delicacy management era from the extensive management era. The application of delicacy ideas is to emphasize precision and perfection of urban management work, and requires urban administrators in all fields to be careful in daily management. The work of urban management must be made into high-quality products to improve the quality of urban life.
3 Domestic and Foreign Practices
3.1 Risk Management Practices in Major Cities
The characteristics of risk management system of megacities in developed countries include the following [3]: Firstly, guided by scientific theories and concepts, the comprehensive risk management is carried out throughout the process. Secondly, the system is highly equipped with security management departments, clear responsibilities, and enhanced integration. Thirdly, the various mechanisms are effectively integrated and operated in the form of projects. The fourth is to highlight the status of the legal system and adhere to scientific and standardized governance. The fifth is to strengthen the preparation and effectiveness of the plan, and to test and enhance the ability through drills. The sixth is to attach importance to the construction of social forces and to promote cooperation between the government and society. The seventh is to strengthen information management and pay attention to the use of technological means.
Domestic cities are more typical in Xicheng District, Beijing. Xicheng District is the political, economic and cultural center of Beijing. In recent years, Xicheng District took the opportunity of innovative social service management, creatively proposed the “four in one” large emergency system management mode, “full response” to the public demand, and relied on advanced technology management services to implement grid management and fine Management. Xicheng District is at the forefront of the city's safe operation, realizing the means innovation, management innovation and service innovation of urban management [4].
In addition, it is worth learning that some cities in China have carried out urban risk assessment work in recent years, and have carried out beneficial research on special, large-scale public activities, major projects, major decisions and major issues, and the whole category of urban risk assessment. In the urban risk assessment area, Besides Shenzhen, which became the earliest area to carry out urban public safety assessment in 2012, domestic cities have carried out assessments in recent years, which has become a phenomenon worthy of attention. According to incomplete statistics, the cities that started risk assessment in 2016–2018 are: Beijing, Guangzhou, Tianjin, Xi'an, Harbin, Kunshan, Fuzhou, Nanchang, Yixing, Chongzhou, Quanzhou and other cities.
3.2 Delicacy Management Practices in Major Cities
The application of delicacy management by foreign governments is to be delicate in every detail of urban management [5]. The practices worthy of reference, such as the series of measures adopted in the New York City’s campaign of Anti-Graffiti, reflect the basic characteristics of urban management refinement, namely: specialization of labor division, legislative definition, technical informationization, diversification of management measures and humanity. Therefore, New York’s anti-graffiti action has achieved remarkable results. The London Intelligent Control Center model in the United Kingdom regards roads as scarce resources and requires excellence in the use of each road. This has become the key to improving roads efficiency in London. It is a successful experience for other countries. The emergence of ‘community-based trends’ in many cities is a major feature of delicacy urban management in Japan. This model promotes the interaction between community organizations and residents and improves the lives of residents.
Many cities in China have introduced delicacy management into urban management [6, 7]. Songjiang District in Shanghai divides the urban jurisdiction into individual “small grids”, and realizes the delicacy management of people, things and things in the jurisdiction, all-round and all-time and space through management of grid. The Taoyuan model from Shenzhen relies on developed modern technology to digitize management information and ultimately improve management. Through the practice of the urban design competition model, Guangzhou has basically established a delicacy management model that takes control of statutory documents and urban design guidelines in key urban development areas to guide urban construction and development.
3.3 Proposal for Delicacy Management of Urban Risk Prevention
Facing the complicated situation of urban operation, the most important thing at present should be to combine delicacy management ideas with urban risk prevention measures, and focus on using delicacy ideas, means and measures to strengthen and improve urban security. This is the main reference from domestic and foreign experiences.
The delicacy management is an inevitable trend of future urban risk management [8]. That is to say, under the current severe situation of urban safety situation and the requirements of delicacy management, it is necessary to use the delicacy mode to carry out urban safety management. On one hand, it is necessary to use delicacy ideas and means to strengthen the prevention of urban risks; on the other hand, strengthening the prevention of urban risk is the main measure to strengthen the overall delicacy management of the city.
4 Construction of Delicacy Management System for Urban Risk Prevention
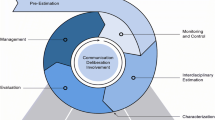
The delicacy management system should be constructed as Fig. 1.
4.1 Short-Term Work in Construction of the Delicacy Management System
4.1.1 Carrying Out Urban Risk Hazard Census and Assessment to Draw Risk Spatial Distribution Map
We will comprehensively mobilize all departments’ levels to extensively investigate safety risks, hazards and potential dangers, and rely on third-party professional technical forces such as scientific research institutes and intermediary service agencies and experts’ to scientifically identify, classify and comprehensively implement policies to accurately ensure safety.
Detailed work includes: (1) Identify the city's various risk; complete urban safety risk assessment and grading by sub-region, sub-sector, and sub-category, master the status of urban safety risks; (2) Build a basic database of urban safety risks; divide the risks into four levels of “red, orange, yellow and blue” according to the risk assessment grading results, and draw an electronic map of safety risk distribution; (3) define risk control measures, and establish “two lists” (risk control responsibility list, risk management and control measures list)to carry out dynamic and differentiated supervision to ensure that security risks are always within the scope of control; (4) Establish a long-term working mechanism for urban safety information update and risk assessment.
4.1.2 Ensure the Urban Safety with Advanced IT to Realize Smart Security Management
At present, the construction of smart and safe cities is being integrated into smart cities. It is necessary to use smart technology to explore a new type of urban security management model to achieve smart security management [9]. Smart security management refers to grasp the dynamic development of special, dangerous situation comprehensively, accurately and in a timely manner to prevent and control of public emergencies in advance through the overall perception of urban affairs, the relationship between things and things, people and things by full use of technologies such as the internet, the internet of Things and cloud computing.
At present, the first priority is to build a new system that is urgently needed in the current safe work to achieve the goal of ensuring the safe operation of the city with the advancement of science and technology. Secondly, we must use the concept of holistic governance to integrate and upgrade the existing systems of various urban departments.
4.2 Long-Term Work in Construction of the Delicacy Management System
4.2.1 Supporting Thought—Ideology Should Be Improved and Ideas Should Be Changed
The first ideology is the concept of safe development, carrying forward the idea of life first, safety first, and strengthening the awareness of the safety red line. The second ideology is the concept of governing risks from the source and resolving the risks at the source. The third is the concept of delicacy management. Urban safety management should change to delicacy mode, strive for excellence, and embed safety awareness and ideas into the whole process of urban planning, construction and management. The fourth is the concept of holistic governance. Establish the concept of integrated governance, break the fragmentation state of segmentation and geographical division, and realize the coordinated urban safety management. The fifth is the concept of risk prevention. From the incident-centered to the risk-centered management, from simply “after-the-fact emergency” to “pre-existing and prevention”. Sixth is the concept of subject role, giving full play to the decisive role of the market in resource allocation, and encouraging the full participation of social organizations, grassroots communities and citizens. Seven is the concept of political and social relations. The passive crisis public relations should be ended, and effective communication between the government and the public should be maintained.
4.2.2 Governing from the Source—Reducing the Sources of Risk Fundamentally
Firstly, urban planning policies should be scientifically and carefully formulated, which is an important way of source control. Especially projects related with urban safety should obey strict access and design policy. Safety supervision, environmental protection, fire protection and other departments must strictly implement the “three simultaneous” review system for large-risk construction projects. Zero tolerance exists for all kinds of illegal acts that violate urban planning and construction laws and regulations.
Secondly, safety regulations and standards should be implemented and improved. Safety laws and regulations system should be strengthened for urban security. Technical standards and standard requirements of urban high-rise buildings, large-scale complexes, integrated transportation hubs, tunnel bridges, pipeline corridors, road traffic, rail transit, gas engineering, drainage flood control, landfills, muck receiving fields, power facilities and elevators, etc. should be improved to enhance the ability to withstand accidents and ensure safe operation.
Thirdly, safety management of urban municipal infrastructure should be strengthened. Strengthen safety supervision and management during the construction and operation of urban transportation, water supply, gas supply and sewage infrastructure, and strictly implement safety precautions measures. Strengthen the construction of safety facilities matched with municipal facilities, and timely replace and upgrade. Strengthen the construction and maintenance of fire safety facilities such as fire stations and water sources. Strengthen the safety supervision and management in the process of urban shantytowns, urban villages and dilapidated buildings, and strictly control the illegal reconstruction of urban built-up areas.
Fourthly, accelerate the upgrading and upgrading of key industries. Key lists and catalogues should be set for key industries, especially those involving high-risk industries. Guide enterprises to gather and develop safety industry, and transform and upgrade the level of traditional industry process technology and safety equipment.
4.2.3 Institutional and Mechanism Guarantee—Core to Improve Risk Prevention
Firstly, strengthen unified leadership and optimize urban operation management system and mechanism. On one hand, the Urban Security Operation Committee should be established to strengthen unified and centralized leadership over the safe operation of cities. The city safety operation committee has three major functional sections: prevention and early warning, potential dangers supervision and rectification, and emergency rescue command and disposal. On the other hand, the Urban Safety Operation Committee should establish a 24-h all-weather operation mode to strengthen the monitoring and coordination of urban safety operations.
Secondly, deepen the investigation and management of potential dangers, find out the real safe situation, and consolidate the foundation of safe operation of the city.
Thirdly, improve urban emergency management and rescue capabilities. Strengthen emergency response and improve the ability to deal with emergencies.
4.2.4 Supervision and Regulation—Way to Improve the Efficiency
Firstly, safety responsibility should be fully implemented. We will fully implement the leadership responsibilities at all levels and the responsibility of the first responsible person. We will implement the duties of safety production and occupational health work in all relevant departments, so that responsibility will be implemented without gaps, and there will be no blind spots for supervision and management. Strictly implement the responsibility of safety production and occupational health of all types of production and business units, and strengthen the all-round safety management of all employees.
Secondly, improve the safety supervision system. Strengthen the work connection between the departments responsible for safety supervision and management, promote comprehensive law enforcement in the field of safety production, and improve the effectiveness of joint enforcement of urban safety supervision. Scientifically define and clarify the corresponding safety supervision and management institutions of various functional areas, and define industry supervision and territorial supervision duties.
Thirdly, enhance the ability of regulatory enforcement. Strengthen the standardization and informatization construction of law enforcement agencies for safety production supervision. Strengthen education and training for safety supervision and law enforcement, train and improve the quality and ability of safety supervision law enforcement personnel. Regularly carry out evaluation of law enforcement effects and strengthen the implementation of law enforcement measures.
Fourthly, regulate regulatory enforcement. Improve the post responsibility system and assessment mechanism for law enforcement personnel strictly, enforce the law enforcement procedures, strengthen on-site accurate law enforcement strictly, and make timely decision-making on violations.
Fifthly, strengthen the mission and enthusiasm of each department to perform their duties and serious accountability should be carried out. Establishing a delicacy, complete, accurate and comprehensive responsibility system to improve the safety supervision department instead of simply “missing blame and strict accountability”.
Sixthly, Grasp the key points and strengthen the overall supervision of key elements of urban operation one by one. People, things, houses, points, roads and networks are the six key elements of safe urban operation.
4.2.5 Collaborative Management—Strengthening Urban Security Capabilities
Firstly, improve the social service system. Pay attention to the role of social service system. Strengthen research and promotion practices in the formulation and improvement of government procurement guidelines for safe production services, vigorous implementation of safety production liability insurance, and promotion of safety credit system construction. Improve the urban community security grid work system and strengthen the management of the terminal. Secondly, strengthen safety technology innovation and application, and ensure the safe operation of cities with the advancement of science and technology. Thirdly, improve the safety and skills of citizens and provide a strong foundation for the safe operation of cities. Fourthly, all parties work together to strengthen overall promotion. Pay attention to the synergy between all parties and enhance the overall synergy of urban safe operation. To strengthen the security of the city, we must focus on the use of socialization and market-based means on the basis of the use of administrative power, and build a multi-disciplinary mechanism.
5 Conclusion
Implementing delicacy management of urban risk prevention can effectively integrate urban safety management forces, optimize the allocation and effective use of urban safety management resources to improve the efficiency of urban safety management and provide the most powerful for accelerating urbanization and building modern cities.
Through the research on the two aspects of risk management and delicacy management in big cities at home and abroad, the concept of “delicacy management of urban operation risk prevention” is put forward. That is, the trend of urban risk management is to carry out urban security with delicacy management methods and means. According to the theory of urban operational risk, in short-term, the risks census and assessment must be carried out, and delicacy management ideas and scientific urban management techniques should be combined to build smart cities with the advancement of science and technology to ensure city safe. This is a task that is urgently needed to be carried out now. In the long run, it is necessary to construct a delicacy management system for urban risk prevention and improve urban endurance.
References
Liu, X. (2016). International comparative study on security risk management and evaluation in megacities. Science Development, 10, 74–84.
Chen, Q., Zhao, L., He, F., et al. (2011). Research on the construction of Shanghai urban operation security system. Science Development, 3, 91–103.
Ruan, W. (2016). Comparison and reference of security risk management in megacities. Journal of the Party School of Hangzhou Municipal Committee, 17(6), 42–48.
Zhou, H. (2014, December). Urban safety: The institutional root of urban operation safety in China. Party School Press of the CPC Central Committee.
Zhang, Y. (2016). Research on the status quo and refined transformation of urban crisis management. Guangxi Social Sciences, 7, 154–157.
Wu, S., & Li, X. (2018). Research report on promoting urban refinement management in Shanghai. Science Development, 1, 87–93.
Shanghai strengthens urban management refinement the “Three-Year Action Plan” defines 13 key tasks and 42 implementation projects. https://www.shanghai.gov.cn/nw2/nw2314/nw2315/nw5827/u21aw1286692.html.
Zong, C. (2017). Refinement and long-term prevention mechanism in urban crisis management. Shanghai City Management, 26(6), 13–18.
Liu, L. (2013). From safe city to smart city. China Public Safety, 15, 100–102.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Yan, X. (2021). The Construction of Delicacy Management System for Urban Risk Prevention. In: Ye, G., Yuan, H., Zuo, J. (eds) Proceedings of the 24th International Symposium on Advancement of Construction Management and Real Estate. CRIOCM 2019. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-8892-1_8
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-8892-1_8
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-15-8891-4
Online ISBN: 978-981-15-8892-1
eBook Packages: Business and ManagementBusiness and Management (R0)