Abstract
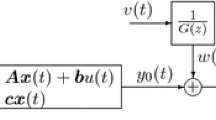
The Wiener system consists of a linear model followed in series with a nonlinear static element. The parameter estimation of a Wiener system, whose linear part is a finite impulse response function and nonlinear inverse function a polynomial, is considered in this paper. The system is polluted by a process noise. Traditional algorithms cost heavy computation because of the parameter product term and give a biased estimate owing to the correlation between the information vector and the noise. To solve these problems, a two-stage input prediction error algorithm is proposed. In the first stage, a least squares estimate is obtained by minimizing the input prediction error. However, this estimate is biased. To get an unbiased estimate, the estimated output of the linear part is taken as an instrumental variable. And an instrumental variable estimate is obtained unbiasedly. A numerical simulation verified the proposed algorithm.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed-Ali, T., Tiels, K., Schoukens, M., Giri, F.: Sampled-data based state and parameter estimation for state-affine systems with uncertain output equation. IFAC-PapersOnLine 51(15), 491–496 (2018)
Al-Duwaish, H.N.: Identification of wiener model using genetic algorithms. In: 2009 5th IEEE GCC Conference & Exhibition, pp. 1–4. IEEE (2009)
Benamor, A., Messaoud, H.: A new adaptive sliding mode control of nonlinear systems using volterra series: application to hydraulic system. Int. J. Model. Ident. Control 29(1), 44–52 (2018)
Chen, H.F.: Recursive identification for wiener model with discontinuous piece-wise linear function. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 51(3), 390–400 (2006)
De-hui, W.: Identification method for nonlinear dynamic system using wiener neural network. Control Theor. Appl. 11, 002 (2009)
Ding, F., Liu, X., Liu, M.: The recursive least squares identification algorithm for a class of wiener nonlinear systems. J. Franklin Inst. 353(7), 1518–1526 (2016)
Ding, F., Ma, J., Xiao, Y.: Newton iterative identification for a class of output nonlinear systems with moving average noises. Nonlinear Dyn. 74(1–2), 21–30 (2013)
Fang, C., Xiao, D.: Process Identification. Tsinghua University Press, Beijing (1988)
Hatanaka, T., Uosaki, K., Koga, M.: Evolutionary computation approach to block oriented nonlinear model identification. In: 5th Asian Control Conference, vol. 1, pp. 90–96. IEEE (2004)
Hu, Y., Liu, B., Zhou, Q., Yang, C.: Recursive extended least squares parameter estimation for Wiener nonlinear systems with moving average noises. Circ. Syst. Sig. Process. 33(2), 655–664 (2014)
Janczak, A.: Instrumental variables approach to identification of a class of mimo Wiener systems. Nonlinear Dyn. 48(3), 275–284 (2007)
Jing, S., Pan, T., Li, Z.: Variable knot-based spline approximation recursive Bayesian algorithm for the identification of Wiener systems with process noise. Nonlinear Dyn. 90(4), 2293–2303 (2017)
Liu, D., Wu, J., Li, S.: Wiener model of pressure management for water distribution network. Int. J. Modell. Ident. Control 30(2), 73–82 (2018)
Ljung, L.: System Identification: Theory for the User. Prentice-Hall, Upper Saddle (1987)
Pal, P.S., Kar, R., Mandal, D., Ghoshal, S.P.: Parametric identification with performance assessment of Wiener systems using brain storm optimization algorithm. Circ. Syst. Sig. Process. 36(8), 3143–3181 (2017)
Retes, P.F.L., Aguirre, L.A.: Narmax model identification using a randomised approach. Int. J. Model. Ident. Control 31(3), 205–216 (2019)
Söderström, T., Stoica, P.: Instrumental variable methods for system identification. Circ. Syst. Sig. Process. 21(1), 1–9 (2002)
Tamboli, D., Chile, R.: Multi-model approach for 2-dof control of nonlinear CSTR process. Int. J. Model. Ident. Control 30(2), 143–161 (2018)
Tang, Y., Qiao, L., Guan, X.: Identification of Wiener model using step signals and particle swarm optimization. Expert Syst. Appl. 37(4), 3398–3404 (2010)
Tiels, K., Schoukens, J.: Wiener system identification with generalized orthonormal basis functions. Automatica 50(12), 3147–3154 (2014)
Wang, D., Ding, F.: Least squares based and gradient based iterative identification for Wiener nonlinear systems. Sig. Process. 91(5), 1182–1189 (2011)
Zhou, L., Li, X., Pan, F.: Gradient-based iterative identification for Wiener nonlinear systems with non-uniform sampling. Nonlinear Dyn. 76(1), 627–634 (2014)
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by National Nature Science Foundation under Grant 61873113, Industry-University Cooperation Project of Jiangsu Province (BY2018231), and Natural Science Research Project of Jiangsu higher school, China (19KJD510001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Jing, S., Pan, T. (2020). Identification of the Wiener System Based on Instrumental Variables. In: Wang, R., Chen, Z., Zhang, W., Zhu, Q. (eds) Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Modelling, Identification and Control (ICMIC2019). Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering, vol 582. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-0474-7_13
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-0474-7_13
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-15-0473-0
Online ISBN: 978-981-15-0474-7
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)