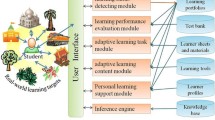
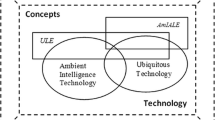
Abstract
Context-aware ubiquitous learning systems use real-time or almost real-time sensor data that is an integral part of learning design for anytime, anywhere learning. Typical examples are situated learning in museums, parks, or gardens where sensors are used to enact unique learning scenarios. This type of embedded learning can be easily extended to cities, continents, or indeed the world. Traditionally, PDAs and smartphones have been used as edge devices in such learning systems; smartphones or PDA’s typically collect sensor data and communicate with back-end servers to enact learning scenarios. Smartwatches can easily replace smartphones to perform these functions. Smartwatches today include a variety of sensors, are wirelessly connected to heterogeneous networks, and possess significant processing power. This paper presents a survey and design framework for using smartwatches in ubiquitous learning. The design framework views smartwatches for ubiquitous learning through the IoT lens and various types of learning designs. In addition, micro-services to implement these pedagogical services are enumerated and evaluated with respect to smartwatches. An analysis of network requirements for smartwatches is also presented. The overall conclusion is that while some challenges like power optimization remain, smartwatches represent a promising next platform for context-aware ubiquitous learning.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hwang, G.-J., Tsai, C.-C., Yang, S.J.H.: Criteria, strategies and research issues of context-aware ubiquitous learning. J. Edu. Tech. Soc. 11, 81–91 (2008)
Buckner, E., Kim, P.: Integrating technology and pedagogy for inquiry-based learning: The Stanford Mobile Inquiry-based Learning Environment (SMILE). Prospects 44, 99–118 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11125-013-9269-7
Li, M., Ogata, H., Hou, B., et al.: Context-aware and personalization method in ubiquitous learning system. J. Edu. Technol. Soc. 16, 362–373 (2013)
Hsu, T., Chiou, C., Tseng, J.C.R., Hwang, G.: Development and evaluation of an active learning support system for context-aware ubiquitous learning. IEEE Trans. Learn. Technol. 9, 37–45 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/TLT.2015.2439683
Chiou, C.-K., Tseng, J.C.R., Hwang, G.-J., Heller, S.: An adaptive navigation support system for conducting context-aware ubiquitous learning in museums. Comput. Educ. 55, 834–845 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2010.03.015
Wang, S.-L., Wu, C.-Y.: Application of context-aware and personalized recommendation to implement an adaptive ubiquitous learning system. Expert Syst. Appl. 38, 10831–10838 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2011.02.083
Chin, K.Y., Lee, K.F., Chen, Y.L.: Impact on student motivation by using a QR-Based U-Learning material production system to create authentic learning experiences. IEEE Trans. Learn. Technol. 8, 367–382 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1109/TLT.2015.2416717
Garcia, B., Chu, S.L., Nam, B., Banigan, C.: Wearables for learning: examining the smartwatch as a tool for situated science reflection. In: Proceedings of the 2018 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems. ACM, New York, NY, USA, pp 256:1–256:13 (2018)
de la Guía, E., Camacho, V.L., Orozco-Barbosa, L., et al.: Introducing IoT and wearable technologies into task-based language learning for young children. IEEE Trans. Learn. Technol. 9, 366–378 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/TLT.2016.2557333
Casano, J., Tee, H., Agapito, J. et al.: Migration and evaluation of a framework for developing embodied cognition learning games. In: Proceedings of the 3rd Asia-Europe Symposium on Simulation & Serious Gaming—VRCAI ’16. ACM Press, Zhuhai, China, pp 199–203 (2016)
Al-Soh, M., Zualkernan, I.A.: An MQTT-based context-aware wearable assessment platform for smart watches. In: 2017 IEEE 17th International Conference on Advanced Learning Technologies (ICALT). pp. 98–100 (2017)
Classroom API.: In: Google Developers. https://developers.google.com/classroom/. Accessed 30 Jan 2019
Chin, K.-Y., Chen, Y.-L.: A mobile learning support system for ubiquitous learning environments. Procedia. Soc. Behav. Sci. 73, 14–21 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2013.02.013
Hwang, G.-J., Kuo, F.-R., Yin, P.-Y., Chuang, K.-H.: A Heuristic Algorithm for planning personalized learning paths for context-aware ubiquitous learning. Comput. Educ. 54, 404–415 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2009.08.024
Lee, W.H., Kuo, M.C.: An NFC E-Learning Platform for Interactive and Ubiquitous Learning. Atlantis Press, Paris (2014)
Hwang, G.-J.: Definition, framework and research issues of smart learning environments—A context-aware ubiquitous learning perspective. Smart. Learn. Environ. 1, 4 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40561-014-0004-5
MQTT. http://mqtt.org/. Accessed 30 Jan 2019
Shapsough, S.Y.: An IoT Architecture for Ubiquitous Context-Aware Assessments. Thesis, American University of Sharjah, UAE, (2017)
Shapsough, S., Amin, S., Ahmed, H., et al.: ARCHI-PODS: Ubiquitous Learning Technology to Teach Architectural Design Principles to Architecture Students. INTED2015, pp 4338–4347 ((2015))
Perera, C., Zaslavsky, A., Christen, P., Georgakopoulos, D.: Context aware computing for the internet of things: a survey. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutorials 16, 414–454 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1109/SURV.2013.042313.00197
Anagnostopoulos, C.B., Tsounis, A., Hadjiefthymiades, S.: Context awareness in mobile computing environments. Wireless Pers. Commun. 42, 445–464 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-006-9187-6
Ai, Y., Peng, M., Zhang, K.: Edge computing technologies for Internet of things: a primer. Digital Commun. Netw. 4, 77–86 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dcan.2017.07.001
Conti, F., Palossi, D., Andri, R., et al.: Accelerated visual context classification on a low-power smartwatch. IEEE Trans. Hum. Mach. Syst. 47, 19–30 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/THMS.2016.2623482
Arriba-Pérez, F. de., Caeiro-Rodríguez, M., Santos-Gago, J.M.: Towards the use of commercial wrist wearables in education. In: 2017 4th Experiment@International Conference (exp.at’17). pp. 323–328 (2017)
Coutand, O.: A Framework for Contextual Personalised Applications. Kassel university press GmbH (2009)
Temdee, P., Prasad, R.: Context-Aware Communication and Computing: Applications for Smart Environment. Springer, Berlin (2017)
JSON. https://www.json.org/. Accessed 13 Feb 2019
Dhillon, H.S., Huang, H., Viswanathan, H.: Wide-area wireless communication challenges for the internet of things. IEEE Commun. Mag. 55, 168–174 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/MCOM.2017.1500269CM
Acknowledgements
The research presented here was supported in part by grant #EFRG18-SCR-CEN-82 from the American University of Sharjah, UAE.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Takiddeen, N., Zualkernan, I. (2020). Smartwatches for Context-Aware Ubiquitous Learning. In: Rehm, M., Saldien, J., Manca, S. (eds) Project and Design Literacy as Cornerstones of Smart Education. Smart Innovation, Systems and Technologies, vol 158. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-9652-6_18
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-9652-6_18
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-13-9651-9
Online ISBN: 978-981-13-9652-6
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)