Abstract
The endoscopic diagnosis of early colorectal neoplasia can be improved by using narrow-band imaging (NBI). Recently, the NBI International Colorectal Endoscopic (NICE) classification has been validated for the diagnosis of colorectal lesions using non-magnifying endoscopy. In addition, Workgroup serrAted polypS and Polyposis (WASP) classification was recommended for optical diagnosis of sessile serrated lesions. This chapter will demonstrate the examples of optical diagnosis of colorectal neoplasia using non-magnifying endoscopy with NBI.
Access provided by Autonomous University of Puebla. Download chapter PDF
Similar content being viewed by others
Keywords
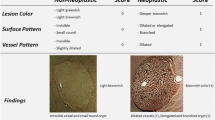
The NICE type 1 polyps are most likely nonneoplastic. The color of polyps is similar to or lighter than the background; there is no blood vessels or only isolated lacy vessels on the surface. The surface may show uniform dark spots (Fig. 18.1), white spots (Fig. 18.2), or absence of surface pattern [1] (Fig. 18.3).
The NICE type 2 polyps are most likely intramucosal neoplasia. Their color is darker than the background. There are brown blood vessels surrounding white structures which represent pit pattern. These surface pit pattern may be oval (Fig. 18.4), tubular (Fig. 18.5), or branched pattern [1] (Fig. 18.6).
The NICE type 3 polyps are most likely invasive cancer. In this group, the color is darker than the background. Moreover, they have area of disrupted blood vessels and the surface pattern are absent [1] (Fig. 18.7).
However, the NICE classification has limitations for differentiation of sessile serrated polyps [2] which are also the precursor lesions of colorectal cancer. The “Workgroup serrAted polypS and Polyposis” (WASP) classification combines four features, namely, cloud-like surface, indistinct border, irregular shape, and dark spots inside the crypts into the NICE classification and the polyps with at least two features should be considered sessile serrated lesions [3] (Figs. 18.8 and 18.9). The mucus cap is a common feature of sessile serrated lesions as well [4] (Fig. 18.10). Some of the sessile serrated lesions may have NICE classification type 1 (Figs. 18.11 and 18.12) while the others may have NICE classification type 2 [3] (Figs. 18.13 and 18.14).
References
Sano Y, Tanaka S, Kudo SE, Saito S, et al. Narrow-band imaging (NBI) magnifying endoscopic classification of colorectal tumors proposed by the Japan NBI Expert Team. Dig Endosc. 2016;28:526–33.
Kumar S, Fioritto A, Mitani A, et al. Optical biopsy of sessile serrated adenomas: do these lesions resemble hyperplastic polyps under narrow-band imaging? Gastrointest Endosc. 2013;78:902–9.
East JE, Vleugels JL, Roelandt P, et al. Advanced endoscopic imaging: European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) Technology Review. Endoscopy. 2016;48:1029–45.
Kolb JM, Soetikno RM, Rao AK, et al. Detection, diagnosis, and resection of sessile serrated adenomas and polyps. Gastroenterology. 2017;153:646–8.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Pisespongsa, P. (2021). Case Atlas and Illustrations of Early GI Cancers: Colon. In: Chiu, P.W.Y., Sano, Y., Uedo, N., Singh, R. (eds) Endoscopy in Early Gastrointestinal Cancers, Volume 1. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-6769-3_18
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-6769-3_18
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-10-6768-6
Online ISBN: 978-981-10-6769-3
eBook Packages: MedicineMedicine (R0)