Abstract
An acute traumatic fracture can be present with high level of 18F-FDG uptake. Nevertheless, FDG-PET/CT is useful in differentiating some rare benign form of bone disease.
Access provided by Autonomous University of Puebla. Download chapter PDF
Similar content being viewed by others
Keywords
These keywords were added by machine and not by the authors. This process is experimental and the keywords may be updated as the learning algorithm improves.
An acute traumatic fracture can be present with a level of 18F-FDG uptake generally considered indicative of neoplasm. It is important to recognize that increased FDG-PET activity in bone should not be accepted as definitive evidence of neoplastic or metastatic disease.
Nevertheless, FDG-PET/CT is useful in differentiating some rare benign form of bone disease, such as eosinophilic granuloma, from more aggressive manifestation.
A 13-year-old boy suffered a traumatic fracture of the left superior articular process of the fifth vertebra while playing football. Coronal (a–c), sagittal (d–f), and axial (g–i) CT with bone window (a, d, g), PET (b, e, h), and PET/CT fusion (c, f, i) images show focal FDG uptake corresponding to the fracture site
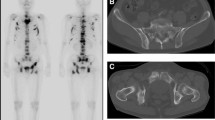
A 15-year-old boy underwent a PET evaluation during chemotherapy for Hodgkin’s lymphoma, stage III. Axial bone window CT (a), PET (b), and PET/CT fusion (c) images show 18F-FDG uptake in the left anterior iliac spine (yellow arrow in a). The diagnosis was a traumatic fracture subsequent to bone marrow biopsy
An 11-year-old girl was admitted for dorsal pain, without trauma. Bone scintigraphy showed an accumulation in the fifth and sixth vertebrae. Axial (a) and sagittal (b) bone window CT shows a lytic lesion in the sixth dorsal vertebra (yellow arrow in b), with pathological findings in the left paravertebral soft tissues
T1 MRI (a) conducted for suspected bone fracture, probably secondary to bone marrow disease such as lymphoproliferative conditions (yellow arrow in a). Alternatively, an eosinophilic granuloma was considered. The patient was referred to our center for metabolic characterization of the bone lesion and to search for other metabolically active areas, more accessible to biopsy and with lower risk of late-onset damage. The PET/CT (b, c) study shows an inhomogeneous lesion with low metabolic activity in the sixth dorsal vertebra, confirming the second hypothesis
Same patient as in Fig. 27.4. Sagittal T1 MRI follow-up at 3 months showed stabilization of the lesion and an area of tissue thickening, indicative of a reparative process (yellow arrow)
It is important to consider that although eosinophilic granuloma is usually a benign form of bone disease, in rare cases, it may be the presenting manifestation of the more serious, multifocal, Langerhans cell histiocytosis. In these patients, the prognosis is more guarded.
Suggested Reading
Cho WI, Chang UK (2011) Comparison of MR imaging and FDG-PET/CT in the differential diagnosis of benign and malignant vertebral compression fractures. J Neurosurg Spine 14(2):177–183, Epub 2011
Shammas A (2009) Nuclear medicine imaging of the pediatric musculoskeletal system. Semin Musculoskelet Radiol 13(3):159–180
Thakur NA, Daniels AH, Schiller J, Valdes MA, Czerwein JK, Schiller A, Esmende S, Terek RMJ (2012) Benign tumors of the spine. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 20(11):715–724
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2014 Springer-Verlag Italia
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Cistaro, A. (2014). Other Bone Lesions. In: Cistaro, A. (eds) Atlas of PET/CT in Pediatric Patients. Springer, Milano. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-88-470-5358-8_27
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-88-470-5358-8_27
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Milano
Print ISBN: 978-88-470-5357-1
Online ISBN: 978-88-470-5358-8
eBook Packages: MedicineMedicine (R0)