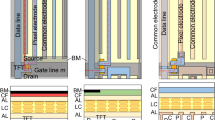
Abstract
The fundamentals of resist materials and chemistry, equipment, and process engineering for thin-film transistor (TFT) liquid crystal display (LCD) photolithography are reviewed with a primary focus on manufacturing technology. The effects of the materials and concentrations of (mainly TFT array) photoresist constituents on the photosensitivity, dissolution behaviors in the developer, contrast, resolution, dark erosion, and stability against plasma etching are presented. Along with the equipment designs and functions, the process engineering to achieve the optimum resolution, better depth of field, higher throughput, and lower cost is explained and discussed. The efforts to address the great difficulty associated with capability/capacity improvement and increasing dimensions and weight of glass substrates and equipment are also reviewed, in response to the rising volume demands of larger displays. Mura issues related to the critical dimension (CD), differential CD, overlay, differential overlay, and total pitch are elucidated, and the essential control factors and approaches are concisely introduced. Guided by the continuing, market-driven industry trends, we report the directions and future challenges for photolithography for TFT LCD applications.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CD:
-
Critical dimension
- DNQ:
-
Diazonaphthoquinone
- DOF:
-
Depth of field
- E op :
-
For practical manufacturing processes the recommended operation dose which enables the complete dissolution of a UV-irradiated positive photoresist during development
- E th :
-
The threshold dose above which an exposed positive resist is fully soluble in the developer
- LCD:
-
Liquid crystal display
- NA:
-
Numerical aperture
- PAC:
-
Photoactive compound
- TFT:
-
Thin-film transistor
Further Reading
Chen Y (2009) unpublished work
Dammel R (1993) Basic chemistry of Novolaks. In: Diazonaphthoquinone-base resists tutorial text. SPIE, vol TT 11. p 39
DisplaySearch PanelTrack (2010). http://www.displaysearch.com
King MC (1981) Principles of optical lithography, vol 1, VLSI electronics. Academic, New York
Kuo Y (2003) Large TFT LCD manufacturing technology. Thin film transistor technologies VI. In: Proceedings of the international symposium, pp 1–6
Lin BJ (1993) Phase-shifting masks gain an edge. IEEE Circuits Devices Mag 9:28–35
Lin WY, Wu WB, Chang JT, Tsai MT, Lin WT (2008) Recent advancements and future challenges of photolithography of TFT-LCD for display applications. Keynote Speech, SPIE Lithography Asia -Taiwan, Nov 2008
Stanly W, Richard NT (2000) Optical aligners and photomask. Silicon processing for the VLSI era 1:628
Thompson LF, Bowden MJ (1994) The lithography process: the physics. In: Introd Microlithograp. pp 19–38
Wake RW, Flanigan MC (1985) A review of contrast in positive resists. Proc SPIE 539:291
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2015 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this entry
Cite this entry
Wu, W.B., Cheng, K.C., Li, H.H. (2015). Photolithography for Thin-Film-Transistor Liquid Crystal Displays. In: Chen, J., Cranton, W., Fihn, M. (eds) Handbook of Visual Display Technology. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-35947-7_58-2
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-35947-7_58-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-35947-7
eBook Packages: Springer Reference EngineeringReference Module Computer Science and Engineering